Numerical Analysis
Numerical Analysis - Orchard Publications
Numerical Analysis - Orchard Publications
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
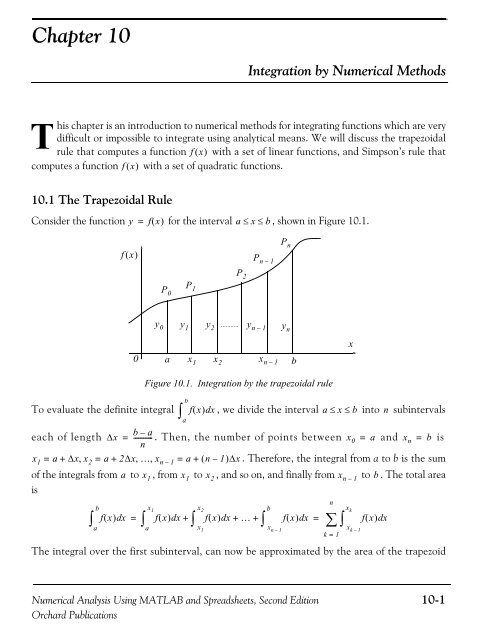
Chapter 10Integration by <strong>Numerical</strong> MethodsThis chapter is an introduction to numerical methods for integrating functions which are verydifficult or impossible to integrate using analytical means. We will discuss the trapezoidalrule that computes a function f ( x)with a set of linear functions, and Simpson’s rule thatcomputes a function f ( x)with a set of quadratic functions.10.1 The Trapezoidal RuleConsider the function y = f( x)for the interval a≤x≤b, shown in Figure 10.1.f ( x)P nP n – 1P 2PP 1 00y 0 y 1 y 2........... y n – 1 y nax 1 x 2x n – 1Figure 10.1. Integration by the trapezoidal rulebxbTo evaluate the definite integral∫fx , we divide the interval a ≤x ≤ b into n subintervalsaeach of length ∆xb–a= ----------- . Then, the number of points between xn0 = a and x n = b isx 1 = a + ∆x, x 2 = a+2∆x, …,x n – 1 = a+ ( n – 1)∆x. Therefore, the integral from a to b is the sumof the integrals from a to x 1 , from x 1 to x 2 , and so on, and finally from x n – 1 to b . The total areais∫abfx ( ) dx=∫fx ( ) dx+∫fx ( ) dx+ … +∫fx ( ) dx=∑ ∫fx ( ) dxax 1x 2x 1The integral over the first subinterval, can now be approximated by the area of the trapezoidbx n – 1nk = 1x kx k – 1<strong>Numerical</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong> Using MATLAB and Spreadsheets, Second Edition 10-1Orchard Publications