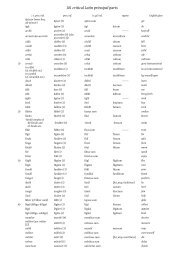
Cambridge Preterm Latin language pack
Cambridge Preterm Latin language pack - CW's language page
Cambridge Preterm Latin language pack - CW's language page
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
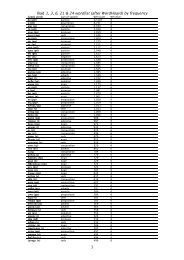
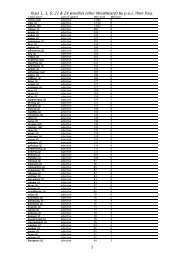
conspectus of Ancient Greek and <strong>Latin</strong> subordinate clauses<br />
Subordinate or dependent clauses are traditionally (Smyth §2189 and Kennedy §410) classified in<br />
three ways:<br />
1. substantival clauses behave like nouns<br />
2. adverbial clauses disclose information that is adverbial (i.e. predicate) to the action at hand<br />
3. adjectival clauses disclose information that is adjectival (i.e. attributive) to the agent or item at<br />
hand<br />
This classification is based on an analogy: clauses are being compared to words. Subordinate clauses are<br />
taken to modify the main clause like nouns, adverbs, and adjectives:<br />
1a. Jim annoys me.<br />
1b. The fact that Jim does that annoys me.<br />
1c. I can't stand Jim.<br />
1d. I can't stand the fact that Jim does that.<br />
2a. Jim ran quickly.<br />
2b. Jim ran when he realized he was late.<br />
2c. Jim ran because he realized he was late.<br />
2d. Jim ran although he didn't need to.<br />
3a. I've made an unforgivable mistake.<br />
3b. I've made a mistake which is unforgivable.<br />
In each of these examples, a clause underlined in a (b), (c) or (d) sentence plays the same role as the<br />
word underlined in the (a) sentence. Each kind of clause has further subclasses:<br />
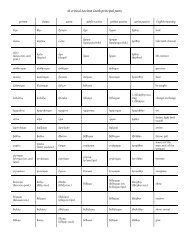
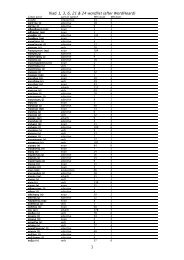
1. substantival clauses<br />
a. relative clauses (best treated as adjectival—see below)<br />
b. indirect speech<br />
c. indirect question<br />
d. indirect command<br />
2. adverbial clauses<br />
a. purpose (a.k.a. "final") clauses<br />
b. object clauses (really belong under substantives but resemble purpose clauses very closely)<br />
—with verbs of effort<br />
—with verbs of fear<br />
c. causal clauses<br />
d. result (a.k.a. "consecutive") clauses<br />
e. proviso clauses<br />
f. conditional clauses<br />
g. concessive clauses<br />
h. temporal clauses<br />
i. comparison<br />
3. adjectival clauses: relative clauses<br />
a. definite<br />
b. indefinite<br />
[c. "conditional" relative clauses in Gk]