Netherlands Journal
NJCC Volume 10, Oktober 2006
NJCC Volume 10, Oktober 2006
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
netherlands journal of critical care<br />
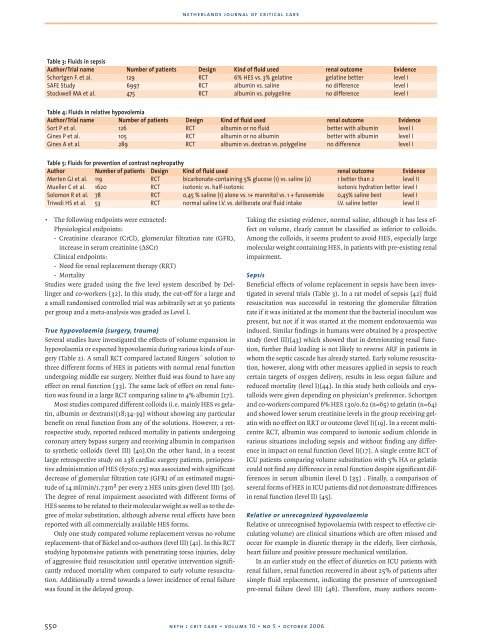
Table 3: Fluids in sepsis<br />
Author/Trial name Number of patients Design Kind of fluid used renal outcome Evidence<br />
Schortgen F. et al. 129 RCT 6% HES vs. 3% gelatine gelatine better level I<br />
SAFE Study 6997 RCT albumin vs. saline no difference level I<br />
Stockwell MA et al. 475 RCT albumin vs. polygeline no difference level I<br />
Table 4: Fluids in relative hypovolemia<br />
Author/Trial name Number of patients Design Kind of fluid used renal outcome Evidence<br />
Sort P et al. 126 RCT albumin or no fluid better with albumin level I<br />
Gines P et al. 105 RCT albumin or no albumin better with albumin level I<br />
Gines A et al. 289 RCT albumin vs. dextran vs. polygeline no difference level I<br />
Table 5: Fluids for prevention of contrast nephropathy<br />
Author Number of patients Design Kind of fluid used renal outcome Evidence<br />
Merten GJ et al. 119 RCT bicarbonate-containing 5% glucose (1) vs. saline (2) 1 better than 2 level II<br />
Mueller C et al. 1620 RCT isotonic vs. half-isotonic isotonic hydration better level I<br />
Solomon R et al. 78 RCT 0,45 % saline (1) alone vs. 1+ mannitol vs. 1 + furosemide 0,45% saline best level I<br />
Trivedi HS et al. 53 RCT normal saline I.V. vs. deliberate oral fluid intake I.V. saline better level II<br />
• The following endpoints were extracted:<br />
Physiological endpoints:<br />
- Creatinine clearance (CrCl), glomerular filtration rate (GFR),<br />
increase in serum creatinine (∆SCr)<br />
Clinical endpoints:<br />
- Need for renal replacement therapy (RRT)<br />
- Mortality<br />
Studies were graded using the five level system described by Dellinger<br />
and co-workers [32]. In this study, the cut-off for a large and<br />
a small randomised controlled trial was arbitrarily set at 50 patients<br />
per group and a meta-analysis was graded as Level I.<br />
True hypovolaemia (surgery, trauma)<br />
Several studies have investigated the effects of volume expansion in<br />
hypovolaemia or expected hypovolaemia during various kinds of surgery<br />
(Table 2). A small RCT compared lactated Ringers´ solution to<br />
three different forms of HES in patients with normal renal function<br />
undergoing middle ear surgery. Neither fluid was found to have any<br />
effect on renal function [33]. The same lack of effect on renal function<br />
was found in a large RCT comparing saline to 4% albumin [17].<br />
Most studies compared different colloids (i.e. mainly HES vs gelatin,<br />
albumin or dextrans)[18;34-39] without showing any particular<br />
benefit on renal function from any of the solutions. However, a retrospective<br />
study, reported reduced mortality in patients undergoing<br />
coronary artery bypass surgery and receiving albumin in comparison<br />
to synthetic colloids (level III) [40].On the other hand, in a recent<br />
large retrospective study on 238 cardiac surgery patients, perioperative<br />
administration of HES (670/0.75) was associated with significant<br />
decrease of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of an estimated magnitude<br />
of 14 ml/min/1.73m 2 per every 2 HES units given (level III) [30].<br />
The degree of renal impairment associated with different forms of<br />
HES seems to be related to their molecular weight as well as to the degree<br />
of molar substitution, although adverse renal effects have been<br />
reported with all commercially available HES forms.<br />
Only one study compared volume replacement versus no volume<br />
replacement- that of Bickel and co-authors (level III) [41]. In this RCT<br />
studying hypotensive patients with penetrating torso injuries, delay<br />
of aggressive fluid resuscitation until operative intervention significantly<br />
reduced mortality when compared to early volume resuscitation.<br />
Additionally a trend towards a lower incidence of renal failure<br />
was found in the delayed group.<br />
Taking the existing evidence, normal saline, although it has less effect<br />
on volume, clearly cannot be classified as inferior to colloids.<br />
Among the colloids, it seems prudent to avoid HES, especially large<br />
molecular weight containing HES, in patients with pre-existing renal<br />
impairment.<br />
Sepsis<br />
Beneficial effects of volume replacement in sepsis have been investigated<br />
in several trials (Table 3). In a rat model of sepsis [42] fluid<br />
resuscitation was successful in restoring the glomerular filtration<br />
rate if it was initiated at the moment that the bacterial inoculum was<br />
present, but not if it was started at the moment endotoxaemia was<br />
induced. Similar findings in humans were obtained by a prospective<br />
study (level III)[43] which showed that in deteriorating renal function,<br />
further fluid loading is not likely to reverse ARF in patients in<br />
whom the septic cascade has already started. Early volume resuscitation,<br />
however, along with other measures applied in sepsis to reach<br />
certain targets of oxygen delivery, results in less organ failure and<br />
reduced mortality (level I)[44]. In this study both colloids and crystalloids<br />
were given depending on physician’s preference. Schortgen<br />
and co-workers compared 6% HES 130/0.62 (n=65) to gelatin (n=64)<br />
and showed lower serum creatinine levels in the group receiving gelatin<br />
with no effect on RRT or outcome (level I)[19]. In a recent multicentre<br />
RCT, albumin was compared to isotonic sodium chloride in<br />
various situations including sepsis and without finding any difference<br />
in impact on renal function (level I)[17]. A single centre RCT of<br />
ICU patients comparing volume substitution with 5% HA or gelatin<br />
could not find any difference in renal function despite significant differences<br />
in serum albumin (level I) [35] . Finally, a comparison of<br />
several forms of HES in ICU patients did not demonstrate differences<br />
in renal function (level II) [45].<br />
Relative or unrecognized hypovolaemia<br />
Relative or unrecognised hypovolaemia (with respect to effective circulating<br />
volume) are clinical situations which are often missed and<br />
occur for example in diuretic therapy in the elderly, liver cirrhosis,<br />
heart failure and positive pressure mechanical ventilation.<br />
In an earlier study on the effect of diuretics on ICU patients with<br />
renal failure, renal function recovered in about 25% of patients after<br />
simple fluid replacement, indicating the presence of unrecognised<br />
pre-renal failure (level III) [46]. Therefore, many authors recom-<br />
550<br />
neth j crit care • volume 10 • no 5 • october 2006