Alevel_C1C2
Alevel_C1C2
Alevel_C1C2
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
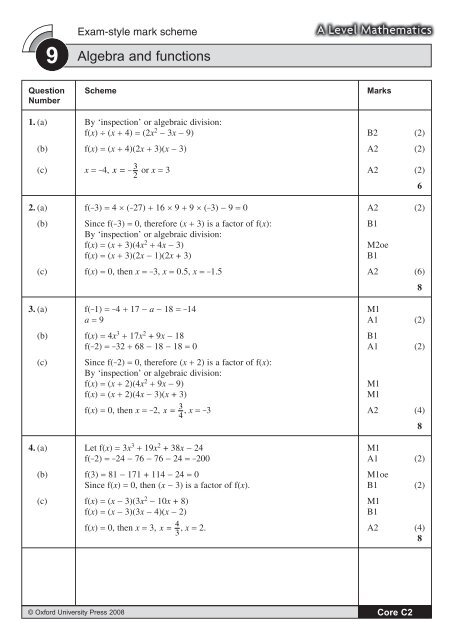
9<br />
Exam-style mark scheme<br />
Algebra and functions<br />
Question Scheme Marks<br />
Number<br />
1. (a) By ‘inspection’ or algebraic division:<br />
f(x) ¸ (x + 4) = (2x 2 - 3x - 9) B2 (2)<br />
(b) f(x) = (x + 4)(2x + 3)(x - 3) A2 (2)<br />
(c) x = -4, x = − 3 2<br />
or x = 3 A2 (2)<br />
6<br />
2. (a) f(-3) = 4 ´ (-27) + 16 ´ 9 + 9 ´ (-3) - 9 = 0 A2 (2)<br />
(b) Since f(-3) = 0, therefore (x + 3) is a factor of f(x): B1<br />
By ‘inspection’ or algebraic division:<br />
f(x) = (x + 3)(4x 2 + 4x - 3)<br />
M2oe<br />
f(x) = (x + 3)(2x - 1)(2x + 3)<br />
B1<br />
(c) f(x) = 0, then x = -3, x = 0.5, x = -1.5 A2 (6)<br />
3. (a) f(-1) = -4 + 17 - a - 18 = -14 M1<br />
a = 9 A1 (2)<br />
(b) f(x) = 4x 3 + 17x 2 + 9x - 18 B1<br />
f(-2) = -32 + 68 - 18 - 18 = 0 A1 (2)<br />
(c)<br />
Since f(-2) = 0, therefore (x + 2) is a factor of f(x):<br />
By ‘inspection’ or algebraic division:<br />
f(x) = (x + 2)(4x 2 + 9x - 9)<br />
f(x) = (x + 2)(4x - 3)(x + 3)<br />
f(x) = 0, then x = -2, x = 3 , x = -3<br />
4<br />
A2 (4)<br />
8<br />
4. (a) Let f(x) = 3x 3 + 19x 2 + 38x - 24 M1<br />
f(-2) = -24 - 76 - 76 - 24 = -200 A1 (2)<br />
(b) f(3) = 81 - 171 + 114 - 24 = 0 M1oe<br />
Since f(x) = 0, then (x - 3) is a factor of f(x). B1 (2)<br />
(c) f(x) = (x - 3)(3x 2 - 10x + 8) M1<br />
f(x) = (x - 3)(3x - 4)(x - 2)<br />
B1<br />
f(x) = 0, then x = 3, x = 4 3<br />
, x = 2. A2 (4)<br />
8<br />
M1<br />
M1<br />
8<br />
© Oxford University Press 2008<br />
Core C2