Alevel_C1C2
Alevel_C1C2
Alevel_C1C2
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
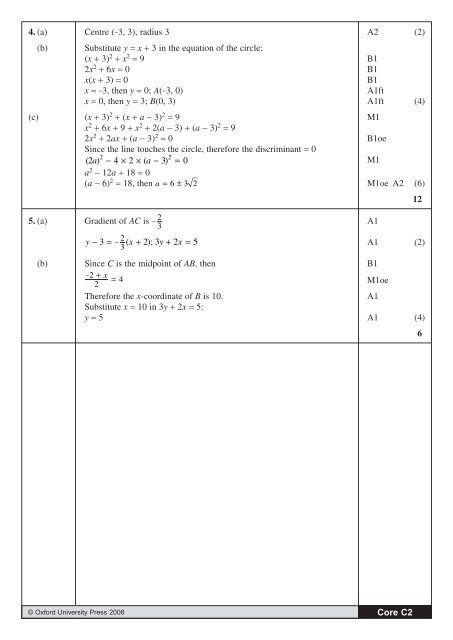
4. (a) Centre (-3, 3), radius 3 A2 (2)<br />
(b)<br />
Substitute y = x + 3 in the equation of the circle:<br />
(x + 3) 2 + x 2 = 9 B1<br />
2x 2 + 6x = 0<br />
B1<br />
x(x + 3) = 0<br />
B1<br />
x = -3, then y = 0; A(-3, 0)<br />
A1ft<br />
x = 0, then y = 3; B(0, 3) A1ft (4)<br />
(c) (x + 3) 2 + (x + a - 3) 2 = 9 M1<br />
x 2 + 6x + 9 + x 2 + 2(a - 3) + (a - 3) 2 = 9<br />
2x 2 + 2ax + (a - 3) 2 = 0<br />
B1oe<br />
Since the line touches the circle, therefore the discriminant = 0<br />
( 2a) − 4 × 2 × ( a − 3)<br />
= 0<br />
M1<br />
a 2 - 12a + 18 = 0<br />
(a - 6) 2 = 18, then a = 6 ± 3 2 M1oe A2 (6)<br />
12<br />
5. (a) Gradient of AC is − 2 3<br />
A1<br />
y − 3 =<br />
2<br />
− ( x + 2); 3y + 2x<br />
= 5<br />
A1 (2)<br />
3<br />
(b) Since C is the midpoint of AB, then B1<br />
− 2 + x<br />
= 4<br />
2<br />
M1oe<br />
Therefore the x-coordinate of B is 10.<br />
A1<br />
Substitute x = 10 in 3y + 2x = 5:<br />
y = 5 A1 (4)<br />
6<br />
© Oxford University Press 2008<br />
Core C2