Alevel_C1C2
Alevel_C1C2
Alevel_C1C2
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
3<br />
Exam-style mark scheme<br />
Quadratic functions<br />
Question Scheme Marks<br />
Number<br />
1. (a) Completing the square of the L.H.S. or expand the bracket of<br />
the R.H.S. and compare the coefficients of the x 2 and x.<br />
2 2 2<br />
( x + 3) − 3 + 4 = ( x + 3) − 5 ⇒ a = 3,<br />
b = −5<br />
A2 (2)<br />
(b) (x + 3) 2 - 5 = 0 B1<br />
(x + 3) 2 = 5<br />
x + 3 = ± 5<br />
x = −3 ± 5 ⇒<br />
B1<br />
p = -3 and q = 1 A2 (4)<br />
6<br />
2. (a) Using the quadratic formula:<br />
x =<br />
2<br />
2 ± ( −2) − 4 × 4 × ( −1)<br />
2 × 4<br />
=<br />
2 ± 20<br />
8<br />
=<br />
1 ± 5<br />
4<br />
B1 A1 (2)<br />
( ) = B1<br />
2<br />
x −<br />
1<br />
( ) −<br />
1<br />
−<br />
1<br />
= 0 B1<br />
4 16 4<br />
( x − 1<br />
2<br />
−<br />
5<br />
) = a = −<br />
1<br />
b = −<br />
5<br />
2<br />
(b) 4 x −<br />
1<br />
x −<br />
1<br />
0<br />
2 4<br />
4<br />
16<br />
0, , A2 (4)<br />
4 16<br />
6<br />
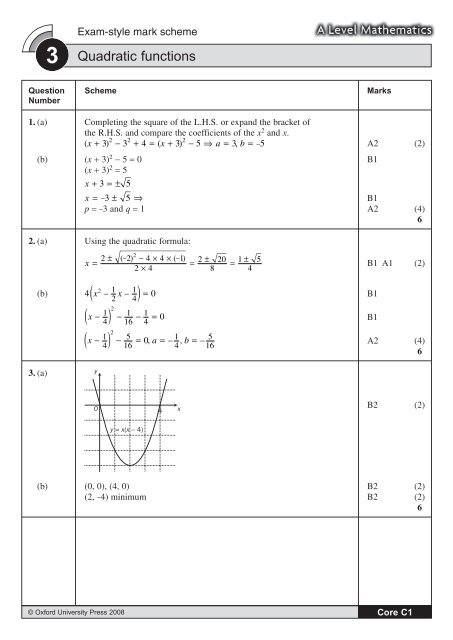
3. (a)<br />
y<br />
O<br />
4<br />
x<br />
B2 (2)<br />
y = x(x – 4)<br />
(b) (0, 0), (4, 0) B2 (2)<br />
(2, -4) minimum B2 (2)<br />
6<br />
© Oxford University Press 2008<br />
Core C1