IMPACT OF TAXES AND TRANSFERS
n?u=RePEc:tul:ceqwps:25&r=lam
n?u=RePEc:tul:ceqwps:25&r=lam
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Enami, Lustig, Aranda, No. 25, November 2016<br />
when T(x)/x is the same for all x--the distribution of post-tax and pre-tax income will be<br />
exactly the same and C T (p) = L X (p).<br />
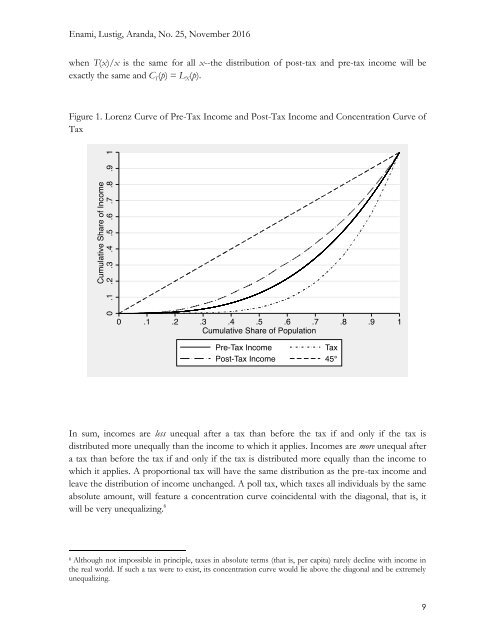
Figure 1. Lorenz Curve of Pre-Tax Income and Post-Tax Income and Concentration Curve of<br />
Tax<br />
In sum, incomes are less unequal after a tax than before the tax if and only if the tax is<br />
distributed more unequally than the income to which it applies. Incomes are more unequal after<br />
a tax than before the tax if and only if the tax is distributed more equally than the income to<br />
which it applies. A proportional tax will have the same distribution as the pre-tax income and<br />
leave the distribution of income unchanged. A poll tax, which taxes all individuals by the same<br />
absolute amount, will feature a concentration curve coincidental with the diagonal, that is, it<br />
will be very unequalizing. 6<br />
6 Although not impossible in principle, taxes in absolute terms (that is, per capita) rarely decline with income in<br />
the real world. If such a tax were to exist, its concentration curve would lie above the diagonal and be extremely<br />
unequalizing.<br />
9