- Page 2: Textbook of Pediatric Gastroenterol
- Page 5 and 6: © 2004 Taylor & Francis, an imprin
- Page 7 and 8: vi Contents 24 Indeterminate coliti
- Page 9 and 10: viii Contributors Moti M Chowdhury
- Page 11 and 12: x Contributors Frank M Ruemmele Ser
- Page 14 and 15: 1 Introduction Microvillus inclusio
- Page 16 and 17: electrolyte concentrations similar
- Page 18 and 19: direct functional consequence, in c
- Page 20 and 21: Figure 1.5 Epithelial dysplasia. Di
- Page 22 and 23: Outcome This neonatal diarrhea, whi
- Page 24: 44. Beaulieu JF. Differential expre
- Page 27 and 28: 14 Congenital problems of the gastr
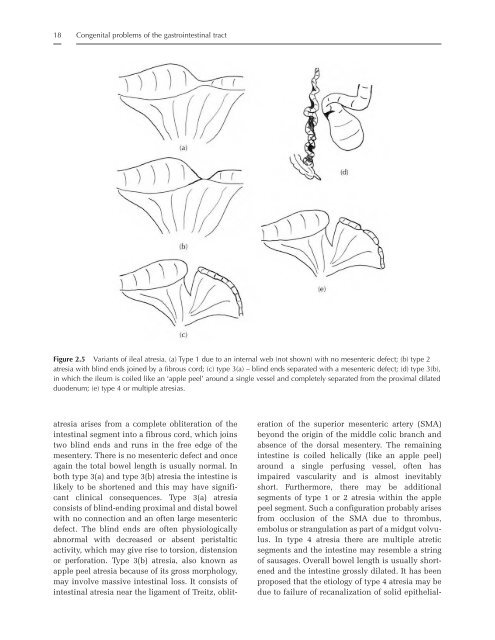
- Page 29: 16 Congenital problems of the gastr
- Page 33 and 34: 20 Congenital problems of the gastr
- Page 35 and 36: 22 Congenital problems of the gastr
- Page 37 and 38: 24 Congenital problems of the gastr
- Page 39 and 40: 26 Congenital problems of the gastr
- Page 41 and 42: 28 Congenital problems of the gastr
- Page 43 and 44: 30 Infectious esophagitis Table 3.1
- Page 45 and 46: 32 Infectious esophagitis Non-invas
- Page 47 and 48: 34 Infectious esophagitis A definit
- Page 49 and 50: 36 Infectious esophagitis Table 3.4
- Page 51 and 52: 38 Infectious esophagitis 5. Connol
- Page 53 and 54: 40 Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Page 55 and 56: 42 Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Page 57 and 58: 44 Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Page 59 and 60: 46 Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Page 61 and 62: 48 Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Page 63 and 64: 50 Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Page 65 and 66: 52 Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Page 67 and 68: 54 Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Page 69 and 70: 56 Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Page 71 and 72: 58 Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Page 74 and 75: 5 Introduction Achalasia Carl-Chris
- Page 76 and 77: are relayed to, and processed by, t
- Page 78 and 79: of achalasia not showing the classi
- Page 80 and 81:
Surgical options The gold standard
- Page 82 and 83:
consensus on the benefit of perform
- Page 84 and 85:
oesophageal junction. Eur J Clin In
- Page 86 and 87:
6 Introduction Helicobacter pylori
- Page 88 and 89:
association with declining specific
- Page 90 and 91:
H. pylori colonizes only the gastri
- Page 92 and 93:
and plasma cells. In the inflamed g
- Page 94 and 95:
eing very effective only in those r
- Page 96 and 97:
Table 6.5 Classification of gastrit
- Page 98 and 99:
urease test, which is based on the
- Page 100 and 101:
ithromycin, and the nitroimidazoles
- Page 102 and 103:
OR Cancer H. pylori+ duodenal ulcer
- Page 104 and 105:
12. Fujisawa T, Kumagai T, Akamatsu
- Page 106:
90. Dohil R, Hassal E, Jevon G, Dim
- Page 109 and 110:
96 Other gastritides Table 7.1 Comm
- Page 111 and 112:
98 Other gastritides including inhi
- Page 113 and 114:
100 Other gastritides Upper gastroi
- Page 115 and 116:
102 Other gastritides Table 7.2 Con
- Page 117 and 118:
104 Other gastritides Table 7.3 Cau
- Page 119 and 120:
106 Other gastritides gastritis in
- Page 121 and 122:
108 Other gastritides Table 7.4 Dif
- Page 123 and 124:
110 Other gastritides Crohn’s dis
- Page 126 and 127:
8 Introduction HIV and the intestin
- Page 128 and 129:
enteropathy or are simply the conse
- Page 130 and 131:
HIV enteropathy Cases/1000 person-y
- Page 132 and 133:
specific as an indicator of HIV inf
- Page 134 and 135:
(11) Where there is persistent pyre
- Page 136 and 137:
REFERENCES 1. McDougal JS, Mawle A,
- Page 138 and 139:
72. Chintu C, Luo C, Baboo S et al.
- Page 140 and 141:
9 Epidemiology and etiology Viral d
- Page 142 and 143:
Pathophysiology of viral diarrhea 1
- Page 144 and 145:
TEER (Ohm/cm 2 ) 800 700 600 500 40
- Page 146 and 147:
Table 9.3 Pathogenesis of rotavirus
- Page 148 and 149:
disease. 39 Acute diarrhea may be a
- Page 150 and 151:
common and may be of emerging impor
- Page 152 and 153:
proposed to assign the Aichi virus
- Page 154 and 155:
though a rotavirus vaccine was lice
- Page 156 and 157:
38. Pang XL, Honma S, Nakata S et a
- Page 158 and 159:
10 Bacterial infections Alessio Fas
- Page 160 and 161:
Vibrio cholerae O1 is transmitted b
- Page 162 and 163:
In contrast to S. typhi, the cases
- Page 164 and 165:
generation cephalosporins, aztreona
- Page 166 and 167:
America and the type most readily i
- Page 168 and 169:
with outbreaks in India, 88 Serbia,
- Page 170 and 171:
REFERENCES 1. Barua D, Greenough WB
- Page 172:
75. Butterton JR, Ryan ET, Acheson
- Page 175 and 176:
162 Table 11.1 Classification of in
- Page 177 and 178:
164 Intestinal parasites low levels
- Page 179 and 180:
166 Intestinal parasites Ascariasis
- Page 181 and 182:
168 Intestinal parasites hookworm,
- Page 183 and 184:
170 Prevention Intestinal parasites
- Page 185 and 186:
172 Intestinal parasites AIDS patie
- Page 187 and 188:
174 Intestinal parasites and sanita
- Page 189 and 190:
176 Intestinal parasites 50% with t
- Page 191 and 192:
178 Intestinal parasites extra-abdo
- Page 193 and 194:
180 Intestinal parasites water cont
- Page 195 and 196:
182 Intestinal parasites fumarate r
- Page 197 and 198:
184 Intestinal parasites of treatme
- Page 199 and 200:
186 Intestinal parasites children,
- Page 201 and 202:
188 Intestinal parasites 46. Cooper
- Page 203 and 204:
190 Intestinal parasites enteropath
- Page 205 and 206:
192 Intestinal parasites long-term
- Page 207 and 208:
194 Post-infectious persistent diar
- Page 209 and 210:
196 Post-infectious persistent diar
- Page 211 and 212:
198 Post-infectious persistent diar
- Page 213 and 214:
200 Post-infectious persistent diar
- Page 215 and 216:
202 Small-bowel bacterial overgrowt
- Page 217 and 218:
204 Small-bowel bacterial overgrowt
- Page 219 and 220:
206 Small-bowel bacterial overgrowt
- Page 221 and 222:
208 Small-bowel bacterial overgrowt
- Page 223 and 224:
210 Small-bowel bacterial overgrowt
- Page 225 and 226:
212 Small-bowel bacterial overgrowt
- Page 227 and 228:
214 Functional abdominal pain and o
- Page 229 and 230:
216 Functional abdominal pain and o
- Page 231 and 232:
218 Functional abdominal pain and o
- Page 233 and 234:
220 Functional abdominal pain and o
- Page 235 and 236:
222 Functional abdominal pain and o
- Page 237 and 238:
224 Functional abdominal pain and o
- Page 239 and 240:
226 Functional abdominal pain and o
- Page 241 and 242:
228 Functional abdominal pain and o
- Page 243 and 244:
230 Functional abdominal pain and o
- Page 245 and 246:
232 Functional abdominal pain and o
- Page 247 and 248:
234 Disorders of sucking and swallo
- Page 249 and 250:
236 Disorders of sucking and swallo
- Page 251 and 252:
238 Disorders of sucking and swallo
- Page 253 and 254:
240 Disorders of sucking and swallo
- Page 255 and 256:
242 Disorders of sucking and swallo
- Page 257 and 258:
244 Disorders of sucking and swallo
- Page 259 and 260:
246 Disorders of sucking and swallo
- Page 261 and 262:
248 Constipation and encopresis in
- Page 263 and 264:
250 Constipation and encopresis in
- Page 265 and 266:
252 Constipation and encopresis in
- Page 267 and 268:
254 Constipation and encopresis in
- Page 269 and 270:
256 Constipation and encopresis in
- Page 271 and 272:
258 Constipation and encopresis in
- Page 273 and 274:
260 Hirschsprung’s disease and in
- Page 275 and 276:
262 Hirschsprung’s disease and in
- Page 277 and 278:
264 Hirschsprung’s disease and in
- Page 279 and 280:
266 Hirschsprung’s disease and in
- Page 281 and 282:
268 Hirschsprung’s disease and in
- Page 283 and 284:
270 Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstr
- Page 285 and 286:
272 Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstr
- Page 287 and 288:
274 Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstr
- Page 289 and 290:
276 Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstr
- Page 291 and 292:
278 Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstr
- Page 293 and 294:
280 Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstr
- Page 295 and 296:
282 Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstr
- Page 297 and 298:
284 Gastrointestinal and nutritiona
- Page 299 and 300:
286 Gastrointestinal and nutritiona
- Page 301 and 302:
288 Gastrointestinal and nutritiona
- Page 303 and 304:
290 Cyclic vomiting syndrome distur
- Page 305 and 306:
292 Cyclic vomiting syndrome non-ga
- Page 307 and 308:
294 Cyclic vomiting syndrome tions
- Page 309 and 310:
296 Cyclic vomiting syndrome freque
- Page 311 and 312:
298 Cyclic vomiting syndrome Figure
- Page 313 and 314:
300 Cyclic vomiting syndrome gastro
- Page 315 and 316:
302 Cyclic vomiting syndrome 28. Ta
- Page 317 and 318:
304 Acute and chronic pancreatitis
- Page 319 and 320:
306 Acute and chronic pancreatitis
- Page 321 and 322:
308 Acute and chronic pancreatitis
- Page 323 and 324:
310 Acute and chronic pancreatitis
- Page 325 and 326:
312 Acute and chronic pancreatitis
- Page 327 and 328:
314 Acute and chronic pancreatitis
- Page 329 and 330:
316 Acute and chronic pancreatitis
- Page 331 and 332:
318 Acute and chronic pancreatitis
- Page 333 and 334:
320 Food allergies supportive inves
- Page 335 and 336:
322 Food allergies appropriate ther
- Page 337 and 338:
324 Food allergies unusual, but an
- Page 339 and 340:
326 (a) Food allergies (b) (c) Figu
- Page 341 and 342:
328 Food allergies In infancy, food
- Page 343 and 344:
330 Food allergies This is usually
- Page 345 and 346:
332 Food allergies food allergic re
- Page 347 and 348:
334 Food allergies There are no con
- Page 349 and 350:
336 Food allergies to specific food
- Page 351 and 352:
338 Food allergies Production of Ig
- Page 353 and 354:
340 Food allergies minimal TGF-β p
- Page 355 and 356:
342 Food allergies REFERENCES 1. Wa
- Page 357 and 358:
344 Food allergies 81. Hill DJ, Hos
- Page 359 and 360:
346 Food allergies 153. Chen Y, Ino
- Page 361 and 362:
348 Crohn’s disease Africa and so
- Page 363 and 364:
350 Crohn’s disease may decrease
- Page 365 and 366:
352 Crohn’s disease Th1 cells. 10
- Page 367 and 368:
354 Crohn’s disease may be a fact
- Page 369 and 370:
356 Crohn’s disease tags usually
- Page 371 and 372:
358 Crohn’s disease Table 23.4 co
- Page 373 and 374:
360 Crohn’s disease predisposes t
- Page 375 and 376:
362 Crohn’s disease (a) (b) (c) (
- Page 377 and 378:
364 Crohn’s disease Figure 23.6 U
- Page 379 and 380:
366 Crohn’s disease pediatric IBD
- Page 381 and 382:
368 Crohn’s disease Table 23.9 Si
- Page 383 and 384:
370 Crohn’s disease Table 23.11 6
- Page 385 and 386:
372 Crohn’s disease 23.13). A sco
- Page 387 and 388:
374 Crohn’s disease 20. Roth MP,
- Page 389 and 390:
376 Crohn’s disease 97. Andersson
- Page 391 and 392:
378 Crohn’s disease 178. Food and
- Page 393 and 394:
380 Indeterminate colitis Table 24.
- Page 395 and 396:
382 Indeterminate colitis Table 24.
- Page 397 and 398:
384 Indeterminate colitis REFERENCE
- Page 399 and 400:
386 Ulcerative colitis germ-free en
- Page 401 and 402:
388 Ulcerative colitis Activated ce
- Page 403 and 404:
390 Ulcerative colitis Such finding
- Page 405 and 406:
392 Ulcerative colitis Table 25.4 T
- Page 407 and 408:
394 Ulcerative colitis Extraintesti
- Page 409 and 410:
396 Ulcerative colitis precipitatin
- Page 411 and 412:
398 Ulcerative colitis Table 25.7 A
- Page 413 and 414:
400 Ulcerative colitis Common side-
- Page 415 and 416:
402 Ulcerative colitis can reach th
- Page 417 and 418:
404 Ulcerative colitis corticoid-re
- Page 419 and 420:
406 Ulcerative colitis If the patie
- Page 421 and 422:
408 Ulcerative colitis frequency of
- Page 423 and 424:
410 Ulcerative colitis 17. Hendrick
- Page 425 and 426:
412 Ulcerative colitis 97. Callen J
- Page 427 and 428:
414 Ulcerative colitis 182. Daniels
- Page 429 and 430:
416 Ulcerative colitis 257. McIntyr
- Page 432 and 433:
26 Introduction Vasculitides Salvat
- Page 434 and 435:
Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodi
- Page 436 and 437:
whether the patient has recently be
- Page 438 and 439:
urea nitrogen, creatinine, liver en
- Page 440 and 441:
vascular wall irregularities. Magne
- Page 442 and 443:
from involvement of the large branc
- Page 444 and 445:
and physical findings. Antinuclear
- Page 446 and 447:
vasculitis such as neuropathy can t
- Page 448 and 449:
27 Introduction Celiac disease Stef
- Page 450 and 451:
change are recognized, as classical
- Page 452 and 453:
It should be noted that the factors
- Page 454 and 455:
controls showed no statistically in
- Page 456 and 457:
Hyposplenism Often seen in older pa
- Page 458 and 459:
suction biopsy tube. Specimens shou
- Page 460 and 461:
tigations, particularly in adults 1
- Page 462 and 463:
Working Group on Coeliac Disease an
- Page 464 and 465:
28 Introduction Protein-losing ente
- Page 466 and 467:
Table 28.1 Main causes of protein-l
- Page 468 and 469:
shown effects in reducing the thora
- Page 470 and 471:
may respond to steroids without rel
- Page 472 and 473:
39. Marino BS. Outcomes after the F
- Page 474 and 475:
29 Introduction Short-bowel syndrom
- Page 476 and 477:
while hypergastrinemia is inconstan
- Page 478 and 479:
Medical therapy Whatever the etiolo
- Page 480 and 481:
tain no fiber, have an osmolality b
- Page 482 and 483:
decrease and enhance intestinal tra
- Page 484 and 485:
D-Lactic acidosis D-Lactic acidosis
- Page 486 and 487:
concentration in the small-bowel mu
- Page 488 and 489:
31. Wilmore DW. Growth factors and
- Page 490 and 491:
108. Goulet O, Baglin-Gobet S, Jais
- Page 492 and 493:
30 Introduction Lymphonodular hyper
- Page 494 and 495:
(a) (b) (c) be disruption but not d
- Page 496 and 497:
terminal ileum and colon, giving a
- Page 498 and 499:
while in subjects with Crohn’s di
- Page 500:
19. Kokkonen J, Tikkanen S, Karttun
- Page 503 and 504:
490 Malnutrition development of the
- Page 505 and 506:
492 Malnutrition profound deficienc
- Page 507 and 508:
494 Malnutrition achieve normal gro
- Page 509 and 510:
496 Malnutrition can be used. Altho
- Page 511 and 512:
498 Malnutrition Figure 31.3 A chil
- Page 513 and 514:
500 Malnutrition deficiency. It is
- Page 515 and 516:
502 Malnutrition Table 31.4 Some ch
- Page 517 and 518:
504 Malnutrition Table 31.5 The mai
- Page 519 and 520:
506 Malnutrition (a) Intracellular
- Page 521 and 522:
508 Malnutrition the diabetic, in t
- Page 523 and 524:
510 Malnutrition Changes that occur
- Page 525 and 526:
512 Malnutrition The acute phase Th
- Page 527 and 528:
514 Malnutrition Table 31.7 The des
- Page 529 and 530:
516 Malnutrition often find this te
- Page 531 and 532:
518 Malnutrition Because these pati
- Page 533 and 534:
520 Malnutrition There should be a
- Page 535 and 536:
522 Malnutrition therapeutic diet o
- Page 538 and 539:
32 Biotherapeutic and nutraceutical
- Page 540 and 541:
nutrients; increased losses, e.g. d
- Page 542 and 543:
long-chain polyunsaturated fatty ac
- Page 544 and 545:
in humans during parenteral nutriti
- Page 546 and 547:
allergens and facilitate their hydr
- Page 548 and 549:
supplementation to prevent and trea
- Page 550:
66. Whelan J. Antagonistic effects
- Page 553 and 554:
540 Enteral nutrition Digestive sec
- Page 555 and 556:
542 Enteral nutrition intestine. Th
- Page 557 and 558:
544 Enteral nutrition Hypermetaboli
- Page 559 and 560:
546 Enteral nutrition atic insuffic
- Page 561 and 562:
548 Enteral nutrition well as the c
- Page 563 and 564:
550 Enteral nutrition support teams
- Page 565 and 566:
552 Enteral nutrition 40. Thomas AG
- Page 567 and 568:
554 Enteral nutrition 121. Goulet O
- Page 569 and 570:
556 Parenteral nutrition in infants
- Page 571 and 572:
558 Parenteral nutrition in infants
- Page 573 and 574:
560 Parenteral nutrition in infants
- Page 575 and 576:
562 Parenteral nutrition in infants
- Page 577 and 578:
564 Parenteral nutrition in infants
- Page 579 and 580:
566 Parenteral nutrition in infants
- Page 581 and 582:
568 Parenteral nutrition in infants
- Page 583 and 584:
570 Parenteral nutrition in infants
- Page 585 and 586:
572 Parenteral nutrition in infants
- Page 587 and 588:
574 Parenteral nutrition in infants
- Page 589 and 590:
576 Parenteral nutrition in infants
- Page 591 and 592:
578 Parenteral nutrition in infants
- Page 593 and 594:
580 Gastrointestinal problems of th
- Page 595 and 596:
582 Gastrointestinal problems of th
- Page 597 and 598:
584 Gastrointestinal problems of th
- Page 599 and 600:
586 Gastrointestinal problems of th
- Page 601 and 602:
588 Gastrointestinal problems of th
- Page 603 and 604:
590 Gastrointestinal problems of th
- Page 605 and 606:
592 Gastrointestinal problems of th
- Page 607 and 608:
594 Gastrointestinal problems of th
- Page 609 and 610:
596 Gastrointestinal problems of th
- Page 611 and 612:
598 Gastrointestinal problems of th
- Page 613 and 614:
600 Enteral nutrition in preterm in
- Page 615 and 616:
602 Enteral nutrition in preterm in
- Page 617 and 618:
604 Enteral nutrition in preterm in
- Page 619 and 620:
606 Enteral nutrition in preterm in
- Page 621 and 622:
608 Enteral nutrition in preterm in
- Page 623 and 624:
610 Enteral nutrition in preterm in
- Page 625 and 626:
612 Enteral nutrition in preterm in
- Page 627 and 628:
614 Enteral nutrition in preterm in
- Page 629 and 630:
616 Enteral nutrition in preterm in
- Page 631 and 632:
618 Enteral nutrition in preterm in
- Page 633 and 634:
620 Z Score compared to Usher & McL
- Page 635 and 636:
622 Parenteral nutrition in prematu
- Page 637 and 638:
624 Parenteral nutrition in prematu
- Page 639 and 640:
626 Parenteral nutrition in prematu
- Page 641 and 642:
628 Parenteral nutrition in prematu
- Page 643 and 644:
630 Parenteral nutrition in prematu
- Page 645 and 646:
632 Parenteral nutrition in prematu
- Page 647 and 648:
634 Parenteral nutrition in prematu
- Page 649 and 650:
636 Parenteral nutrition in prematu
- Page 651 and 652:
638 Parenteral nutrition in prematu
- Page 653 and 654:
640 Approach to gastrointestinal bl
- Page 655 and 656:
642 Approach to gastrointestinal bl
- Page 657 and 658:
644 Approach to gastrointestinal bl
- Page 659 and 660:
646 Approach to gastrointestinal bl
- Page 661 and 662:
648 Approach to gastrointestinal bl
- Page 663 and 664:
650 Approach to gastrointestinal bl
- Page 665 and 666:
652 Approach to gastrointestinal bl
- Page 667 and 668:
654 Approach to gastrointestinal bl
- Page 669 and 670:
656 Approach to the child with acut
- Page 671 and 672:
658 Approach to the child with acut
- Page 673 and 674:
660 Approach to the child with acut
- Page 675 and 676:
662 Approach to the child with acut
- Page 677 and 678:
664 Approach to the child with acut
- Page 679 and 680:
666 Approach to the child with acut
- Page 681 and 682:
668 Approach to the child with acut
- Page 683 and 684:
670 Approach to the child with acut
- Page 685 and 686:
672 Approach to the child with acut
- Page 687 and 688:
674 Approach to the child with acut
- Page 690 and 691:
40 Introduction Approach to the chi
- Page 692 and 693:
must be meticulously inspected, loo
- Page 694 and 695:
hide the clinical evolution of the
- Page 696 and 697:
MRI cholangiography gives full info
- Page 698 and 699:
it becomes irreversible and by inst
- Page 700 and 701:
a case of rectal perforation in a p
- Page 702:
in children. J Pediatr Gastroentero
- Page 705 and 706:
692 Management of ingested foreign
- Page 707 and 708:
694 Management of ingested foreign
- Page 709 and 710:
696 Management of ingested foreign
- Page 711 and 712:
698 Management of ingested foreign
- Page 713 and 714:
700 Management of ingested foreign
- Page 715 and 716:
702 Medical aspects of intestinal t
- Page 717 and 718:
704 Medical aspects of intestinal t
- Page 719 and 720:
706 Medical aspects of intestinal t
- Page 721 and 722:
708 Medical aspects of intestinal t
- Page 723 and 724:
710 Medical aspects of intestinal t
- Page 725 and 726:
712 Medical aspects of intestinal t
- Page 727 and 728:
714 Medical aspects of intestinal t
- Page 729 and 730:
716 Medical aspects of intestinal t
- Page 732 and 733:
43 Introduction Intussusception Ado
- Page 734 and 735:
stools is rarely seen early. In oth
- Page 736 and 737:
Figure 43.2 Ultrasonogram showing t
- Page 738 and 739:
Figure 43.5 Barium contrast radiogr
- Page 740 and 741:
not required in patients aged less
- Page 742 and 743:
44 Introduction Meckel’s divertic
- Page 744 and 745:
Figure 44.4 Histology of a Meckel
- Page 746 and 747:
Figure 44.6 Drawing demonstrating t
- Page 748 and 749:
Figure 44.9 Positive Tc-99m pertech
- Page 750 and 751:
Figure 44.11 Laparoscopic stapling
- Page 752 and 753:
45 Introduction Acute appendicitis
- Page 754 and 755:
Simple appendicitis The first clini
- Page 756 and 757:
physical examination is to take the
- Page 758 and 759:
technology will make this the diagn
- Page 760 and 761:
Spain), we currently use treatment
- Page 762:
25. Raffensperger JC. El abdomen ag
- Page 765 and 766:
752 Vascular lesions of the gastroi
- Page 767 and 768:
754 Vascular lesions of the gastroi
- Page 769 and 770:
756 Vascular lesions of the gastroi
- Page 771 and 772:
758 Vascular lesions of the gastroi
- Page 773 and 774:
760 Vascular lesions of the gastroi
- Page 775 and 776:
762 The role of minimally invasive
- Page 777 and 778:
764 The role of minimally invasive
- Page 779 and 780:
766 The role of minimally invasive
- Page 781 and 782:
768 The role of minimally invasive
- Page 784 and 785:
48 Introduction Polyps and other tu
- Page 786 and 787:
Table 48.4 History and examination
- Page 788 and 789:
Figure 48.2 Macular pigmentation of
- Page 790 and 791:
adolescents with PJS should be awar
- Page 792 and 793:
Attenuated APC 168 1578 Common muta
- Page 794 and 795:
The timing of primary preventative
- Page 796 and 797:
had either distant metastases, lymp
- Page 798 and 799:
20. McGarrity TJ, Kulin HE, Zaino R
- Page 800 and 801:
Index abdominal migraine 218, 219 a
- Page 802 and 803:
udesonide Crohn’s disease treatme
- Page 804 and 805:
desmoid disease 781 diabetes mellit
- Page 806 and 807:
egg allergy 334 elimination diets 5
- Page 808 and 809:
treatment 85-88 indications for 85-
- Page 810 and 811:
causes 2 classification 1-2 outcome
- Page 812 and 813:
technical considerations 761-762 mi
- Page 814 and 815:
minerals 607-609, 630-631 protein 6
- Page 816 and 817:
Trichuris trichiuria 170 see also t