The Riding School in the Royal Palace of Naples: Transformations ...
The Riding School in the Royal Palace of Naples: Transformations ...
The Riding School in the Royal Palace of Naples: Transformations ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
effective support<strong>in</strong>g elements. Moreover a relevant overload, 250 kg/m 2 , due to <strong>the</strong> new function <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong> attic as a storehouse, has been considered act<strong>in</strong>g on <strong>the</strong> tie-beam <strong>in</strong> between <strong>the</strong> two lateral<br />
posts. Calculus, made with <strong>the</strong> s<strong>of</strong>tware Nolian by S<strong>of</strong>t<strong>in</strong>g, has given <strong>the</strong> stress distribution which<br />
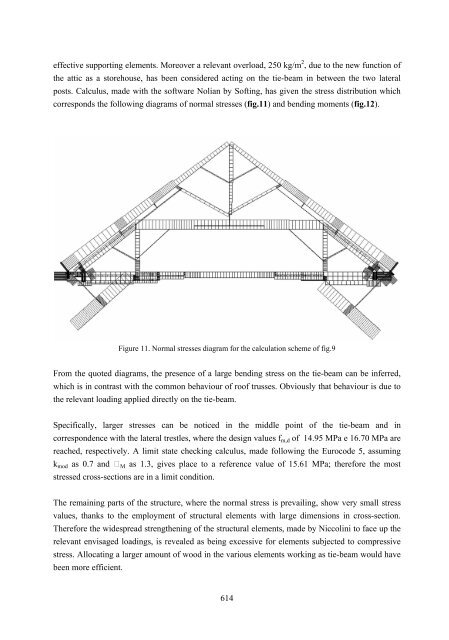
corresponds <strong>the</strong> follow<strong>in</strong>g diagrams <strong>of</strong> normal stresses (fig.11) and bend<strong>in</strong>g moments (fig.12).<br />
Figure 11. Normal stresses diagram for <strong>the</strong> calculation scheme <strong>of</strong> fig.9<br />
From <strong>the</strong> quoted diagrams, <strong>the</strong> presence <strong>of</strong> a large bend<strong>in</strong>g stress on <strong>the</strong> tie-beam can be <strong>in</strong>ferred,<br />
which is <strong>in</strong> contrast with <strong>the</strong> common behaviour <strong>of</strong> ro<strong>of</strong> trusses. Obviously that behaviour is due to<br />
<strong>the</strong> relevant load<strong>in</strong>g applied directly on <strong>the</strong> tie-beam.<br />
Specifically, larger stresses can be noticed <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> middle po<strong>in</strong>t <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> tie-beam and <strong>in</strong><br />
correspondence with <strong>the</strong> lateral trestles, where <strong>the</strong> design values fm,d <strong>of</strong> 14.95 MPa e 16.70 MPa are<br />
reached, respectively. A limit state check<strong>in</strong>g calculus, made follow<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> Eurocode 5, assum<strong>in</strong>g<br />
kmod as 0.7 and M as 1.3, gives place to a reference value <strong>of</strong> 15.61 MPa; <strong>the</strong>refore <strong>the</strong> most<br />
stressed cross-sections are <strong>in</strong> a limit condition.<br />
<strong>The</strong> rema<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g parts <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> structure, where <strong>the</strong> normal stress is prevail<strong>in</strong>g, show very small stress<br />
values, thanks to <strong>the</strong> employment <strong>of</strong> structural elements with large dimensions <strong>in</strong> cross-section.<br />
<strong>The</strong>refore <strong>the</strong> widespread streng<strong>the</strong>n<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> structural elements, made by Niccol<strong>in</strong>i to face up <strong>the</strong><br />
relevant envisaged load<strong>in</strong>gs, is revealed as be<strong>in</strong>g excessive for elements subjected to compressive<br />
stress. Allocat<strong>in</strong>g a larger amount <strong>of</strong> wood <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> various elements work<strong>in</strong>g as tie-beam would have<br />
been more efficient.<br />
614