Coyne Healthcare - Bio-Curcumin
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Boswellia serrata<br />
Boswellia (also commonly known as Frankincense) is a plant native to India and Pakistan, used extensively<br />
in traditional Ayurveda medicine and to a lesser degree Chinese traditional medicine. The gum resin is<br />
extracted from which one obtains the active boswellic acids. The major anti-inflammatory benefit arises<br />
from its novel inhibition of a pro-inflammatory enzyme called 5-Lipoxygenase (LOX) as well as it’s positive<br />
effect on NF-kB. Over and above the anti-inflammatory benefit, Boswellia has also been proven to have<br />
an effective analgesic effect and is well tolerated with a strong long term safety profile. This makes it an<br />
excellent consideration for those challenged with chronic conditions resulting in pain and inflammation.<br />
There are two major points of consideration when wanting to utilise boswellic acids therapeutically.<br />
3-Acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid = 3-Acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid - referred to as AKBA - has<br />
been clinically shown to be the most potent anti-inflammatory acid of boswellia, whereas β-boswellic acid<br />
has been shown to stimulate the platelet-induced generation of thrombin, liberate arachidonic acid, and<br />
induce platelet aggregation. It therefore makes sense to consider supplementation rich in AKBA which is<br />
free from β-boswellic acid for the purpose of reducing pain and inflammation.<br />
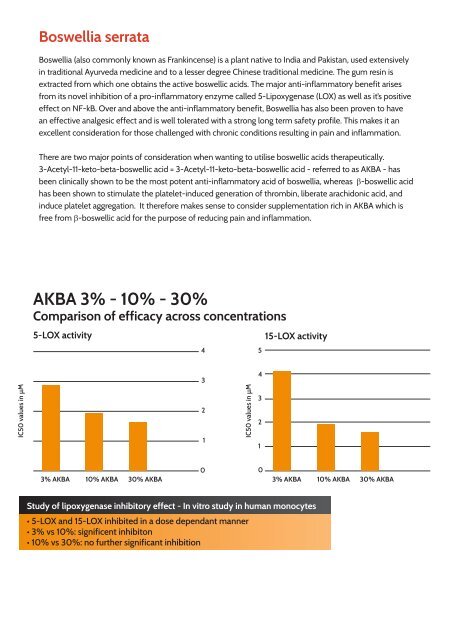
AKBA 3% - 10% - 30%<br />
Comparison of efficacy across concentrations<br />
5-LOX activity<br />
15-LOX activity<br />
4<br />
5<br />
3<br />
4<br />
IC50 values in µM<br />
2<br />
1<br />
IC50 values in µM<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1<br />
3% AKBA 10% AKBA 30% AKBA<br />
0<br />
0<br />
3% AKBA 10% AKBA 30% AKBA<br />
Study of lipoxygenase inhibitory effect - In vitro study in human monocytes<br />
• 5-LOX and 15-LOX inhibited in a dose dependant manner<br />
• 3% vs 10%: significent inhibiton<br />
• 10% vs 30%: no further significant inhibition