The production capacity of intercropped model of maize (Zea mays) with black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia)
A study was conducted to investigate the intercropping of legumes with cereals in different space as an approach to improve the soil nutrient content, the forage quality and the yield of cereals. Black locust was cultivated alone and intercropped with maize as follows: 2 rows maize to 2 rows Black locust (2M2R), 2 rows maize to 4 rows Black locust (2M4R), 2 rows maize to 6 rows Black locust (2M6R); 4 rows maize to 2 rows Black locust (4M2R), 4 rows maize to 4 rows Black locust (4M4R), 4 rows maize to 6 rows Black locust (4M6R) and 6 rows maize to 2 rows Black locust (6M2R), 6 rows maize to 4 rows Black locust (6M4R), 6 rows maize to 6 rows Black locust (6M6R).The experiment was laid out in randomized complete block design with three treatments and three replications. The results indicated significant increase of soil available phosphorus and soil organic matter in 2017 at harvest, while soil total nitrogen and soil available potassium decreased. However, total nitrogen and organic matter were higher in black locust leaves, black locust stems and maize stem. Low maize yield were founded in the major part of treatments while the highest biomass was founded in plants stem diameter. An increase is observed in maize and black locust height. Significant differences were founded in the character of black locust stem basal diameter. Also, significant differences in Chlorophyll concentration and WUE were observed.
A study was conducted to investigate the intercropping of legumes with cereals in different space as an approach to improve the soil nutrient content, the forage quality and the yield of cereals. Black locust was cultivated alone and intercropped with maize as follows: 2 rows maize to 2 rows Black locust (2M2R), 2 rows maize to 4 rows Black locust (2M4R), 2 rows maize to 6 rows Black locust (2M6R); 4 rows maize to 2 rows Black locust (4M2R), 4 rows maize to 4 rows Black locust (4M4R), 4 rows maize to 6 rows Black locust (4M6R) and 6 rows maize to 2 rows Black locust (6M2R), 6 rows maize to 4 rows Black locust (6M4R), 6 rows maize to 6 rows Black locust (6M6R).The experiment was laid out in randomized complete block design with three treatments and three replications. The results indicated significant increase of soil available phosphorus and soil organic matter in 2017 at harvest, while soil total nitrogen and soil available potassium decreased. However, total nitrogen and organic matter were higher in black locust leaves, black locust stems and maize stem. Low maize yield were founded in the major part of treatments while the highest biomass was founded in plants stem diameter. An increase is observed in maize and black locust height. Significant differences were founded in the character of black locust stem basal diameter. Also, significant differences in Chlorophyll concentration and WUE were observed.
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Int. J. Agron. Agri. R.<br />
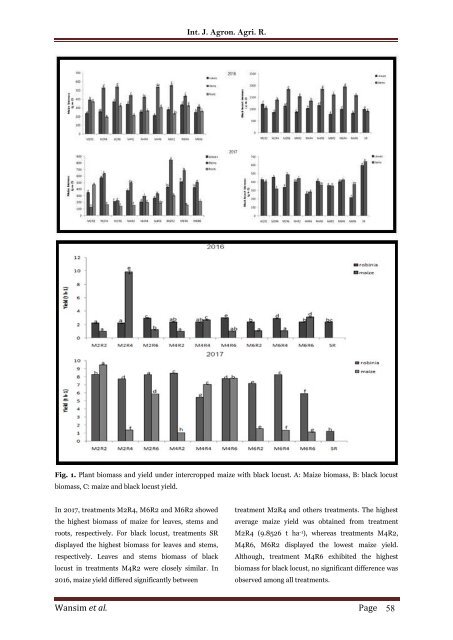
Fig. 1. Plant biomass and yield under <strong>intercropped</strong> <strong>maize</strong> <strong>with</strong> <strong>black</strong> <strong>locust</strong>. A: Maize biomass, B: <strong>black</strong> <strong>locust</strong><br />
biomass, C: <strong>maize</strong> and <strong>black</strong> <strong>locust</strong> yield.<br />
In 2017, treatments M2R4, M6R2 and M6R2 showed<br />
the highest biomass <strong>of</strong> <strong>maize</strong> for leaves, stems and<br />
roots, respectively. For <strong>black</strong> <strong>locust</strong>, treatments SR<br />
displayed the highest biomass for leaves and stems,<br />
respectively. Leaves and stems biomass <strong>of</strong> <strong>black</strong><br />
<strong>locust</strong> in treatments M4R2 were closely similar. In<br />
2016, <strong>maize</strong> yield differed significantly between<br />
treatment M2R4 and others treatments. <strong>The</strong> highest<br />
average <strong>maize</strong> yield was obtained from treatment<br />
M2R4 (9.8526 t ha -1 ), whereas treatments M4R2,<br />
M4R6, M6R2 displayed the lowest <strong>maize</strong> yield.<br />
Although, treatment M4R6 exhibited the highest<br />
biomass for <strong>black</strong> <strong>locust</strong>, no significant difference was<br />
observed among all treatments.<br />
Wansim et al. Page 58