Active IQ Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing (Children) (sample manual)
For more information, please visit http://www.activeiq.co.uk/qualifications/level-2/active-iq-level-2-certificate-in-fitness-instructing-(children)
For more information, please visit http://www.activeiq.co.uk/qualifications/level-2/active-iq-level-2-certificate-in-fitness-instructing-(children)
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
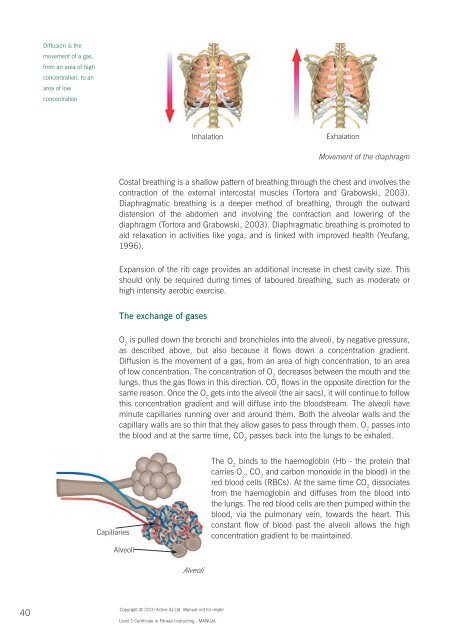
Diffusion is the<br />
movement of a gas,<br />
from an area of high<br />
concentration, to an<br />
area of low<br />
concentration<br />
Inhalation<br />
Exhalation<br />
Movement of the diaphragm<br />
Costal breath<strong>in</strong>g is a shallow pattern of breath<strong>in</strong>g through the chest and <strong>in</strong>volves the<br />
contraction of the external <strong>in</strong>tercostal muscles (Tortora and Grabowski, 2003).<br />
Diaphragmatic breath<strong>in</strong>g is a deeper method of breath<strong>in</strong>g, through the outward<br />
distension of the abdomen and <strong>in</strong>volv<strong>in</strong>g the contraction and lower<strong>in</strong>g of the<br />
diaphragm (Tortora and Grabowski, 2003). Diaphragmatic breath<strong>in</strong>g is promoted to<br />
aid relaxation <strong>in</strong> activities like yoga, and is l<strong>in</strong>ked with improved health (Yeufang,<br />
1996).<br />
Expansion of the rib cage provides an additional <strong>in</strong>crease <strong>in</strong> chest cavity size. This<br />
should only be required dur<strong>in</strong>g times of laboured breath<strong>in</strong>g, such as moderate or<br />
high <strong>in</strong>tensity aerobic exercise.<br />
The exchange of gases<br />
O 2<br />
is pulled down the bronchi and bronchioles <strong>in</strong>to the alveoli, by negative pressure,<br />
as described above, but also because it flows down a concentration gradient.<br />
Diffusion is the movement of a gas, from an area of high concentration, to an area<br />
of low concentration. The concentration of O 2<br />
decreases between the mouth and the<br />
lungs, thus the gas flows <strong>in</strong> this direction. CO 2<br />
flows <strong>in</strong> the opposite direction for the<br />
same reason. Once the O 2<br />
gets <strong>in</strong>to the alveoli (the air sacs), it will cont<strong>in</strong>ue to follow<br />
this concentration gradient and will diffuse <strong>in</strong>to the bloodstream. The alveoli have<br />
m<strong>in</strong>ute capillaries runn<strong>in</strong>g over and around them. Both the alveolar walls and the<br />
capillary walls are so th<strong>in</strong> that they allow gases to pass through them. O 2<br />
passes <strong>in</strong>to<br />
the blood and at the same time, CO 2<br />
passes back <strong>in</strong>to the lungs to be exhaled.<br />
Capillaries<br />
Alveoli<br />
The O 2<br />
b<strong>in</strong>ds to the haemoglob<strong>in</strong> (Hb - the prote<strong>in</strong> that<br />
carries O 2<br />
, CO 2<br />
and carbon monoxide <strong>in</strong> the blood) <strong>in</strong> the<br />
red blood cells (RBCs). At the same time CO 2<br />
dissociates<br />
from the haemoglob<strong>in</strong> and diffuses from the blood <strong>in</strong>to<br />
the lungs. The red blood cells are then pumped with<strong>in</strong> the<br />
blood, via the pulmonary ve<strong>in</strong>, towards the heart. This<br />
constant flow of blood past the alveoli allows the high<br />
concentration gradient to be ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong>ed.<br />
Alveoli<br />
40<br />
Copyright © 2010 <strong>Active</strong> <strong>IQ</strong> Ltd. Manual not for resale<br />
<strong>Level</strong> 2 <strong>Certificate</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Fitness</strong> Instruct<strong>in</strong>g - MANUAL