Dirt ad Trail Online Nov 2020
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
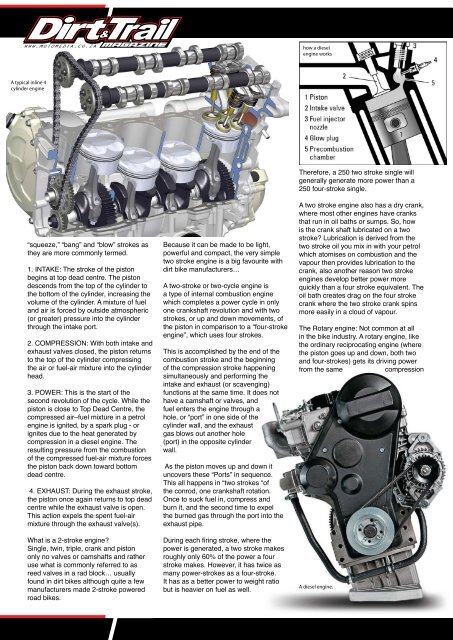
how a diesel<br />
engine works<br />
HONDA CRF1100 D<br />
<strong>2020</strong><br />
0 KM’S<br />
R240 300<br />
HONDA ELITE 125<br />
<strong>2020</strong><br />
0 KM’S<br />
R25 900<br />
CUSTOM<br />
HONDA CBR215R<br />
2013<br />
8 400 KM’S<br />
R26 900<br />
A typical inline 4<br />
cylinder engine<br />
HONDA CRF1100 D4<br />
<strong>2020</strong><br />
2 900 KM’S<br />
R269 900<br />
HONDA CRF1000<br />
2018<br />
7 900 KM’S<br />
R129 900<br />
BMW F850 GS<br />
2019<br />
5 800 KM’S<br />
R169 900<br />
“squeeze,” “bang” and “blow” strokes as<br />
they are more commonly termed.<br />
1. INTAKE: The stroke of the piston<br />
begins at top de<strong>ad</strong> centre. The piston<br />
descends from the top of the cylinder to<br />
the bottom of the cylinder, increasing the<br />
volume of the cylinder. A mixture of fuel<br />
and air is forced by outside atmospheric<br />
(or greater) pressure into the cylinder<br />
through the intake port.<br />
2. COMPRESSION: With both intake and<br />
exhaust valves closed, the piston returns<br />
to the top of the cylinder compressing<br />
the air or fuel-air mixture into the cylinder<br />
he<strong>ad</strong>.<br />
3. POWER: This is the start of the<br />
second revolution of the cycle. While the<br />
piston is close to Top De<strong>ad</strong> Centre, the<br />
compressed air–fuel mixture in a petrol<br />
engine is ignited, by a spark plug - or<br />
ignites due to the heat generated by<br />
compression in a diesel engine. The<br />
resulting pressure from the combustion<br />
of the compressed fuel-air mixture forces<br />
the piston back down toward bottom<br />
de<strong>ad</strong> centre.<br />
4. EXHAUST: During the exhaust stroke,<br />
the piston once again returns to top de<strong>ad</strong><br />
centre while the exhaust valve is open.<br />
This action expels the spent fuel-air<br />
mixture through the exhaust valve(s).<br />
Because it can be m<strong>ad</strong>e to be light,<br />
powerful and compact, the very simple<br />
two stroke engine is a big favourite with<br />
dirt bike manufacturers…<br />
A two-stroke or two-cycle engine is<br />
a type of internal combustion engine<br />
which completes a power cycle in only<br />
one crankshaft revolution and with two<br />
strokes, or up and down movements, of<br />
the piston in comparison to a “four-stroke<br />
engine”, which uses four strokes.<br />
This is accomplished by the end of the<br />
combustion stroke and the beginning<br />
of the compression stroke happening<br />
simultaneously and performing the<br />
intake and exhaust (or scavenging)<br />
functions at the same time. It does not<br />
have a camshaft or valves, and<br />
fuel enters the engine through a<br />
hole, or “port” in one side of the<br />
cylinder wall, and the exhaust<br />
gas blows out another hole<br />
(port) in the opposite cylinder<br />
wall.<br />
As the piston moves up and down it<br />
uncovers these “Ports” in sequence.<br />
This all happens in “two strokes “of<br />
the conrod, one crankshaft rotation.<br />
Once to suck fuel in, compress and<br />
burn it, and the second time to expel<br />
the burned gas through the port into the<br />
exhaust pipe.<br />
Therefore, a 250 two stroke single will<br />
generally generate more power than a<br />
250 four-stroke single.<br />
A two stroke engine also has a dry crank,<br />
where most other engines have cranks<br />
that run in oil baths or sumps. So, how<br />
is the crank shaft lubricated on a two<br />
stroke? Lubrication is derived from the<br />
two stroke oil you mix in with your petrol<br />
which atomises on combustion and the<br />
vapour then provides lubrication to the<br />
crank, also another reason two stroke<br />
engines develop better power more<br />
quickly than a four stroke equivalent. The<br />
oil bath creates drag on the four stroke<br />
crank where the two stroke crank spins<br />
more easily in a cloud of vapour.<br />
The Rotary engine: Not common at all<br />
in the bike industry. A rotary engine, like<br />
the ordinary reciprocating engine (where<br />
the piston goes up and down, both two<br />
and four-strokes) gets its driving power<br />
from the same<br />
compression<br />
HONDA CRF1000<br />
2019<br />
12 000 KM’S<br />
R159 900<br />
HONDA NC750x<br />
2019<br />
3 800 KM’S<br />
R95 000<br />
KAWASAKI ER6N<br />
2016<br />
3 400 KM’S<br />
R64 900<br />
What is a 2-stroke engine?<br />
Single, twin, triple, crank and piston<br />
only no valves or camshafts and rather<br />
use what is commonly referred to as<br />
reed valves in a r<strong>ad</strong> block… usually<br />
found in dirt bikes although quite a few<br />
manufacturers m<strong>ad</strong>e 2-stroke powered<br />
ro<strong>ad</strong> bikes.<br />
During each firing stroke, where the<br />
power is generated, a two stroke makes<br />
roughly only 60% of the power a four<br />
stroke makes. However, it has twice as<br />
many power-strokes as a four-stroke.<br />
It has as a better power to weight ratio<br />
but is heavier on fuel as well.<br />
A diesel engine.