IUCN Red List Guidelines - The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species
IUCN Red List Guidelines - The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species
IUCN Red List Guidelines - The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Red</strong> <strong>List</strong> <strong>Guidelines</strong> 30<br />
Index <strong>of</strong> abundance<br />
100<br />
10<br />
1<br />
100<br />
10<br />
1<br />
100<br />
10<br />
1<br />
100<br />
10<br />
1<br />
100<br />
10<br />
1<br />
Time<br />
(a)<br />
(c)<br />
(e)<br />
(g)<br />
(i)<br />
100<br />
10<br />
1<br />
100<br />
10<br />
1<br />
100<br />
10<br />
1<br />
100<br />
10<br />
4.8 Severely fragmented (criterion B)<br />
1<br />
(b)<br />
(f)<br />
(h)<br />
(d)<br />
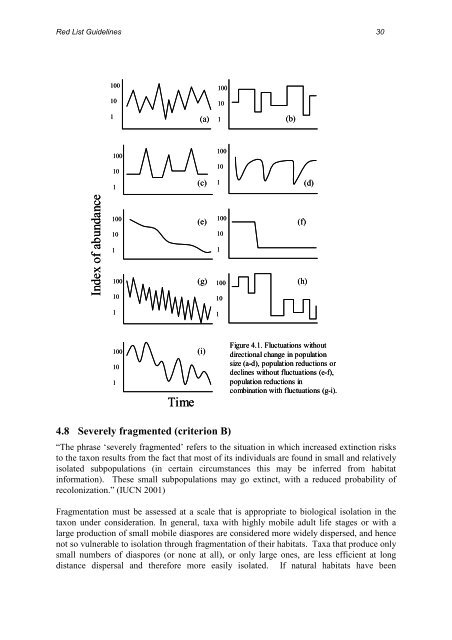
Figure 4.1. Fluctuations without<br />
directional change in population<br />
size (a-d), population reductions or<br />
declines without fluctuations (e-f),<br />
population reductions in<br />
combination with fluctuations (g-i).<br />
“<strong>The</strong> phrase ‘severely fragmented’ refers to the situation in which increased extinction risks<br />
to the taxon results from the fact that most <strong>of</strong> its individuals are found in small and relatively<br />
isolated subpopulations (in certain circumstances this may be inferred from habitat<br />
information). <strong>The</strong>se small subpopulations may go extinct, with a reduced probability <strong>of</strong><br />
recolonization.” (<strong>IUCN</strong> 2001)<br />
Fragmentation must be assessed at a scale that is appropriate to biological isolation in the<br />
taxon under consideration. In general, taxa with highly mobile adult life stages or with a<br />
large production <strong>of</strong> small mobile diaspores are considered more widely dispersed, and hence<br />
not so vulnerable to isolation through fragmentation <strong>of</strong> their habitats. Taxa that produce only<br />
small numbers <strong>of</strong> diaspores (or none at all), or only large ones, are less efficient at long<br />
distance dispersal and therefore more easily isolated. If natural habitats have been