2010 RWISO Journal - Roth Williams International Society of ...
2010 RWISO Journal - Roth Williams International Society of ...
2010 RWISO Journal - Roth Williams International Society of ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Figure 2 The zymogen pro-MMP is transcribed in the nucleus<br />
and then attached to the cell membrane. It is activated when<br />
it is cleaved from the membrane. The zinc (Zn) portion binds<br />
to protein and the enzyme cleaves the protein, destroying the<br />
extracellular matrix.<br />
In joints, MMPs are produced by monocytes, mac-<br />
rophages, polymorphonuclear neutrophils, synoviocytes, osteoblasts,<br />
and osteoclasts. MMPs are generally classified by<br />
the kind <strong>of</strong> matrix they degrade; thus collagenase, gelatinase<br />
and stromelysin (Figure 3).<br />
Figure 3 A list <strong>of</strong> the 28 known MMPs. They are generally<br />
named after the extracellular protein that they degrade.<br />
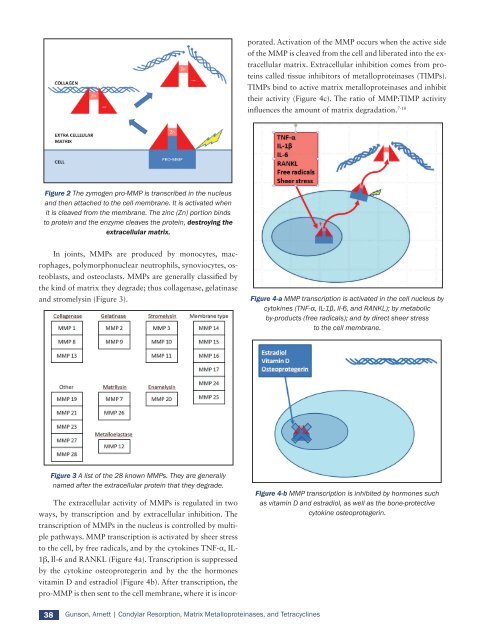
The extracellular activity <strong>of</strong> MMPs is regulated in two<br />
ways, by transcription and by extracellular inhibition. The<br />
transcription <strong>of</strong> MMPs in the nucleus is controlled by multiple<br />
pathways. MMP transcription is activated by sheer stress<br />
to the cell, by free radicals, and by the cytokines TNF-α, IL-<br />
1β, Il-6 and RANKL (Figure 4a). Transcription is suppressed<br />
by the cytokine osteoprotegerin and by the the hormones<br />
vitamin D and estradiol (Figure 4b). After transcription, the<br />
pro-MMP is then sent to the cell membrane, where it is incor-<br />
38 Gunson, Arnett | Condylar Resorption, Matrix Metalloproteinases, and Tetracyclines<br />
porated. Activation <strong>of</strong> the MMP occurs when the active side<br />
<strong>of</strong> the MMP is cleaved from the cell and liberated into the extracellular<br />
matrix. Extracellular inhibition comes from proteins<br />
called tissue inhibitors <strong>of</strong> metalloproteinases (TIMPs).<br />
TIMPs bind to active matrix metalloproteinases and inhibit<br />
their activity (Figure 4c). The ratio <strong>of</strong> MMP:TIMP activity<br />
influences the amount <strong>of</strong> matrix degradation. 7-10<br />
Figure 4-a MMP transcription is activated in the cell nucleus by<br />
cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, Il-6, and RANKL); by metabolic<br />
by-products (free radicals); and by direct sheer stress<br />
to the cell membrane.<br />
Figure 4-b MMP transcription is inhibited by hormones such<br />
as vitamin D and estradiol, as well as the bone-protective<br />
cytokine osteoprotegerin.