Dissecting the Role of Glucocorticoids on Pancreas ... - Diabetes
Dissecting the Role of Glucocorticoids on Pancreas ... - Diabetes
Dissecting the Role of Glucocorticoids on Pancreas ... - Diabetes
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
cells were too few to allow any reliable quantificati<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g>ir proliferati<strong>on</strong> rate.<br />
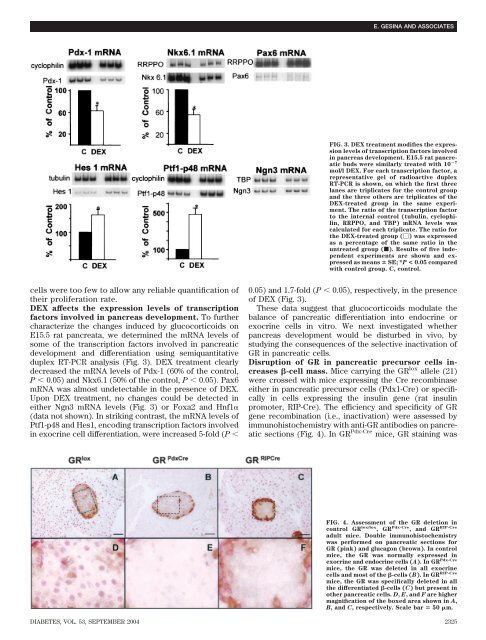
DEX affects <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> expressi<strong>on</strong> levels <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> transcripti<strong>on</strong><br />
factors involved in pancreas development. To fur<str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g>r<br />
characterize <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> changes induced by glucocorticoids <strong>on</strong><br />
E15.5 rat pancreata, we determined <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> mRNA levels <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
some <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> transcripti<strong>on</strong> factors involved in pancreatic<br />
development and differentiati<strong>on</strong> using semiquantitative<br />
duplex RT-PCR analysis (Fig. 3). DEX treatment clearly<br />
decreased <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> mRNA levels <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Pdx-1 (60% <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> c<strong>on</strong>trol,<br />
P � 0.05) and Nkx6.1 (50% <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> c<strong>on</strong>trol, P � 0.05). Pax6<br />
mRNA was almost undetectable in <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> presence <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> DEX.<br />
Up<strong>on</strong> DEX treatment, no changes could be detected in<br />
ei<str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g>r Ngn3 mRNA levels (Fig. 3) or Foxa2 and Hnf1�<br />
(data not shown). In striking c<strong>on</strong>trast, <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> mRNA levels <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
Ptf1-p48 and Hes1, encoding transcripti<strong>on</strong> factors involved<br />
in exocrine cell differentiati<strong>on</strong>, were increased 5-fold (P �<br />
E. GESINA AND ASSOCIATES<br />
FIG. 3. DEX treatment modifies <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> expressi<strong>on</strong><br />
levels <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> transcripti<strong>on</strong> factors involved<br />
in pancreas development. E15.5 rat pancreatic<br />
buds were similarly treated with 10 �7<br />
mol/l DEX. For each transcripti<strong>on</strong> factor, a<br />
representative gel <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> radioactive duplex<br />
RT-PCR is shown, <strong>on</strong> which <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> first three<br />
lanes are triplicates for <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> c<strong>on</strong>trol group<br />
and <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> three o<str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g>rs are triplicates <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
DEX-treated group in <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> same experiment.<br />
The ratio <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> transcripti<strong>on</strong> factor<br />
to <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> internal c<strong>on</strong>trol (tubulin, cyclophilin,<br />
RRPPO, and TBP) mRNA levels was<br />
calculated for each triplicate. The ratio for<br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> DEX-treated group (�) was expressed<br />
as a percentage <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> same ratio in <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
untreated group (f). Results <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> five independent<br />
experiments are shown and expressed<br />
as means � SE; *P < 0.05 compared<br />
with c<strong>on</strong>trol group. C, c<strong>on</strong>trol.<br />
0.05) and 1.7-fold (P � 0.05), respectively, in <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> presence<br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> DEX (Fig. 3).<br />
These data suggest that glucocorticoids modulate <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
balance <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> pancreatic differentiati<strong>on</strong> into endocrine or<br />
exocrine cells in vitro. We next investigated whe<str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g>r<br />
pancreas development would be disturbed in vivo, by<br />
studying <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> c<strong>on</strong>sequences <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> selective inactivati<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
GR in pancreatic cells.<br />
Disrupti<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> GR in pancreatic precursor cells increases<br />
�-cell mass. Mice carrying <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> GR lox allele (21)<br />
were crossed with mice expressing <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> Cre recombinase<br />
ei<str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g>r in pancreatic precursor cells (Pdx1-Cre) or specifically<br />
in cells expressing <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> insulin gene (rat insulin<br />
promoter, RIP-Cre). The efficiency and specificity <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> GR<br />
gene recombinati<strong>on</strong> (i.e., inactivati<strong>on</strong>) were assessed by<br />
immunohistochemistry with anti-GR antibodies <strong>on</strong> pancreatic<br />
secti<strong>on</strong>s (Fig. 4). In GR Pdx-Cre mice, GR staining was<br />
FIG. 4. Assessment <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> GR deleti<strong>on</strong> in<br />
c<strong>on</strong>trol GR lox/lox , GR Pdx-Cre , and GR RIP-Cre<br />
adult mice. Double immunohistochemistry<br />
was performed <strong>on</strong> pancreatic secti<strong>on</strong>s for<br />
GR (pink) and glucag<strong>on</strong> (brown). In c<strong>on</strong>trol<br />
mice, <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> GR was normally expressed in<br />
exocrine and endocrine cells (A). In GR Pdx-Cre<br />
mice, <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> GR was deleted in all exocrine<br />
cells and most <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> �-cells (B). In GR RIP-Cre<br />
mice, <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> GR was specifically deleted in all<br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> differentiated �-cells (C) but present in<br />
o<str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g>r pancreatic cells. D, E, and F are higher<br />
magnificati<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> boxed area shown in A,<br />
B, and C, respectively. Scale bar � 50 �m.<br />
DIABETES, VOL. 53, SEPTEMBER 2004 2325