WHO Good Governance for Medicines programme: an innovative ...
WHO Good Governance for Medicines programme: an innovative ...
WHO Good Governance for Medicines programme: an innovative ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
health <strong>an</strong>d national medicines regulatory authorities <strong>an</strong>d is currently running at different stages in the<br />
26 countries 9 across the six <strong>WHO</strong> regions.<br />
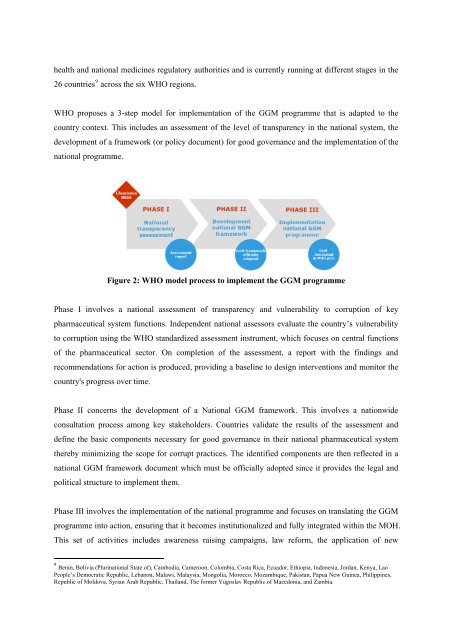
<strong>WHO</strong> proposes a 3-step model <strong>for</strong> implementation of the GGM <strong>programme</strong> that is adapted to the<br />
country context. This includes <strong>an</strong> assessment of the level of tr<strong>an</strong>sparency in the national system, the<br />
development of a framework (or policy document) <strong>for</strong> good govern<strong>an</strong>ce <strong>an</strong>d the implementation of the<br />
national <strong>programme</strong>.<br />
Figure 2: <strong>WHO</strong> model process to implement the GGM <strong>programme</strong><br />
Phase I involves a national assessment of tr<strong>an</strong>sparency <strong>an</strong>d vulnerability to corruption of key<br />
pharmaceutical system functions. Independent national assessors evaluate the country’s vulnerability<br />
to corruption using the <strong>WHO</strong> st<strong>an</strong>dardized assessment instrument, which focuses on central functions<br />
of the pharmaceutical sector. On completion of the assessment, a report with the findings <strong>an</strong>d<br />
recommendations <strong>for</strong> action is produced, providing a baseline to design interventions <strong>an</strong>d monitor the<br />
country's progress over time.<br />
Phase II concerns the development of a National GGM framework. This involves a nationwide<br />
consultation process among key stakeholders. Countries validate the results of the assessment <strong>an</strong>d<br />
define the basic components necessary <strong>for</strong> good govern<strong>an</strong>ce in their national pharmaceutical system<br />
thereby minimizing the scope <strong>for</strong> corrupt practices. The identified components are then reflected in a<br />
national GGM framework document which must be officially adopted since it provides the legal <strong>an</strong>d<br />
political structure to implement them.<br />
Phase III involves the implementation of the national <strong>programme</strong> <strong>an</strong>d focuses on tr<strong>an</strong>slating the GGM<br />
<strong>programme</strong> into action, ensuring that it becomes institutionalized <strong>an</strong>d fully integrated within the MOH.<br />
This set of activities includes awareness raising campaigns, law re<strong>for</strong>m, the application of new<br />
9 Benin, Bolivia (Plurinational State of), Cambodia, Cameroon, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Ethiopia, Indonesia, Jord<strong>an</strong>, Kenya, Lao<br />
People’s Democratic Republic, Leb<strong>an</strong>on, Malawi, Malaysia, Mongolia, Morocco, Mozambique, Pakist<strong>an</strong>, Papua New Guinea, Philippines,<br />
Republic of Moldova, Syri<strong>an</strong> Arab Republic, Thail<strong>an</strong>d, The <strong>for</strong>mer Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia, <strong>an</strong>d Zambia.<br />
7