Hormonas Tiroideas y Cerebro. Notas Sobre La Relación Bocio y ...
Hormonas Tiroideas y Cerebro. Notas Sobre La Relación Bocio y ...
Hormonas Tiroideas y Cerebro. Notas Sobre La Relación Bocio y ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
The DNA-bound, ligand-free TR, or aporeceptor interacts with corepressors and inhibit target gene<br />
transcription. Hormone binding induces a conformational change of the receptor which facilitates<br />
corepressor dissociation, binding of coactivators and stimulation of transcription.<br />
In the human, T 3 receptors are present in brain after 8–10 weeks of gestation. In subsequent<br />
weeks, the receptor concentration greatly increases in brain and other tissues, supporting the view of<br />
an important role of thyroid hormones on developmental processes taking place during the second<br />
trimester (8).<br />
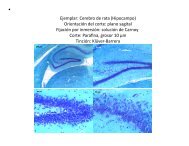
In the rat brain, the T 3 receptor is already present at embryonic day 14 (E14), and messenger<br />
RNA for the receptor is present by E11.5 in the neural tube and by E12.5 in certain areas of the<br />
diencephalon and ventral rhombencephalon (9). Despite this, most actions of thyroid hormones<br />
during rat brain development occur after birth, and many genes are thyroid hormone-dependent during<br />
the first two postnatal weeks. Nevertheless, actions of thyroid hormones on cell migration in the<br />
cerebral cortex have been found before onset of fetal thyroid gland function, stressing the importance<br />
of maternally derived hormones (4).<br />
Both thyroid hormone receptor genes—THRA and THRB—are expressed in brain, with<br />
partially unique and partially overlapping patterns, but the product of the THRA gene, TR1, accounts<br />
for 70-80% of al T3 receptor (8). Most effects of thyroid hormone in brain are therefore likely to be<br />
mediated through this receptor subtype. However, TR1 deletion does not cause the same<br />
impairments of brain development as hypothyroidism. We have shown that the difference between<br />
hypothyroidism and receptor deletion is that in the former, the activity of the unliganded receptor may<br />
interfere with developmental processes (10).<br />
References.<br />
1. Delong GR, Stanbury JB, Fierro-Benítez R 1985 Neurological signs in congenital iodine-deficiency disorder<br />
(endemic cretinism). Develop Med Child Neurol, 27:317-324.<br />
2. Guadaño-Ferraz A, Obregon MJ, St Germain DL, Bernal J 1997 The type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase is<br />
expressed primarily in glial cells in the neonatal rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:10391-10396.<br />
3. Tu HM, Legradi G, Bartha T, Salvatore D, Lechan RM, <strong>La</strong>rsen PR 1999 Regional expression of the type 3<br />
iodothyronine deiodinase messenger ribonucleic acid in the rat central nervous system and its regulation by<br />
thyroid hormone. Endocrinology 140:784-790.<br />
4. Morreale de Escobar G, Obregon MJ, Escobar del Rey F 2004 Role of thyroid hormone during early brain<br />
development. Eur J Endocrinol 151: Suppl 3, U25-37.<br />
5. Bernal J, Guadaño-Ferraz A, Morte B 2003 Perspectives in the study of thyroid hormone action on brain<br />
development and function. Thyroid 13: 1005-1012.<br />
6. Anderson GW, Schoonover CM, Jones SA 2003 Control of thyroid hormone action in the developing rat brain.<br />
Thyroid 13:1039-1056.<br />
7. O'Shea PJ, Williams GR 2002 Insight into the physiological actions of thyroid hormone receptors from<br />
genetically modified mice. J Endocrinol 175: 553-570.<br />
8. Bernal J 2007 Thyroid hormone receptors in brain development and function. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol<br />
Metab, 3:249-259.<br />
9. Bradley DJ, Towle HC, Young WS, 3rd 1992 Spatial and temporal expression of alpha- and beta-thyroid<br />
hormone receptor mRNAs, including the beta 2-subtype, in the developing mammalian nervous system. J<br />
Neurosci 12:2288-2302.<br />
10. Morte B, Manzano J, Scanlan T, Vennstrom B, Bernal J 2002 Deletion of the thyroid hormone receptor alpha<br />
1 prevents the structural alterations of the cerebellum induced by hypothyroidism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A<br />
99:3985-3989.<br />
26