CHAPITRE 1: Notions de thermodynamique - Master 2 en ...
CHAPITRE 1: Notions de thermodynamique - Master 2 en ...
CHAPITRE 1: Notions de thermodynamique - Master 2 en ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
1. Energie géothermique<br />
Types <strong>de</strong> géothermie<br />
Gestion <strong>de</strong> l’Energie et Environnem<strong>en</strong>t<br />
Selon le niveau <strong>de</strong> température, on distingue différ<strong>en</strong>ts types <strong>de</strong> géothermie, auxquels<br />
correspon<strong>de</strong>nt différ<strong>en</strong>ts usages :<br />
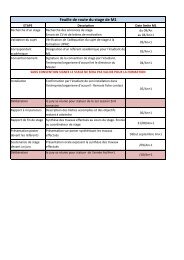
Type <strong>de</strong> géothermie Caractéristiques du ‘réservoir’ Utilisations<br />
Très basse<br />
Nappe à moins <strong>de</strong> 100 m<br />
T < à 30°C<br />
Chauffage et climatisation<br />
(Pompe à chaleur)<br />
Basse énergie Aquifères à 30°C < T < 150°C Chauffage urbain, utilisations<br />
industrielles, thermalisme…<br />
Moy<strong>en</strong>ne et Haute énergie<br />
Entre 1500 et 3000 m <strong>de</strong><br />
profon<strong>de</strong>ur<br />
180°C < T < 350°C<br />
Production d’électricité<br />
<strong>CHAPITRE</strong> 3 : Les énergies r<strong>en</strong>ouvelables<br />
89