L'hybridation génomique comparative en microréseau d'ADN (HGCM)
L'hybridation génomique comparative en microréseau d'ADN (HGCM)
L'hybridation génomique comparative en microréseau d'ADN (HGCM)
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
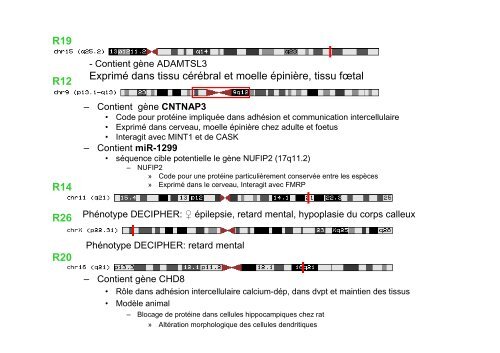
R19R12- Conti<strong>en</strong>t gène ADAMTSL3Exprimé dans tissu cérébral et moelle épinière, tissu fœtalR14– Conti<strong>en</strong>t gène CNTNAP3• Code pour protéine impliquée dans adhésion et communication intercellulaire• Exprimé dans cerveau, moelle épinière chez adulte et foetus• Interagit avec MINT1 et de CASK– Conti<strong>en</strong>t miR-1299• séqu<strong>en</strong>ce cible pot<strong>en</strong>tielle le gène NUFIP2 (17q11.2)– NUFIP2» Code pour une protéine particulièrem<strong>en</strong>t conservée <strong>en</strong>tre les espèces» Exprimé dans le cerveau, Interagit avec FMRPR26Phénotype DECIPHER: ♀ épilepsie, retard m<strong>en</strong>tal, hypoplasie du corps calleuxR20Phénotype DECIPHER: retard m<strong>en</strong>tal– Conti<strong>en</strong>t gène CHD8• Rôle dans adhésion intercellulaire calcium-dép, dans dvpt et mainti<strong>en</strong> des tissus• Modèle animal– Blocage de protéine dans cellules hippocampiques chez rat» Altération morphologique des cellules d<strong>en</strong>dritiques