MATLAB 1) Introdução 2) Geração de Sinais Amostrados
MATLAB 1) Introdução 2) Geração de Sinais Amostrados
MATLAB 1) Introdução 2) Geração de Sinais Amostrados
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Tópicos em Processamento <strong>de</strong> <strong>Sinais</strong><br />
Departamento <strong>de</strong> Engenharia Elétrica<br />
Faculda<strong>de</strong> <strong>de</strong> Tecnologia<br />
Universida<strong>de</strong> <strong>de</strong> Brasília<br />
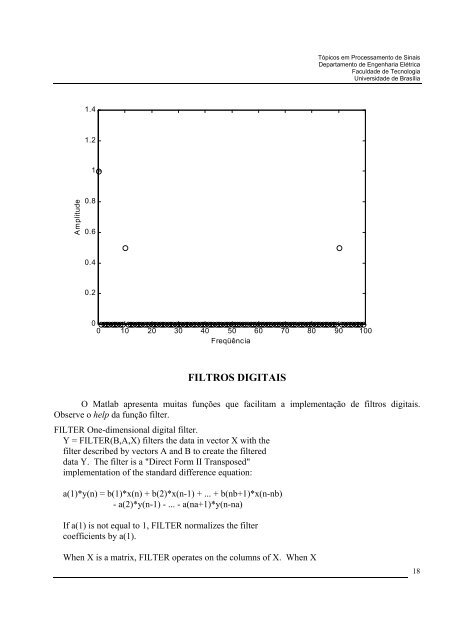
1.4<br />
1.2<br />
1<br />
Amplitu<strong>de</strong><br />
0.8<br />
0.6<br />
0.4<br />
0.2<br />
0<br />
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100<br />
Freqüência<br />
FILTROS DIGITAIS<br />
O Matlab apresenta muitas funções que facilitam a implementação <strong>de</strong> filtros digitais.<br />
Observe o help da função filter.<br />
FILTER One-dimensional digital filter.<br />
Y = FILTER(B,A,X) filters the data in vector X with the<br />
filter <strong>de</strong>scribed by vectors A and B to create the filtered<br />
data Y. The filter is a "Direct Form II Transposed"<br />
implementation of the standard difference equation:<br />
a(1)*y(n) = b(1)*x(n) + b(2)*x(n-1) + ... + b(nb+1)*x(n-nb)<br />
- a(2)*y(n-1) - ... - a(na+1)*y(n-na)<br />
If a(1) is not equal to 1, FILTER normalizes the filter<br />
coefficients by a(1).<br />
When X is a matrix, FILTER operates on the columns of X. When X<br />
18