Farmacologia da transmissão não adrenérgica
Farmacologia da transmissão não adrenérgica
Farmacologia da transmissão não adrenérgica
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
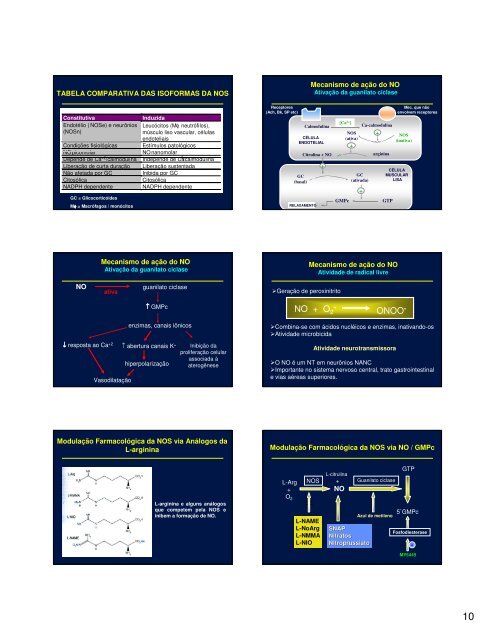
TABELA COMPARATIVA DAS ISOFORMAS DA NOS<br />
Mecanismo de ação do NO<br />
Ativação <strong>da</strong> guanilato ciclase<br />
Constitutiva<br />
Endotélio ( NOSe) e neurônios<br />
(NOSn)<br />
Condições fisiológicas<br />
NO picomolar<br />
Depende de Ca +2 /calmodulina<br />
Liberação de curta duração<br />
Não afeta<strong>da</strong> por GC<br />
Citosólica<br />
NADPH dependente<br />
GC = Glicocorticóides<br />
Mφ = Macrófagos / monócitos<br />
Induzi<strong>da</strong><br />
Leucócitos (Mφ,, neutrófilos),<br />
músculo liso vascular, células<br />
endoteliais<br />
Estímulos patológicos<br />
NO nanomolar<br />
Independe de Ca<br />
+2 /calmodulina<br />
Liberação sustenta<strong>da</strong><br />
Inibi<strong>da</strong> por GC<br />
Citosólica<br />
NADPH dependente<br />
Receptores<br />
(Ach, Bk, SP etc)<br />
Calmodulina<br />
CÉLULA<br />
ENDOTELIAL<br />
GC<br />
(basal)<br />
Citrulina + NO<br />
RELAXAMENTO<br />
+<br />
[Ca 2+ ]<br />
NOS<br />
(ativa)<br />
+<br />
GMPc<br />
GC<br />
(ativa<strong>da</strong>)<br />
Ca-calmodulina<br />
+<br />
+<br />
arginina<br />
Mec. que não<br />
envolvem receptores<br />
NOS<br />
(inativa)<br />
CÉLULA<br />
MUSCULAR<br />
LISA<br />
GTP<br />
Mecanismo de ação do NO<br />
Ativação <strong>da</strong> guanilato ciclase<br />
Mecanismo de ação do NO<br />
Ativi<strong>da</strong>de de radical livre<br />
NO<br />
ativa<br />
guanilato ciclase<br />
Geração de peroxinitrito<br />
↑ GMPc<br />
NO + O 2<br />
+<br />
ONOO -<br />
enzimas, canais iônicos<br />
↓ resposta ao Ca +2 ↑ abertura canais K +<br />
hiperpolarização<br />
Inibição <strong>da</strong><br />
proliferação celular<br />
associa<strong>da</strong> à<br />
aterogênese<br />
Vasodilatação<br />
Combina-se com ácidos nucléicos e enzimas, inativando-os<br />
Ativi<strong>da</strong>de microbici<strong>da</strong><br />
Ativi<strong>da</strong>de neurotransmissora<br />
O NO é um NT em neurônios NANC<br />
Importante no sistema nervoso central, trato gastrointestinal<br />
e vias aéreas superiores.<br />
Modulação Farmacológica <strong>da</strong> NOS via Análogos <strong>da</strong><br />
L-arginina<br />
Modulação Farmacológica <strong>da</strong> NOS via NO / GMPc<br />
L-arginina e alguns análogos<br />
que competem pela NOS e<br />
inibem a formação de NO.<br />
L-Arg<br />
+<br />
O 2<br />
NOS<br />
L-NAME<br />
L-NoArg<br />
L-NMMA<br />
L-NIO<br />
L-citrulina<br />
+<br />
NO<br />
SNAP<br />
Nitratos<br />
Nitroprussiato<br />
Guanilato ciclase<br />
Azul de metileno<br />
GTP<br />
5`GMPc<br />
Fosfodiesterase<br />
-<br />
MY5445<br />
10