WORLD POPULATION TO 2300
WORLD POPULATION TO 2300
WORLD POPULATION TO 2300
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
of the Asian population. China will have 24 per<br />
cent of the Asian population, South-central Asia<br />
outside India 20 per cent, South-eastern Asia<br />
15 per cent, Western Asia 9 per cent, and Eastern<br />
Asia outside China 3 per cent. Despite the twists<br />
and turns of subsequent growth rates, this distribution<br />
will not change much up to <strong>2300</strong>.<br />
Unlike growth rates in the 2000-2050 period,<br />
the fertility and mortality trends that underlie<br />
them are not strictly parallel. Total fertility in<br />
Western Asia is somewhat lower than in Southcentral<br />
Asia outside India, but is projected to decline<br />
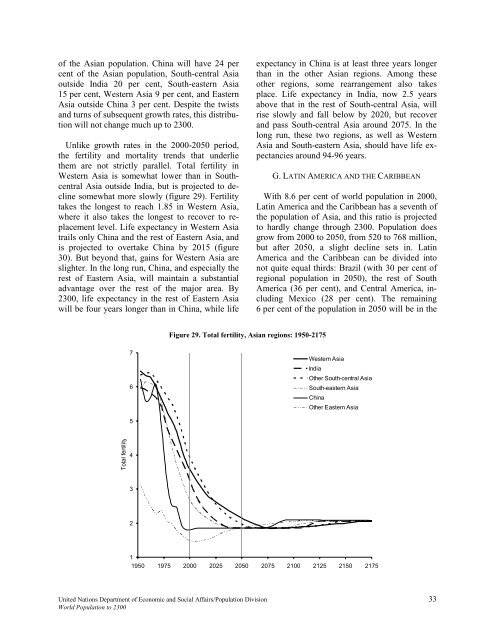
somewhat more slowly (figure 29). Fertility<br />
takes the longest to reach 1.85 in Western Asia,<br />
where it also takes the longest to recover to replacement<br />
level. Life expectancy in Western Asia<br />
trails only China and the rest of Eastern Asia, and<br />
is projected to overtake China by 2015 (figure<br />
30). But beyond that, gains for Western Asia are<br />
slighter. In the long run, China, and especially the<br />
rest of Eastern Asia, will maintain a substantial<br />
advantage over the rest of the major area. By<br />
<strong>2300</strong>, life expectancy in the rest of Eastern Asia<br />
will be four years longer than in China, while life<br />
Total fertility<br />
7<br />
6<br />
5<br />
4<br />
3<br />
2<br />
Figure 29. Total fertility, Asian regions: 1950-2175<br />
expectancy in China is at least three years longer<br />
than in the other Asian regions. Among these<br />
other regions, some rearrangement also takes<br />
place. Life expectancy in India, now 2.5 years<br />
above that in the rest of South-central Asia, will<br />
rise slowly and fall below by 2020, but recover<br />
and pass South-central Asia around 2075. In the<br />
long run, these two regions, as well as Western<br />
Asia and South-eastern Asia, should have life expectancies<br />
around 94-96 years.<br />
G. LATIN AMERICA AND THE CARIBBEAN<br />
With 8.6 per cent of world population in 2000,<br />
Latin America and the Caribbean has a seventh of<br />
the population of Asia, and this ratio is projected<br />
to hardly change through <strong>2300</strong>. Population does<br />
grow from 2000 to 2050, from 520 to 768 million,<br />
but after 2050, a slight decline sets in. Latin<br />
America and the Caribbean can be divided into<br />
not quite equal thirds: Brazil (with 30 per cent of<br />
regional population in 2050), the rest of South<br />
America (36 per cent), and Central America, including<br />
Mexico (28 per cent). The remaining<br />
6 per cent of the population in 2050 will be in the<br />
Western Asia<br />
1<br />
1950 1975 2000 2025 2050 2075 2100 2125 2150 2175<br />
United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs/Population Division 33<br />
World Population to <strong>2300</strong><br />
India<br />
Other South-central Asia<br />
South-eastern Asia<br />
China<br />
Other Eastern Asia