- Page 1 and 2: Junos ® OS for EX Series E
- Page 3 and 4: Table of Contents Part 1 Overview A
- Page 5 and 6: Limitations for Q-in-Q Tunneling .
- Page 7 and 8: Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 9 and 10: Part 4 Troubleshooting Chapter 11 T
- Page 11 and 12: List of Figures Part 1 Overview Cha
- Page 13 and 14: List of Tables Part 1 Overview Abou
- Page 15 and 16: About the Documentation • Documen
- Page 17 and 18: Documentation Conventions Table 1:
- Page 19 and 20: Documentation Feedback We encourage
- Page 21 and 22: PART 1 Overview Copyright © 2012,
- Page 23 and 24: CHAPTER 1 Bridging and VLANs • Un
- Page 25: network. As packets are sent, the s
- Page 29 and 30: Assigning Traffic to VLANs Forwardi
- Page 31 and 32: Understanding Routed VLAN Interface
- Page 33 and 34: Viewing RVI Statistics Figure 2: Cr
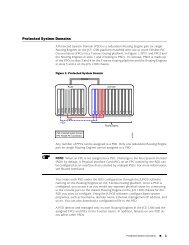
- Page 35 and 36: known hosts. Service providers use
- Page 37 and 38: Figure 4: PVLAN Spanning Multiple S
- Page 39 and 40: • Promiscuous port—A promiscuou
- Page 41 and 42: Configuring a PVLAN on Multiple Swi
- Page 43 and 44: Figure 8: Community VLAN Sends Unta
- Page 45 and 46: Related Documentation Copyright ©
- Page 47 and 48: Understanding Multiple VLAN Registr
- Page 49 and 50: Compatibility Issues With Junos OS
- Page 51 and 52: Related Documentation hierarchy, de
- Page 53 and 54: How Does EVB Work? functionality to
- Page 55 and 56: Ring Node States Failure Detection
- Page 57 and 58: • term 2: if [source MAC address
- Page 59 and 60: Related Documentation Copyright ©
- Page 61 and 62: CHAPTER 2 Q-in-Q Tunneling • Unde
- Page 63 and 64: If you configure multiple methods,
- Page 65 and 66: CHAPTER 3 Layer 2 Protocol Tunnelin
- Page 67 and 68: Figure 13: L2PT Example L2PT suppor
- Page 69 and 70: CHAPTER 4 Redundant Trunk Groups
- Page 71 and 72: Related Documentation Copyright ©
- Page 73 and 74: CHAPTER 5 Proxy ARP • Understandi
- Page 75 and 76: PART 2 Configuration Copyright © 2
- Page 77 and 78:
CHAPTER 6 Configuration Examples
- Page 79 and 80:
Table 7: Components of the Basic Br
- Page 81 and 82:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 83 and 84:
Verification ge-0/1/3 { unit 0 { fa
- Page 85 and 86:
Requirements Overview and Topology
- Page 87 and 88:
Step-by-Step Procedure Copyright ©
- Page 89 and 90:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 91 and 92:
Action List the Layer 3 routes in t
- Page 93 and 94:
Figure 16: Topology for Configurati
- Page 95 and 96:
Step-by-Step Procedure Copyright ©
- Page 97 and 98:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 99 and 100:
5. Configure the support VLAN: [edi
- Page 101 and 102:
user@switch> show vlans Name Tag In
- Page 103 and 104:
Configuration CLI Quick Configurati
- Page 105 and 106:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 107 and 108:
Number of interfaces: Tagged 2 (Act
- Page 109 and 110:
Verification [edit] user@switch# se
- Page 111 and 112:
Requirements Overview and Topology
- Page 113 and 114:
Table 11: Components of the Network
- Page 115 and 116:
} } ge-0/0/3 { unit 0 { family ethe
- Page 117 and 118:
family ethernet-switching { vlan {
- Page 119 and 120:
MVRP timers (ms): Interface Join Le
- Page 121 and 122:
__mvrp_200__ unblocked __mvrp_300__
- Page 123 and 124:
Step-by-Step Procedure Copyright ©
- Page 125 and 126:
Requirements Overview and Topology
- Page 127 and 128:
Configuration CLI Quick Configurati
- Page 129 and 130:
Layer2 Protocol Tunneling informati
- Page 131 and 132:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 133 and 134:
Verification user@switch# set proto
- Page 135 and 136:
Configuration Verification CLI Quic
- Page 137 and 138:
Requirements Overview and Topology
- Page 139 and 140:
Table 14: Components of Switch 1 in
- Page 141 and 142:
Step-by-Step Procedure Copyright ©
- Page 143 and 144:
Step-by-Step Procedure Copyright ©
- Page 145 and 146:
Configuring a PVLAN on Switch 3 CLI
- Page 147 and 148:
Verifying That the Primary VLAN and
- Page 149 and 150:
Number of interfaces: Tagged 0 (Act
- Page 151 and 152:
Example: Configuring Edge Virtual B
- Page 153 and 154:
Table 17: Components of the Topolog
- Page 155 and 156:
Verification admin@host# show edge-
- Page 157 and 158:
Overview and Topology • Configure
- Page 159 and 160:
Step-by-Step Procedure To configure
- Page 161 and 162:
CLI Quick Configuration } } Copyrig
- Page 163 and 164:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 165 and 166:
user@switch# set control-vlan erp-c
- Page 167 and 168:
CLI Quick Configuration Step-by-Ste
- Page 169 and 170:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 171 and 172:
CHAPTER 7 Configuration Tasks • C
- Page 173 and 174:
Table 19: VLAN Configuration Detail
- Page 175 and 176:
Create a VLAN Using All of the Opti
- Page 177 and 178:
Configuring Routed VLAN Interfaces
- Page 179 and 180:
Related Documentation • Example:
- Page 181 and 182:
Related Documentation • NOTE: Whe
- Page 183 and 184:
Related Documentation NOTE: Do not
- Page 185 and 186:
Disabling MVRP Disabling Dynamic VL
- Page 187 and 188:
Related Documentation you must alte
- Page 189 and 190:
Related Documentation Copyright ©
- Page 191 and 192:
Table 20: RTG Configuration Fields
- Page 193 and 194:
Creating a Private VLAN Spanning Mu
- Page 195 and 196:
Related Documentation • set stati
- Page 197 and 198:
Configuring Ethernet</stron
- Page 199 and 200:
Related Documentation Copyright ©
- Page 201 and 202:
CHAPTER 8 Configuration Statements
- Page 203 and 204:
Related Documentation Copyright ©
- Page 205 and 206:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 207 and 208:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 209 and 210:
Related Documentation • proxy-arp
- Page 211 and 212:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 213 and 214:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 215 and 216:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 217 and 218:
Related Documentation • bpdu-bloc
- Page 219 and 220:
Related Documentation add-attribute
- Page 221 and 222:
arp-on-stp Syntax arp-on-stp; Hiera
- Page 223 and 224:
List of Sample Output clear etherne
- Page 225 and 226:
customer-vlans Syntax customer-vlan
- Page 227 and 228:
description Syntax description text
- Page 229 and 230:
dot1q-tunneling (VLANs) Syntax dot1
- Page 231 and 232:
east-interface Syntax east-interfac
- Page 233 and 234:
ether-type Syntax ether-type (0x810
- Page 235 and 236:
ethernet-switching-options Syntax e
- Page 237 and 238:
Hierarchy Level [edit] } } traceopt
- Page 239 and 240:
group Syntax group name { interface
- Page 241 and 242:
instance-type Syntax instance-type
- Page 243 and 244:
interface Syntax interface interfac
- Page 245 and 246:
interface (MVRP) Syntax interface (
- Page 247 and 248:
join-timer (MVRP) Syntax join-timer
- Page 249 and 250:
Required Privilege Level Related Do
- Page 251 and 252:
leaveall-timer (MVRP) Syntax leavea
- Page 253 and 254:
mac Syntax mac mac-address { next-h
- Page 255 and 256:
Required Privilege Level Related Do
- Page 257 and 258:
mapping Syntax mapping (native (pus
- Page 259 and 260:
Required Privilege Level Related Do
- Page 261 and 262:
native-vlan-id Syntax native-vlan-i
- Page 263 and 264:
no-mac-learning Syntax no-mac-learn
- Page 265 and 266:
port-mode Syntax port-mode mode; Hi
- Page 267 and 268:
primary-vlan Syntax primary-vlan vl
- Page 269 and 270:
estore-interval number; traceoption
- Page 271 and 272:
pvlan-trunk Syntax pvlan-trunk; Hie
- Page 273 and 274:
ing-protection-link-end Syntax ring
- Page 275 and 276:
shutdown-threshold Syntax shutdown-
- Page 277 and 278:
traceoptions (Ethernet</str
- Page 279 and 280:
vlan Required Privilege Level Relat
- Page 281 and 282:
vlan-id Syntax vlan-id number; Hier
- Page 283 and 284:
vlans Syntax vlans { vlan-name { de
- Page 285 and 286:
vsi-discovery Syntax vsi-discovery
- Page 287 and 288:
west-interface Syntax west-interfac
- Page 289 and 290:
PART 3 Administration Copyright ©
- Page 291 and 292:
CHAPTER 9 Routine Monitoring • Ve
- Page 293 and 294:
__employee_130__ 130 ge-0/0/22.0* M
- Page 295 and 296:
Display Layer 2 VLANs, including an
- Page 297 and 298:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 299 and 300:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 301 and 302:
Related Documentation Also, for the
- Page 303 and 304:
Verifying That Proxy ARP Is Working
- Page 305 and 306:
Related Documentation Copyright ©
- Page 307 and 308:
CHAPTER 10 Operational Commands Cop
- Page 309 and 310:
clear ethernet-switching layer2-pro
- Page 311 and 312:
List of Sample Output clear etherne
- Page 313 and 314:
show edge-virtual-bridging Syntax s
- Page 315 and 316:
show edge-virtual-bridging vsi-prof
- Page 317 and 318:
Table 23: show ethernet-switching i
- Page 319 and 320:
show ethernet-switching interfaces
- Page 321 and 322:
Sample Output show ethernet-switchi
- Page 323 and 324:
Table 25: show ethernet-switching l
- Page 325 and 326:
show ethernet-switching layer2-prot
- Page 327 and 328:
show ethernet-switching mac-learnin
- Page 329 and 330:
show ethernet-switching mac-notific
- Page 331 and 332:
Sample Output show ethernet-switchi
- Page 333 and 334:
Table 30: show ethernet-switching s
- Page 335 and 336:
show ethernet-switching table Synta
- Page 337 and 338:
Sample Output show ethernet-switchi
- Page 339 and 340:
show ethernet-switching table persi
- Page 341 and 342:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 343 and 344:
show mvrp statistics Syntax show mv
- Page 345 and 346:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 347 and 348:
Sample Output show protection-group
- Page 349 and 350:
Table 36: show protection-group eth
- Page 351 and 352:
Sample Output show protection-group
- Page 353 and 354:
Sample Output show protection-group
- Page 355 and 356:
show protection-group ethernet-ring
- Page 357 and 358:
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks
- Page 359 and 360:
show system statistics arp Syntax s
- Page 361 and 362:
Required Privilege Level Related Do
- Page 363 and 364:
Table 41: show vlans Output Fields
- Page 365 and 366:
show vlans extensive (for a PVLAN s
- Page 367 and 368:
show vlans extensive (Port-based) C
- Page 369 and 370:
show vlans sort-by name show vlans
- Page 371 and 372:
PART 4 Troubleshooting Copyright ©
- Page 373 and 374:
CHAPTER 11 Troubleshooting Procedur