CBD Fourth National Report - Azerbaijan (English version)
CBD Fourth National Report - Azerbaijan (English version)
CBD Fourth National Report - Azerbaijan (English version)
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Country Study on Biodiversity and <strong>Fourth</strong> <strong>National</strong> <strong>Report</strong><br />
The Republic of <strong>Azerbaijan</strong><br />
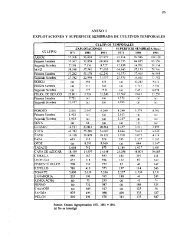
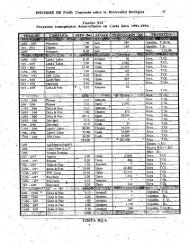
1.1.4.2. Rare, endemic or threatened plant communities and habitats<br />
In <strong>Azerbaijan</strong>, a number of specific habitats or plant communities are rare or threatened, for<br />
example:<br />
1. Psammophytic coastal plant community (Astragalus bakuensis, Melilotus caspicus,<br />
Calligonum bakuensis, Nitradia schoberi);<br />
2. Xerophytic plant communities in Nakchivan Autonomus Republic near the village of<br />
Badanli and in Shabuz region (Dorema glabrum, Iris lycotis, Astragalus badamlensis,<br />
Thymus collinus);<br />
3. Wetland communities around Akushchay and Sarisu Lakes (Trapa hyrcana, Nelumbo<br />
caspica, Nymphaeca alba,, N. peltata);<br />
4. Dry forest communities in <strong>Azerbaijan</strong> and Nakchivan (Pistacia mutica, Celtis<br />
caucasica, Punica granatum, Rhus coriaria, Juniperus oblonga, J. polycarpus, J.<br />
sabina, J. depressa, J. foetidissima);<br />
5. Eldar pine (Pinus eldarica) forest is only found on the Eldar plain in the Samukh<br />
region, and the oak forests (Quercus longipes) around the Nabran region are<br />
threatened;<br />
6. Humid, sub-tropical forest, supporting the rare and threatened iron tree (Parrotia<br />
persica), is unique to the Hyrcan forest of Lenkoran region in Talysh province;<br />
7. Rare and threatened alpine meadows around the lakes of Gey-gol and Maral-gol are<br />
typified by the lily Lilium ledebourii.<br />
Steppe communities dominated by Ferula oopoda and by Colutea comarovii are globally<br />
unique for the Nakhichevan Autonomous Republic. In the mountain pastures of the Shahbuz<br />
region a rare and unique plant community is dominated by the endemic species Rheum ribes.<br />
1.1.5. Status review of species<br />
1.1.5.1. Microorganisms<br />
Although there is little information on the diversity of micro-organisms in <strong>Azerbaijan</strong>, there<br />
are estimated to be between 1,200 and 1,250 species, but to date no endemic micro-organisms<br />
have been described. No specific measures are in place for the protection of microorganisms.<br />
As in the rest of <strong>Azerbaijan</strong>, there is a lack of knowledge about the diversity of<br />
microorganisms present in the Autonomous Republic of Nakhichevan. The presence of<br />
bacteria (Monera) is clear, particularly from their impacts through diseases in humans,<br />
animals and plants, and in their use in food production and processing (such as Lactobacillus<br />
etc.), and in healthcare (e. g. Penicillium). Microorganism cultures are kept in a number of<br />
institutes and epidemiological stations in the region.<br />
1.1.5.2. Protozoa<br />
Protozoa are cellular organisms that live either independently, or as part of a larger organism.<br />
Protozoa provide many varied and essential roles in an ecosystem, for example providing<br />
food for fish larvae and fry, and increasing soil fertility. They are also the pathogens of<br />
human and animal diseases. The protozoa described in <strong>Azerbaijan</strong> are distributed from the<br />
following groups:<br />
31<br />
2009