Download PDF - The Pancreapedia
Download PDF - The Pancreapedia
Download PDF - The Pancreapedia
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
This designation, although arbitrary, seems<br />
justified because of apparent functional<br />
differences between this and the remaining<br />
segments of the common bile duct, as will be<br />
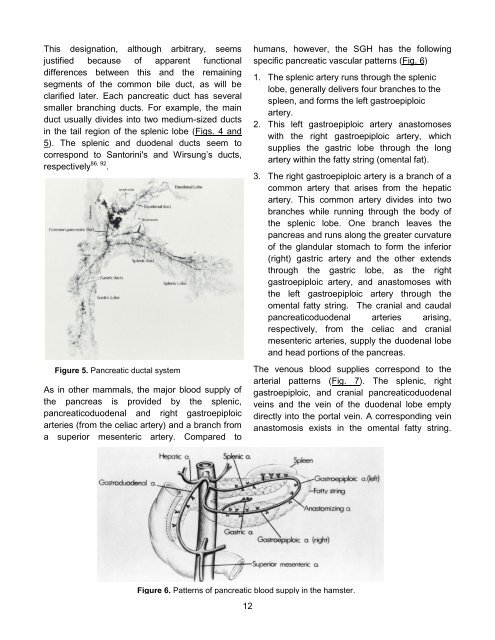
clarified later. Each pancreatic duct has several<br />
smaller branching ducts. For example, the main<br />
duct usually divides into two medium-sized ducts<br />
in the tail region of the splenic lobe (Figs. 4 and<br />
5). <strong>The</strong> splenic and duodenal ducts seem to<br />
correspond to Santorini's and Wirsung’s ducts,<br />
respectively 86, 92 .<br />
Figure 5. Pancreatic ductal system<br />
As in other mammals, the major blood supply of<br />
the pancreas is provided by the splenic,<br />
pancreaticoduodenal and right gastroepiploic<br />
arteries (from the celiac artery) and a branch from<br />
a superior mesenteric artery. Compared to<br />
12<br />
humans, however, the SGH has the following<br />
specific pancreatic vascular patterns (Fig. 6)<br />
1. <strong>The</strong> splenic artery runs through the splenic<br />
lobe, generally delivers four branches to the<br />
spleen, and forms the left gastroepiploic<br />
artery.<br />
2. This left gastroepiploic artery anastomoses<br />
with the right gastroepiploic artery, which<br />
supplies the gastric lobe through the long<br />
artery within the fatty string (omental fat).<br />
3. <strong>The</strong> right gastroepiploic artery is a branch of a<br />
common artery that arises from the hepatic<br />
artery. This common artery divides into two<br />
branches while running through the body of<br />
the splenic lobe. One branch leaves the<br />
pancreas and runs along the greater curvature<br />
of the glandular stomach to form the inferior<br />
(right) gastric artery and the other extends<br />
through the gastric lobe, as the right<br />
gastroepiploic artery, and anastomoses with<br />
the left gastroepiploic artery through the<br />
omental fatty string. <strong>The</strong> cranial and caudal<br />
pancreaticoduodenal arteries arising,<br />
respectively, from the celiac and cranial<br />
mesenteric arteries, supply the duodenal lobe<br />
and head portions of the pancreas.<br />
<strong>The</strong> venous blood supplies correspond to the<br />
arterial patterns (Fig. 7). <strong>The</strong> splenic, right<br />
gastroepiploic, and cranial pancreaticoduodenal<br />
veins and the vein of the duodenal lobe empty<br />
directly into the portal vein. A corresponding vein<br />
anastomosis exists in the omental fatty string.<br />
Figure 6. Patterns of pancreatic blood supply in the hamster.