Download PDF - The Pancreapedia
Download PDF - The Pancreapedia
Download PDF - The Pancreapedia
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
shape with an almost transparent cytoplasm may<br />
be why they escaped the attention of anatomic<br />
histologists. <strong>The</strong>se almost transparent cells<br />
contain oval or spindle-shaped nuclei with a<br />
lesser chromatin content than those of acini (Fig.<br />
12).<br />
Figure 12. Acinar and centroacinar cells (CAC) in<br />
the pancreas of the hamster. Acinar cells have<br />
various number of zymogen granules of different<br />
size and plenty of RER and microvilli on the luminal<br />
surface. In contrast, CAC cells have many<br />
mitochondria (M) and junctional complex (arrows)<br />
but fewer microvilli. TEM X 4,122.<br />
<strong>The</strong>se cells merge imperceptibly into those of<br />
intercalated ductules, which have oval, or flask-shaped,<br />
dentated or convoluted vesicular nuclei<br />
within the scanty, ill defined, light acidophilic<br />
cytoplasm when stained with H&E. <strong>The</strong><br />
intercalated ductules (Fig. 13) communicate with<br />
the peri-insular ductules, which often form a circuit<br />
around the islets and into which several<br />
neighboring intercalated ductules enter (Fig. 14).<br />
Figure 13. Intercalated ductal cells with microvilli.<br />
TEM X 3,600.<br />
16<br />
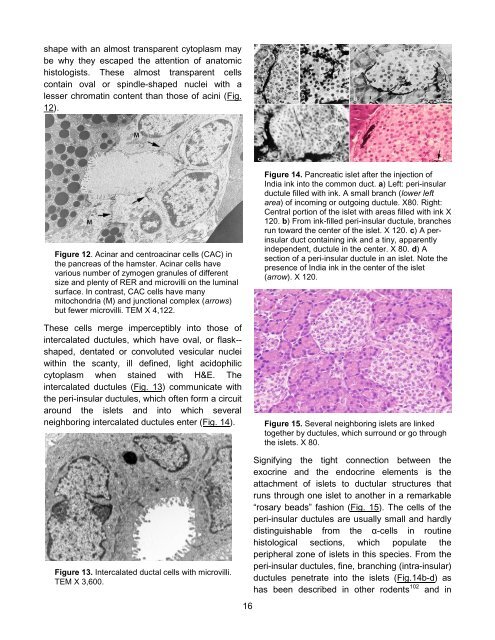
Figure 14. Pancreatic islet after the injection of<br />
India ink into the common duct. a) Left: peri-insular<br />
ductule filled with ink. A small branch (lower left<br />
area) of incoming or outgoing ductule. X80. Right:<br />
Central portion of the islet with areas filled with ink X<br />
120. b) From ink-filled peri-insular ductule, branches<br />
run toward the center of the islet. X 120. c) A perinsular<br />
duct containing ink and a tiny, apparently<br />
independent, ductule in the center. X 80. d) A<br />
section of a peri-insular ductule in an islet. Note the<br />
presence of India ink in the center of the islet<br />
(arrow). X 120.<br />
Figure 15. Several neighboring islets are linked<br />
together by ductules, which surround or go through<br />
the islets. X 80.<br />
Signifying the tight connection between the<br />
exocrine and the endocrine elements is the<br />
attachment of islets to ductular structures that<br />
runs through one islet to another in a remarkable<br />
“rosary beads” fashion (Fig. 15). <strong>The</strong> cells of the<br />
peri-insular ductules are usually small and hardly<br />
distinguishable from the α-cells in routine<br />
histological sections, which populate the<br />
peripheral zone of islets in this species. From the<br />
peri-insular ductules, fine, branching (intra-insular)<br />
ductules penetrate into the islets (Fig.14b-d) as<br />
has been described in other rodents 102 and in