Download PDF - The Pancreapedia
Download PDF - The Pancreapedia
Download PDF - The Pancreapedia
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
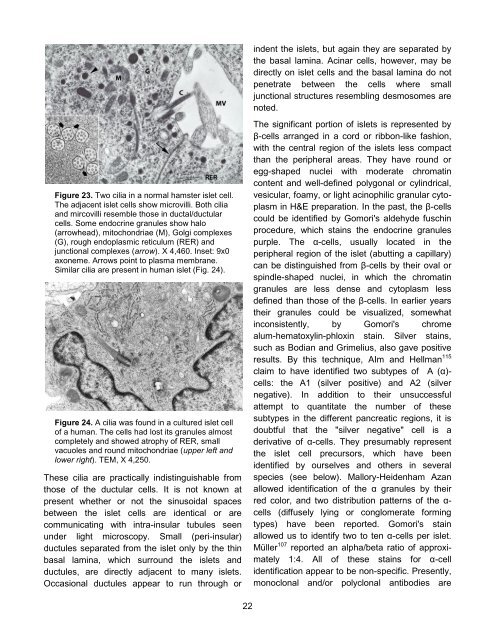
Figure 23. Two cilia in a normal hamster islet cell.<br />
<strong>The</strong> adjacent islet cells show microvilli. Both cilia<br />
and mircovilli resemble those in ductal/ductular<br />
cells. Some endocrine granules show halo<br />
(arrowhead), mitochondriae (M), Golgi complexes<br />
(G), rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and<br />
junctional complexes (arrow). X 4,460. Inset: 9x0<br />
axoneme. Arrows point to plasma membrane.<br />
Similar cilia are present in human islet (Fig. 24).<br />
Figure 24. A cilia was found in a cultured islet cell<br />
of a human. <strong>The</strong> cells had lost its granules almost<br />
completely and showed atrophy of RER, small<br />
vacuoles and round mitochondriae (upper left and<br />
lower right). TEM, X 4,250.<br />
<strong>The</strong>se cilia are practically indistinguishable from<br />
those of the ductular cells. It is not known at<br />
present whether or not the sinusoidal spaces<br />
between the islet cells are identical or are<br />
communicating with intra-insular tubules seen<br />
under light microscopy. Small (peri-insular)<br />
ductules separated from the islet only by the thin<br />
basal lamina, which surround the islets and<br />
ductules, are directly adjacent to many islets.<br />
Occasional ductules appear to run through or<br />
22<br />
indent the islets, but again they are separated by<br />
the basal lamina. Acinar cells, however, may be<br />
directly on islet cells and the basal lamina do not<br />
penetrate between the cells where small<br />
junctional structures resembling desmosomes are<br />
noted.<br />
<strong>The</strong> significant portion of islets is represented by<br />
β-cells arranged in a cord or ribbon-like fashion,<br />
with the central region of the islets less compact<br />
than the peripheral areas. <strong>The</strong>y have round or<br />
egg-shaped nuclei with moderate chromatin<br />
content and well-defined polygonal or cylindrical,<br />
vesicular, foamy, or light acinophilic granular cytoplasm<br />
in H&E preparation. In the past, the β-cells<br />
could be identified by Gomori's aldehyde fuschin<br />
procedure, which stains the endocrine granules<br />
purple. <strong>The</strong> α-cells, usually located in the<br />
peripheral region of the islet (abutting a capillary)<br />
can be distinguished from β-cells by their oval or<br />
spindle-shaped nuclei, in which the chromatin<br />
granules are less dense and cytoplasm less<br />
defined than those of the β-cells. In earlier years<br />
their granules could be visualized, somewhat<br />
inconsistently, by Gomori's chrome<br />
alum-hematoxylin-phloxin stain. Silver stains,<br />
such as Bodian and Grimelius, also gave positive<br />
results. By this technique, AIm and Hellman 115<br />
claim to have identified two subtypes of A (α)cells:<br />
the A1 (silver positive) and A2 (silver<br />
negative). In addition to their unsuccessful<br />
attempt to quantitate the number of these<br />
subtypes in the different pancreatic regions, it is<br />
doubtful that the "silver negative" cell is a<br />
derivative of α-cells. <strong>The</strong>y presumably represent<br />
the islet cell precursors, which have been<br />
identified by ourselves and others in several<br />
species (see below). Mallory-Heidenham Azan<br />
allowed identification of the α granules by their<br />
red color, and two distribution patterns of the αcells<br />
(diffusely lying or conglomerate forming<br />
types) have been reported. Gomori's stain<br />
allowed us to identify two to ten α-cells per islet.<br />
Müller 107 reported an alpha/beta ratio of approximately<br />
1:4. All of these stains for α-cell<br />
identification appear to be non-specific. Presently,<br />
monoclonal and/or polyclonal antibodies are