Etudes des proprietes des neutrinos dans les contextes ...
Etudes des proprietes des neutrinos dans les contextes ...
Etudes des proprietes des neutrinos dans les contextes ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
tel-00450051, version 1 - 25 Jan 2010<br />
Flux Ratio<br />
4<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1<br />
0<br />
0 20 40 60 80 100 120<br />
Neutrino Energy (MeV)<br />
Flux Ratio<br />
1.1<br />
1.05<br />
1<br />
0.95<br />
0 20 40 60 80 100 120<br />
Neutrino Energy (MeV)<br />
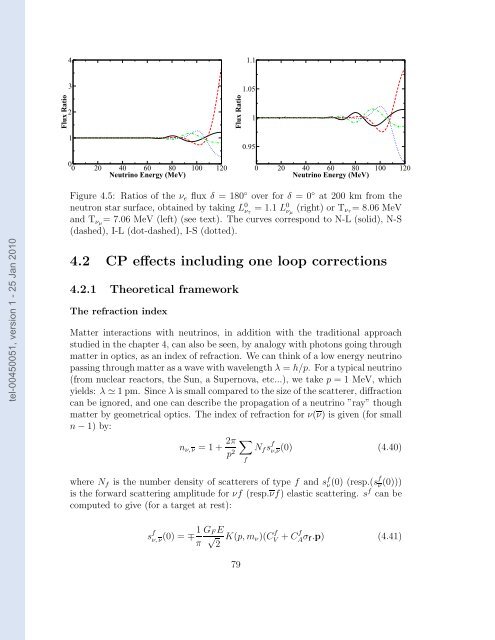
Figure 4.5: Ratios of the νe flux δ = 180 ◦ over for δ = 0 ◦ at 200 km from the<br />
neutron star surface, obtained by taking L 0 ντ = 1.1 L0 νµ (right) or Tντ= 8.06 MeV<br />
and Tνµ= 7.06 MeV (left) (see text). The curves correspond to N-L (solid), N-S<br />
(dashed), I-L (dot-dashed), I-S (dotted).<br />
4.2 CP effects including one loop corrections<br />
4.2.1 Theoretical framework<br />
The refraction index<br />
Matter interactions with <strong>neutrinos</strong>, in addition with the traditional approach<br />
studied in the chapter 4, can also be seen, by analogy with photons going through<br />
matter in optics, as an index of refraction. We can think of a low energy neutrino<br />
passing through matter as a wave with wavelength λ = h/p. For a typical neutrino<br />
(from nuclear reactors, the Sun, a Supernova, etc...), we take p = 1 MeV, which<br />
yields: λ ≃ 1 pm. Since λ is small compared to the size of the scatterer, diffraction<br />
can be ignored, and one can <strong>des</strong>cribe the propagation of a neutrino ”ray” though<br />
matter by geometrical optics. The index of refraction for ν(ν) is given (for small<br />
n − 1) by:<br />
nν, ν = 1 + 2π<br />
p 2<br />
<br />
f<br />
Nfs f<br />
ν,ν (0) (4.40)<br />
where Nf is the number density of scatterers of type f and sf ν (0) (resp.(sfν<br />
(0)))<br />
is the forward scattering amplitude for νf (resp.νf) elastic scattering. sf can be<br />
computed to give (for a target at rest):<br />
s f GFE<br />
ν, ν (0) = ∓1 √ K(p, mν)(C<br />
π 2 f<br />
V<br />
79<br />
+ Cf<br />
A σf.p) (4.41)