- Page 1 and 2:
Choguita Rarámuri (Tarahumara) Pho
- Page 3 and 4:
Abstract Choguita Rarámuri (Tarahu
- Page 5 and 6:
i For my grandparents, Carmen & Ari
- Page 7 and 8:
2.3.2 Syllables ...................
- Page 9 and 10:
5.4.2 Lack of Multiple Exponence in
- Page 11 and 12:
Abbreviations 1 First person 2 Seco
- Page 13 and 14:
Acknowledgements I have many people
- Page 15 and 16:
Linguistics Department, the Survey
- Page 17 and 18:
theoretical formalisms that might m
- Page 19 and 20:
This analysis also assumes that lan
- Page 21 and 22:
Map 1: Location of Choguita Rarámu
- Page 23 and 24:
spoken in the northwestern Mexican
- Page 25 and 26:
variation between the different Rar
- Page 27 and 28:
people) and their language, rarámu
- Page 29 and 30:
Choguita with mestizo enclaves in t
- Page 31 and 32:
to a linguistic analysis of Rarámu
- Page 33 and 34:
elicitation and transcription, for
- Page 35 and 36:
Table 2: Names and initials of cont
- Page 37 and 38:
phonological, semantic or templatic
- Page 39 and 40:
or lexically conditioned. Many inst
- Page 41 and 42:
Table 3: Phonemic Inventory of Chog
- Page 43 and 44:
3) /b/ vs. /’/ vs. /w/ a. kabí
- Page 45 and 46:
9) /"/ vs. /j/ a. "ojá ‘shrink
- Page 47 and 48:
13) /i/ vs. /e/ in pre-tonic positi
- Page 49 and 50:
18) Word-medial allophones of /b/ F
- Page 51 and 52:
Alveopalatal affricates can optiona
- Page 53 and 54:
stop. The posttonic front, high vow
- Page 55 and 56:
2.2.3.4 Nasals Nasal phonemes in Ch
- Page 57 and 58:
2.2.3.5 Rhotics Recall from §2.2.1
- Page 59 and 60:
37) Pre- and postconsonantal alloph
- Page 61 and 62:
39) p ~ b alternations a. wi"ó-bo
- Page 63 and 64:
kidding!/how come!’ (Sp. ‘a poc
- Page 65 and 66:
47) Post-consonantal voiceless oral
- Page 67 and 68:
discussion of the distinction betwe
- Page 69 and 70:
In terms of its distribution, stres
- Page 71 and 72:
These patterns of untrsessed vowel
- Page 73 and 74:
As will be discussed in Chapter 3 (
- Page 75 and 76:
Unstressed vowel reduction is attes
- Page 77 and 78:
61) Optional posttonic reduction to
- Page 79 and 80:
63) Morphologically conditioned pre
- Page 81 and 82:
65) Word-medial CV syllables a. a.k
- Page 83 and 84:
There are, thus, no surface sequenc
- Page 85 and 86:
s $ opés-!ani ‘vomit-Ev’/‘vo
- Page 87 and 88:
2.3.2.3 Vowel sequences 2.3.2.3.1 D
- Page 89 and 90:
These falling diphthongs occur morp
- Page 91 and 92:
monomorphemic hiatus sequences with
- Page 93 and 94:
In (88), I show examples where ther
- Page 95 and 96:
(realized as a voiced bilabial appr
- Page 97 and 98:
Finally, when roots bearing a glott
- Page 99 and 100:
2.3.4 Minimal word size There is ev
- Page 101 and 102:
101) Vowel duration of monosyllabic
- Page 103 and 104:
q. napó ‘plow’/‘escardar’
- Page 105 and 106:
as glottal stop) is a feature assoc
- Page 107 and 108:
The first suffixation layer, the
- Page 109 and 110:
disyllabic suffixes are related to
- Page 111 and 112:
2) Stressed roots Form Gloss Stress
- Page 113 and 114:
efer to as Class 2) has vowels that
- Page 115 and 116:
exception, these roots end in a in
- Page 117 and 118:
Under the conjugation class analysi
- Page 119 and 120:
to the interactions of the differen
- Page 121 and 122:
levels defined below). Given the hi
- Page 123 and 124:
schematizes the three-way contrast
- Page 125 and 126:
The Guarijío cognates of these sem
- Page 127 and 128:
d. serrú"o ripú-ni-ri kusí saw c
- Page 129 and 130:
strong mophological contexts, thus,
- Page 131 and 132:
3.4.1.1 Conversion Some nominal ste
- Page 133 and 134:
f. kapírame kabírame ‘cylindric
- Page 135 and 136:
Some of the nouns that undergo this
- Page 137 and 138:
nouns (mo’ó ‘head’, busí
- Page 139 and 140:
3.4.4 Number marking: suppletion an
- Page 141 and 142:
c. sipu-tá-a "ukú skirt-Vblz-Prog
- Page 143 and 144:
Finally, the verbalizer -e, with th
- Page 145 and 146:
Table 15: Choguita Rarámuri verbal
- Page 147 and 148:
verbs. There are three morphologica
- Page 149 and 150:
Table 17: Characteristics of the Ch
- Page 151 and 152:
34) Tr (S2) - Appl (S3) a. we ne mo
- Page 153 and 154:
37) Appl-Caus -ki-ti order a. to, j
- Page 155 and 156:
c. ne isíi-n-si-a ináro 1sgN urin
- Page 157 and 158:
d. rokó mi bo’órri na harré mo
- Page 159 and 160:
46) Ev (S8) - MPass (S9) a. ne i"í
- Page 161 and 162:
In addition, the suffixes in the sy
- Page 163 and 164:
degrees of morphophonological fusio
- Page 165 and 166:
51) Inner stem suffix-suffix haplol
- Page 167 and 168:
Cases of CL triggered by deletion o
- Page 169 and 170:
3.5.2.3 Dominance effects: past pas
- Page 171 and 172:
While the lengthening in (59a) coul
- Page 173 and 174:
the domain of lengthening is restri
- Page 175 and 176:
While round harmony in Choguita Rar
- Page 177 and 178:
There are cases where harmony appea
- Page 179 and 180:
Table 20: Distribution of stress-sh
- Page 181 and 182:
Demonstratives (within a noun phras
- Page 183 and 184:
Finally, deletion between the final
- Page 185 and 186:
Rarámuri verb accounts for a zone
- Page 187 and 188:
of the phonology-morphology interfa
- Page 189 and 190:
f) In words containing an unstresse
- Page 191 and 192:
Reduction is mostly attested confin
- Page 193 and 194:
ealized as stress in output forms;
- Page 195 and 196:
This class contrasts with another c
- Page 197 and 198:
e. /rono/ ‘boil’/‘hervir’ r
- Page 199 and 200:
The forms in (13-14) show that stre
- Page 201 and 202:
condition of being assigned within
- Page 203 and 204:
4.2.3 Multiple affixation construct
- Page 205 and 206:
21) Left alignment of stress Forms
- Page 207 and 208:
23) Stress properties of verb root
- Page 209 and 210:
27) Uninterpretable, non-truncated
- Page 211 and 212:
accounted for through either lexica
- Page 213 and 214:
Blevins & Harrison (1999), and Zoll
- Page 215 and 216:
STEMSTRESS when bearing stress. Str
- Page 217 and 218:
37) Monosyllabic unstressed root pl
- Page 219 and 220:
41) Branching morphological structu
- Page 221 and 222:
While a monostratal analysis of str
- Page 223 and 224:
FAITH. 49) Truncation in body-part
- Page 225 and 226:
50) Grammar lattice for stress assi
- Page 227 and 228:
According to this hypothesis, we sh
- Page 229 and 230:
54) Three stress cophonologies a. C
- Page 231 and 232:
In an RCA analysis, prosodic faithf
- Page 233 and 234:
59) Trisyllabic unstressed root plu
- Page 235 and 236:
over affixes through positional mar
- Page 237 and 238:
trochaic feet). However, it would b
- Page 239 and 240:
Chapter 5: Multiple Exponence 5.1 I
- Page 241 and 242:
only one exponent). And third, they
- Page 243 and 244:
c. “Among equally expressive expr
- Page 245 and 246:
different, partially overlapping fe
- Page 247 and 248:
GC] a single word can be realized a
- Page 249 and 250:
parallel semantic recursivity. As s
- Page 251 and 252:
Rarámuri in fact exhibits more tha
- Page 253 and 254:
5.3.2 Applicative stems with applic
- Page 255 and 256:
c. rahé-ma rahé-ki-ra ‘light.up
- Page 257 and 258:
causative suffix, the reduced allom
- Page 259 and 260:
With these roots, non-final stress
- Page 261 and 262:
c. ma=ni mi pá-si-ri pelota alread
- Page 263 and 264:
5.3.5 Summary There are four differ
- Page 265 and 266:
the next section I provide an analy
- Page 267 and 268:
McCarthy & Prince (1993); Prince &
- Page 269 and 270:
why other potentially opaque marker
- Page 271 and 272:
vocalic nucleus and the onset conso
- Page 273 and 274:
PARSE-! yields a non-iterating stre
- Page 275 and 276:
suboptimal Stem form into a possibl
- Page 277 and 278:
This analysis also yields the corre
- Page 279 and 280:
phonological constraints (which req
- Page 281 and 282:
ut rather by adding the more produc
- Page 283 and 284:
34) Stem level evaluation, input ro
- Page 285 and 286: The only difference between pluract
- Page 287 and 288: Table 28: Other stress-neutral suff
- Page 289 and 290: output of an input root and associa
- Page 291 and 292: Furthermore, the suffixes in this s
- Page 293 and 294: Table 29: Unproductive processes in
- Page 295 and 296: 46) Hypothetical doubly incorporate
- Page 297 and 298: 5.4.3 Summary I have proposed that
- Page 299 and 300: estrictions as to the types of morp
- Page 301 and 302: In Choguita Rarámuri there are fou
- Page 303 and 304: 1) Choguita Rarámuri disyllabic su
- Page 305 and 306: are often neutralized in height. Th
- Page 307 and 308: phonotactically illicit consonant c
- Page 309 and 310: 6.3 Allomorph distribution In this
- Page 311 and 312: The distribution of long and short
- Page 313 and 314: In contrast, long allomorphs largel
- Page 315 and 316: . sutubé"i-nar-a /sutubé"i-nale-a
- Page 317 and 318: In sum, the distribution of unstres
- Page 319 and 320: g. i’né-si-na ‘look-Mot-Caus:I
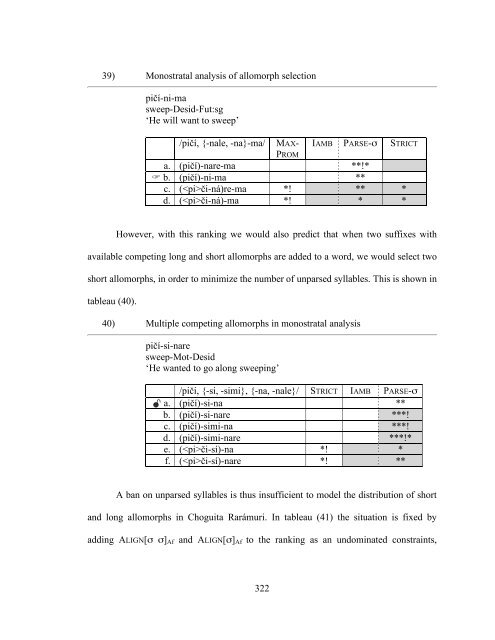
- Page 321 and 322: The comparison between these attest
- Page 323 and 324: 23) Allomorphy vs. morphophonology
- Page 325 and 326: 25) Pre-tonic nominal root shorteni
- Page 327 and 328: allomorphs are added in a final ste
- Page 329 and 330: that two competing allomorphs will
- Page 331 and 332: 32) Stem level output with short al
- Page 333 and 334: 35) No vowel deletion of long allom
- Page 335: 37) Optionality in Indirect Causati
- Page 339 and 340: deletion and with posttonic vowel d
- Page 341 and 342: there would be no independent evide
- Page 343 and 344: edge restriction is completely exce
- Page 345 and 346: (Chichewa (Hyman 2003); Pulaar (Pas
- Page 347 and 348: system first described in Hyman 200
- Page 349 and 350: 5) Morphologically conditioned phon
- Page 351 and 352: described in this chapter) are two
- Page 353 and 354: The Mirror Principle can be assumed
- Page 355 and 356: (‘to go along wanting to do X’)
- Page 357 and 358: c. nará-ti-si-ma ré riwéel-"an-i
- Page 359 and 360: predictor of unattested suffix perm
- Page 361 and 362: 17) Hypothetical cases of Applicati
- Page 363 and 364: the predicate, the Auditory evident
- Page 365 and 366: After posttonic vowel deletion appl
- Page 367 and 368: c. to, jéni dúlse íw-ki-ti-ri ja
- Page 369 and 370: Discussion of each one of the examp
- Page 371 and 372: Thus, the same speakers that produc
- Page 373 and 374: 7.4 The interaction of phonological
- Page 375 and 376: 31) SCOPE >> TEMPLATE (Desiderative
- Page 377 and 378: 34) Alignment (ALIGNEV) >> SCOPE a.
- Page 379 and 380: 37) TEMPLATE >> SCOPE (Causative an
- Page 381 and 382: order reflects scope. In this ranki
- Page 383 and 384: of variable ranking. I present data
- Page 385 and 386: stem is used in the second response
- Page 387 and 388:
proposal that morphological express
- Page 389 and 390:
conditioned, is ordered after an in
- Page 391 and 392:
Chapter 8: Conclusion 8.1 Piecing t
- Page 393 and 394:
or a Weak (stress-neutral) Cophonol
- Page 395 and 396:
5) Morphological and prosodic struc
- Page 397 and 398:
Variably ordered suffixes belong to
- Page 399 and 400:
Specifically, in any such model, wo
- Page 401 and 402:
Choguita Rarámuri departs from the
- Page 403 and 404:
Anttila, A. 2002. Morphologically c
- Page 405 and 406:
Brambila, D. 1983. Diccionario Cast
- Page 407 and 408:
Dayley, J. P. 1989. Tumpisa (Panami
- Page 409 and 410:
Hale, K. 1965. Some preliminary obs
- Page 411 and 412:
Hyman, L. 2003. Suffix ordering in
- Page 413 and 414:
Lewis, G.L. 1967. Turkish Language.
- Page 415 and 416:
Mutaka, N. & L. Hyman. 1990. ‘Syl
- Page 417 and 418:
Plank, F. 1986. Paradigm size econo
- Page 419 and 420:
Tranel, B. 1996. Exceptionality in
- Page 421 and 422:
Appendix 1: Rarámuri language refe
- Page 423 and 424:
Coordinación Estatal de la Tarahum
- Page 425 and 426:
Paciotto, C. 2004. Language Policy,
- Page 427 and 428:
1. S1: Inchoative -ba suffix. The i
- Page 429 and 430:
Transitive construction b. nihé ra
- Page 431 and 432:
4. S4: Causative -ti suffix. The Ca
- Page 433 and 434:
. a’rí na mo’o"íki "ukúri-ri
- Page 435 and 436:
17) Future passive suffix example A
- Page 437 and 438:
As described in Chapter 3 (§3.6),
- Page 439 and 440:
. tamí ku á-ki-pi-si 1sgA Rev loo
- Page 441 and 442:
. nuru-ría birá ba"á ará náti-
- Page 443 and 444:
Different referent c. á birá oká
- Page 445 and 446:
effects on the base to which it att
- Page 447 and 448:
clauses). The base for affixation o
- Page 449 and 450:
Appendix 3: Narrative Texts Title:
- Page 451 and 452:
12: a’rí... a’rí "ihónsa a
- Page 453 and 454:
ko"í ma kó"i ma kó’a-nura nuru
- Page 455 and 456:
38: "ú riká nári... kíti ko a
- Page 457 and 458:
é"i rihóo ko ba Det man Emph Cl
- Page 459 and 460:
19: ikíi-ra ru-á=m pa é"i... "ab
- Page 461 and 462:
33: pe birá ko nápu riká tamó "