K. Kobayashi and S. Tsumura
K. Kobayashi and S. Tsumura
K. Kobayashi and S. Tsumura
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
AOI–AOX<br />
0.002<br />
0<br />
–0.002<br />
B C<br />
A<br />
D E<br />
–0.004<br />
–0.01 –0.005 0 0.005<br />
AOP–AOX<br />
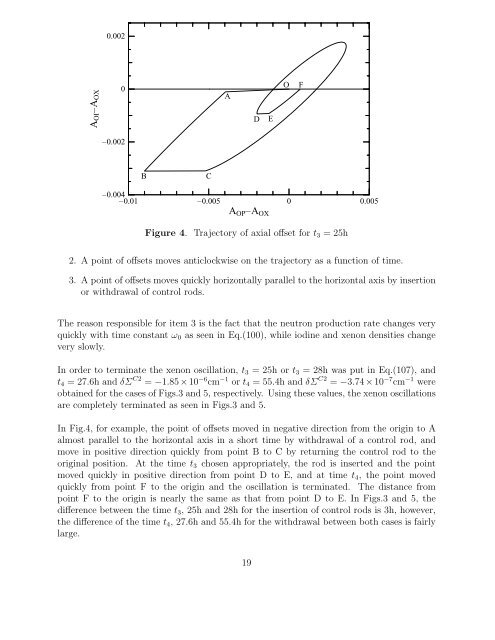
Figure 4. Trajectory of axial offset for t3 = 25h<br />
2. A point of offsets moves anticlockwise on the trajectory as a function of time.<br />
3. A point of offsets moves quickly horizontally parallel to the horizontal axis by insertion<br />
or withdrawal of control rods.<br />
The reason responsible for item 3 is the fact that the neutron production rate changes very<br />
quickly with time constant ω0 as seen in Eq.(100), while iodine <strong>and</strong> xenon densities change<br />
very slowly.<br />
In order to terminate the xenon oscillation, t3 = 25h or t3 = 28h was put in Eq.(107), <strong>and</strong><br />
t4 =27.6h <strong>and</strong> δΣ C2 = −1.85 × 10 −6 cm −1 or t4 =55.4h <strong>and</strong> δΣ C2 = −3.74 × 10 −7 cm −1 were<br />
obtained for the cases of Figs.3 <strong>and</strong> 5, respectively. Using these values, the xenon oscillations<br />
are completely terminated as seen in Figs.3 <strong>and</strong> 5.<br />
In Fig.4, for example, the point of offsets moved in negative direction from the origin to A<br />
almost parallel to the horizontal axis in a short time by withdrawal of a control rod, <strong>and</strong><br />
move in positive direction quickly from point B to C by returning the control rod to the<br />
original position. At the time t3 chosen appropriately, the rod is inserted <strong>and</strong> the point<br />
moved quickly in positive direction from point D to E, <strong>and</strong> at time t4, the point moved<br />
quickly from point F to the origin <strong>and</strong> the oscillation is terminated. The distance from<br />
point F to the origin is nearly the same as that from point D to E. In Figs.3 <strong>and</strong> 5, the<br />
difference between the time t3, 25h <strong>and</strong> 28h for the insertion of control rods is 3h, however,<br />
the difference of the time t4, 27.6h <strong>and</strong> 55.4h for the withdrawal between both cases is fairly<br />
large.<br />
19<br />
O<br />
F