GPR for river dyke - GSB
GPR for river dyke - GSB
GPR for river dyke - GSB
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
In Figure 20, there is no continuous layering of either sediment or road materials. This may<br />
be due to plastic nature of the underlying sediment. When heavy traffic moves over the road<br />
it initiates a vibration of the underlying materials. Due to its plastic nature (Density lower than<br />
the overlying sediment), it try to move upward (indicated by red arrow) and destroy the<br />
continuous layering of the sediment as well as road materials.<br />
5 <strong>GPR</strong> theory revisited: Ground material property, wave speed and propagation<br />
attenuation<br />
There are two types of the material properties, which have effects on the electromagnetic<br />
wave propagating inside the material. One is the relative dielectric constant ε r, and the other<br />
is the resistivity. Tables 1 and 2 show respectively the dielectric constants εr and the<br />
resistivities R <strong>for</strong> common ground materials.<br />
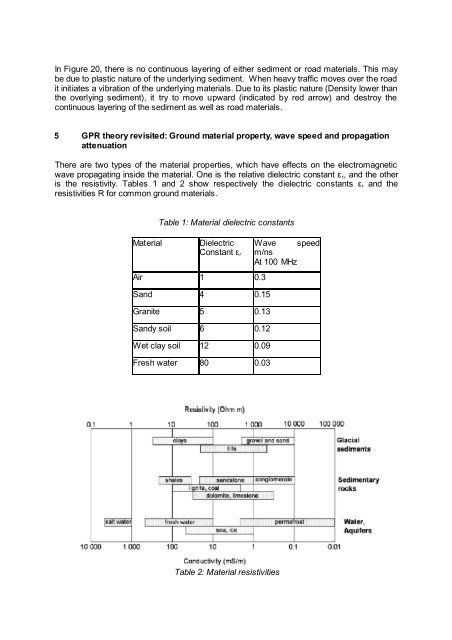
Table 1: Material dielectric constants<br />
Material Dielectric<br />
Constant εr<br />
Air 1 0.3<br />
Sand 4 0.15<br />
Granite 5 0.13<br />
Sandy soil 6 0.12<br />
Wet clay soil 12 0.09<br />
Fresh water 80 0.03<br />
Table 2: Material resistivities<br />
Wave speed<br />
m/ns<br />
At 100 MHz