Het gebruik van kinesitherapie en van fysische geneeskunde ... - KCE
Het gebruik van kinesitherapie en van fysische geneeskunde ... - KCE
Het gebruik van kinesitherapie en van fysische geneeskunde ... - KCE
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
84 Physiotherapy & Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine <strong>KCE</strong> Reports 87<br />
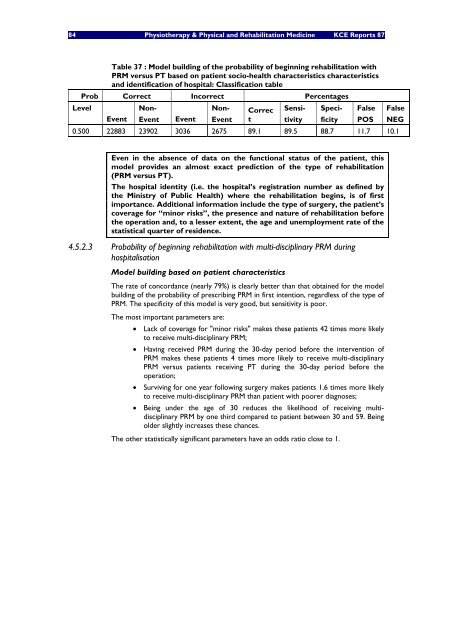
Table 37 : Model building of the probability of beginning rehabilitation with<br />
PRM versus PT based on pati<strong>en</strong>t socio-health characteristics characteristics<br />
and id<strong>en</strong>tification of hospital: Classification table<br />
Prob Correct Incorrect Perc<strong>en</strong>tages<br />
Level Non- Non- Correc S<strong>en</strong>si- Speci- False False<br />
Ev<strong>en</strong>t Ev<strong>en</strong>t Ev<strong>en</strong>t Ev<strong>en</strong>t t tivity ficity POS NEG<br />
0.500 22883 23902 3036 2675 89.1 89.5 88.7 11.7 10.1<br />
Ev<strong>en</strong> in the abs<strong>en</strong>ce of data on the functional status of the pati<strong>en</strong>t, this<br />
model provides an almost exact prediction of the type of rehabilitation<br />
(PRM versus PT).<br />
The hospital id<strong>en</strong>tity (i.e. the hospital’s registration number as defined by<br />
the Ministry of Public Health) where the rehabilitation begins, is of first<br />
importance. Additional information include the type of surgery, the pati<strong>en</strong>t’s<br />
coverage for “minor risks”, the pres<strong>en</strong>ce and nature of rehabilitation before<br />
the operation and, to a lesser ext<strong>en</strong>t, the age and unemploym<strong>en</strong>t rate of the<br />
statistical quarter of resid<strong>en</strong>ce.<br />
4.5.2.3 Probability of beginning rehabilitation with multi-disciplinary PRM during<br />
hospitalisation<br />
Model building based on pati<strong>en</strong>t characteristics<br />
The rate of concordance (nearly 79%) is clearly better than that obtained for the model<br />
building of the probability of prescribing PRM in first int<strong>en</strong>tion, regardless of the type of<br />
PRM. The specificity of this model is very good, but s<strong>en</strong>sitivity is poor.<br />
The most important parameters are:<br />
• Lack of coverage for "minor risks" makes these pati<strong>en</strong>ts 42 times more likely<br />
to receive multi-disciplinary PRM;<br />
• Having received PRM during the 30-day period before the interv<strong>en</strong>tion of<br />
PRM makes these pati<strong>en</strong>ts 4 times more likely to receive multi-disciplinary<br />
PRM versus pati<strong>en</strong>ts receiving PT during the 30-day period before the<br />
operation;<br />
• Surviving for one year following surgery makes pati<strong>en</strong>ts 1.6 times more likely<br />
to receive multi-disciplinary PRM than pati<strong>en</strong>t with poorer diagnoses;<br />
• Being under the age of 30 reduces the likelihood of receiving multidisciplinary<br />
PRM by one third compared to pati<strong>en</strong>t betwe<strong>en</strong> 30 and 59. Being<br />
older slightly increases these chances.<br />
The other statistically significant parameters have an odds ratio close to 1.