Awareness Training Goals - Salinas Valley Ammonia Safety Day
Awareness Training Goals - Salinas Valley Ammonia Safety Day
Awareness Training Goals - Salinas Valley Ammonia Safety Day
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
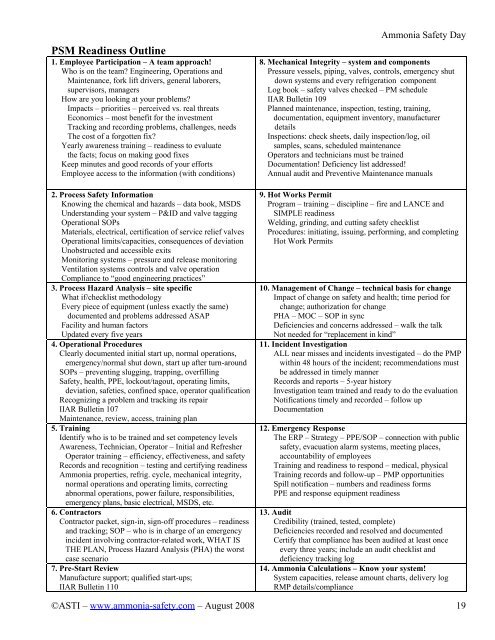
PSM Readiness Outline<br />
1. Employee Participation – A team approach!<br />
Who is on the team? Engineering, Operations and<br />
Maintenance, fork lift drivers, general laborers,<br />
supervisors, managers<br />
How are you looking at your problems?<br />
Impacts – priorities – perceived vs. real threats<br />
Economics – most benefit for the investment<br />
Tracking and recording problems, challenges, needs<br />
The cost of a forgotten fix?<br />
Yearly awareness training – readiness to evaluate<br />
the facts; focus on making good fixes<br />
Keep minutes and good records of your efforts<br />
Employee access to the information (with conditions)<br />
2. Process <strong>Safety</strong> Information<br />
Knowing the chemical and hazards – data book, MSDS<br />
Understanding your system – P&ID and valve tagging<br />
Operational SOPs<br />
Materials, electrical, certification of service relief valves<br />
Operational limits/capacities, consequences of deviation<br />
Unobstructed and accessible exits<br />
Monitoring systems – pressure and release monitoring<br />
Ventilation systems controls and valve operation<br />
Compliance to “good engineering practices”<br />
3. Process Hazard Analysis – site specific<br />
What if/checklist methodology<br />
Every piece of equipment (unless exactly the same)<br />
documented and problems addressed ASAP<br />
Facility and human factors<br />
Updated every five years<br />
4. Operational Procedures<br />
Clearly documented initial start up, normal operations,<br />
emergency/normal shut down, start up after turn-around<br />
SOPs – preventing slugging, trapping, overfilling<br />
<strong>Safety</strong>, health, PPE, lockout/tagout, operating limits,<br />
deviation, safeties, confined space, operator qualification<br />
Recognizing a problem and tracking its repair<br />
IIAR Bulletin 107<br />
Maintenance, review, access, training plan<br />
5. <strong>Training</strong><br />
Identify who is to be trained and set competency levels<br />
<strong>Awareness</strong>, Technician, Operator – Initial and Refresher<br />
Operator training – efficiency, effectiveness, and safety<br />
Records and recognition – testing and certifying readiness<br />
<strong>Ammonia</strong> properties, refrig. cycle, mechanical integrity,<br />
normal operations and operating limits, correcting<br />
abnormal operations, power failure, responsibilities,<br />
emergency plans, basic electrical, MSDS, etc.<br />
6. Contractors<br />
Contractor packet, sign-in, sign-off procedures – readiness<br />
and tracking; SOP – who is in charge of an emergency<br />
incident involving contractor-related work, WHAT IS<br />
THE PLAN, Process Hazard Analysis (PHA) the worst<br />
case scenario<br />
7. Pre-Start Review<br />
Manufacture support; qualified start-ups;<br />
IIAR Bulletin 110<br />
<strong>Ammonia</strong> <strong>Safety</strong> <strong>Day</strong><br />
8. Mechanical Integrity – system and components<br />
Pressure vessels, piping, valves, controls, emergency shut<br />
down systems and every refrigeration component<br />
Log book – safety valves checked – PM schedule<br />
IIAR Bulletin 109<br />
Planned maintenance, inspection, testing, training,<br />
documentation, equipment inventory, manufacturer<br />
details<br />
Inspections: check sheets, daily inspection/log, oil<br />
samples, scans, scheduled maintenance<br />
Operators and technicians must be trained<br />
Documentation! Deficiency list addressed!<br />
Annual audit and Preventive Maintenance manuals<br />
9. Hot Works Permit<br />
Program – training – discipline – fire and LANCE and<br />
SIMPLE readiness<br />
Welding, grinding, and cutting safety checklist<br />
Procedures: initiating, issuing, performing, and completing<br />
Hot Work Permits<br />
10. Management of Change – technical basis for change<br />
Impact of change on safety and health; time period for<br />
change; authorization for change<br />
PHA – MOC – SOP in sync<br />
Deficiencies and concerns addressed – walk the talk<br />
Not needed for “replacement in kind”<br />
11. Incident Investigation<br />
ALL near misses and incidents investigated – do the PMP<br />
within 48 hours of the incident; recommendations must<br />
be addressed in timely manner<br />
Records and reports – 5-year history<br />
Investigation team trained and ready to do the evaluation<br />
Notifications timely and recorded – follow up<br />
Documentation<br />
12. Emergency Response<br />
The ERP – Strategy – PPE/SOP – connection with public<br />
safety, evacuation alarm systems, meeting places,<br />
accountability of employees<br />
<strong>Training</strong> and readiness to respond – medical, physical<br />
<strong>Training</strong> records and follow-up – PMP opportunities<br />
Spill notification – numbers and readiness forms<br />
PPE and response equipment readiness<br />
13. Audit<br />
Credibility (trained, tested, complete)<br />
Deficiencies recorded and resolved and documented<br />
Certify that compliance has been audited at least once<br />
every three years; include an audit checklist and<br />
deficiency tracking log<br />
14. <strong>Ammonia</strong> Calculations – Know your system!<br />
System capacities, release amount charts, delivery log<br />
RMP details/compliance<br />
©ASTI – www.ammonia-safety.com – August 2008 19