Dynamic Macroeconomic Modeling with Matlab
Dynamic Macroeconomic Modeling with Matlab
Dynamic Macroeconomic Modeling with Matlab
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
2 An Outline of the Theory<br />
x(t)<br />
1<br />
0.9<br />
0.8<br />
0.7<br />
0.6<br />
0.5<br />
0.4<br />
0.3<br />
0.2<br />
Correct and numerical solution (explicit Euler method)<br />
0.1<br />
0 1 2 3 4 5<br />
t<br />
6 7 8 9 10<br />
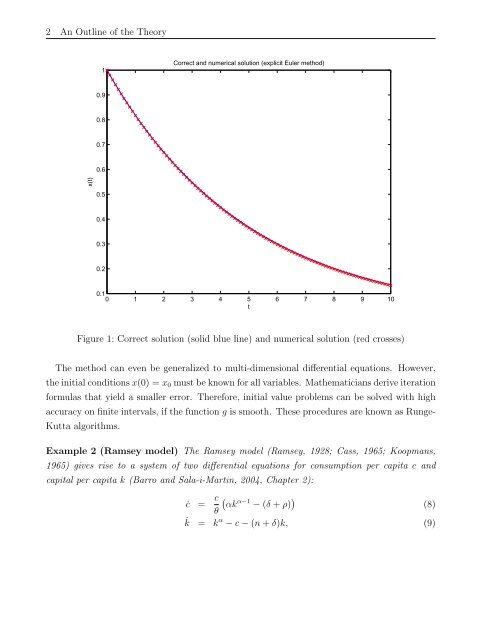
Figure 1: Correct solution (solid blue line) and numerical solution (red crosses)<br />
The method can even be generalized to multi-dimensional differential equations. However,<br />
the initial conditions x(0) = x0 must be known for all variables. Mathematicians derive iteration<br />
formulas that yield a smaller error. Therefore, initial value problems can be solved <strong>with</strong> high<br />
accuracy on finite intervals, if the function g is smooth. These procedures are known as Runge-<br />
Kutta algorithms.<br />
Example 2 (Ramsey model) The Ramsey model (Ramsey, 1928; Cass, 1965; Koopmans,<br />
1965) gives rise to a system of two differential equations for consumption per capita c and<br />
capital per capita k (Barro and Sala-i-Martin, 2004, Chapter 2):<br />
˙c = c <br />
α−1<br />
αk − (δ + ρ) (8)<br />
θ<br />
˙k = k α − c − (n + δ)k, (9)