Dynamic Macroeconomic Modeling with Matlab
Dynamic Macroeconomic Modeling with Matlab
Dynamic Macroeconomic Modeling with Matlab
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
2 An Outline of the Theory<br />
<br />
<br />
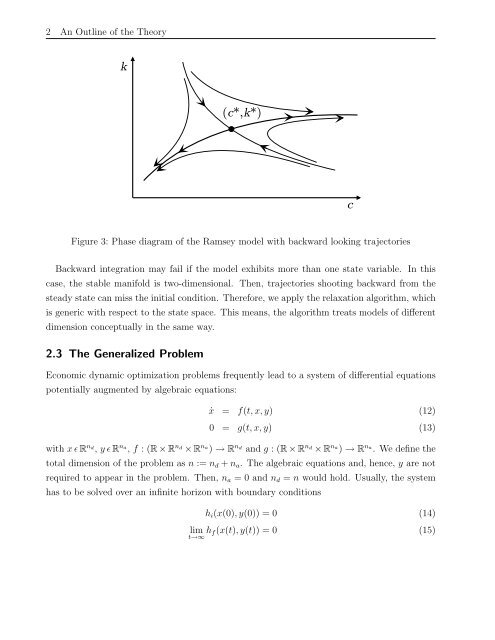
Figure 3: Phase diagram of the Ramsey model <strong>with</strong> backward looking trajectories<br />
Backward integration may fail if the model exhibits more than one state variable. In this<br />
case, the stable manifold is two-dimensional. Then, trajectories shooting backward from the<br />
steady state can miss the initial condition. Therefore, we apply the relaxation algorithm, which<br />
is generic <strong>with</strong> respect to the state space. This means, the algorithm treats models of different<br />
dimension conceptually in the same way.<br />
2.3 The Generalized Problem<br />
Economic dynamic optimization problems frequently lead to a system of differential equations<br />
potentially augmented by algebraic equations:<br />
˙x = f(t,x,y) (12)<br />
0 = g(t,x,y) (13)<br />
<strong>with</strong> xǫR nd, y ǫ R na , f : (R × R nd × R na ) → R nd and g : (R × R nd × R na ) → R na . We define the<br />
total dimension of the problem as n := nd + na. The algebraic equations and, hence, y are not<br />
required to appear in the problem. Then, na = 0 and nd = n would hold. Usually, the system<br />
has to be solved over an infinite horizon <strong>with</strong> boundary conditions<br />
hi(x(0),y(0)) = 0 (14)<br />
lim<br />
t→∞ hf(x(t),y(t)) = 0 (15)