Technical Paper by A. Fakher and C.J.F.P. Jones WHEN THE ...
Technical Paper by A. Fakher and C.J.F.P. Jones WHEN THE ...
Technical Paper by A. Fakher and C.J.F.P. Jones WHEN THE ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
FAKHER & JONES • When Bending Stiffness of Geosynthetic Reinforcement is Important<br />
Vertical stress under footing (N/mm)<br />
2.4<br />
2.0<br />
1.6<br />
1.2<br />
0.8<br />
0.4<br />
0.0<br />
f-29, I = 2.15e-6 f-20, I = 7.64 e-7<br />
f-26, I = 2e-7 f-27, I = 8.5e-8<br />
f-28, I = 1e-8 f-20, no reinf.<br />
f-20, cable<br />
0 5 10 15 20 25<br />
Vertical displacement (mm)<br />
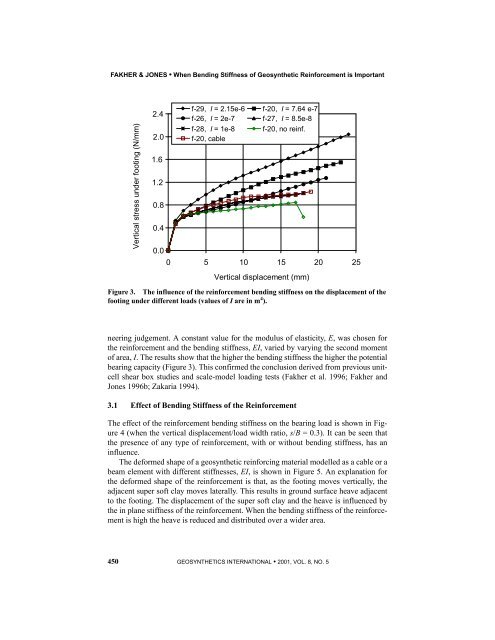
Figure 3. The influence of the reinforcement bending stiffness on the displacement of the<br />
footing under different loads (values of I are in m 4 ).<br />
neering judgement. A constant value for the modulus of elasticity, E, was chosen for<br />
the reinforcement <strong>and</strong> the bending stiffness, EI, varied <strong>by</strong> varying the second moment<br />
of area, I. The results show that the higher the bending stiffness the higher the potential<br />
bearing capacity (Figure 3). This confirmed the conclusion derived from previous unitcell<br />
shear box studies <strong>and</strong> scale-model loading tests (<strong>Fakher</strong> et al. 1996; <strong>Fakher</strong> <strong>and</strong><br />
<strong>Jones</strong> 1996b; Zakaria 1994).<br />
3.1 Effect of Bending Stiffness of the Reinforcement<br />
The effect of the reinforcement bending stiffness on the bearing load is shown in Figure<br />
4 (when the vertical displacement/load width ratio, s/B = 0.3). It can be seen that<br />
the presence of any type of reinforcement, with or without bending stiffness, has an<br />
influence.<br />
The deformed shape of a geosynthetic reinforcing material modelled as a cable or a<br />
beam element with different stiffnesses, EI, is shown in Figure 5. An explanation for<br />
the deformed shape of the reinforcement is that, as the footing moves vertically, the<br />
adjacent super soft clay moves laterally. This results in ground surface heave adjacent<br />
to the footing. The displacement of the super soft clay <strong>and</strong> the heave is influenced <strong>by</strong><br />
the in plane stiffness of the reinforcement. When the bending stiffness of the reinforcement<br />
is high the heave is reduced <strong>and</strong> distributed over a wider area.<br />
450 GEOSYN<strong>THE</strong>TICS INTERNATIONAL • 2001, VOL. 8, NO. 5