Biodiversity - a GRI Reporting Resource - Global Reporting Initiative
Biodiversity - a GRI Reporting Resource - Global Reporting Initiative
Biodiversity - a GRI Reporting Resource - Global Reporting Initiative
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Annex IV<br />
Key articles of the CBD for organizations<br />
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)<br />
promotes the conservation and sustainable<br />
use of biodiversity and the fair and equitable<br />
sharing of the benefits resulting from the<br />
use of genetic resources. In the table in this<br />
Annex a selection of key articles of the CBD<br />
for organizations is presented 17 .<br />
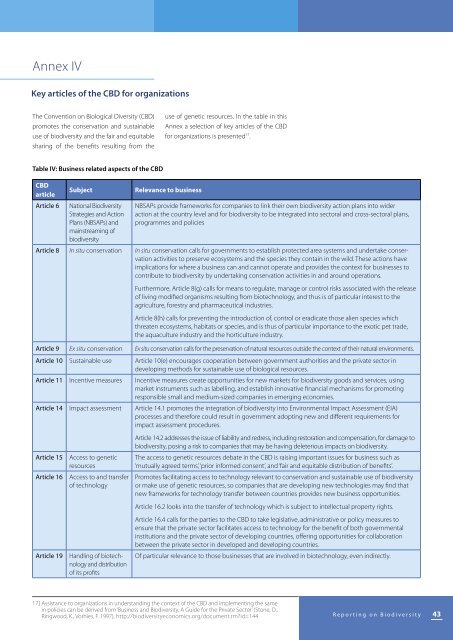
Table IV: Business related aspects of the CBD<br />
CBD<br />
article<br />
Article 6<br />
Subject<br />
National <strong>Biodiversity</strong><br />
Strategies and Action<br />
Plans (NBSAPs) and<br />
mainstreaming of<br />
biodiversity<br />
Relevance to business<br />
NBSAPs provide frameworks for companies to link their own biodiversity action plans into wider<br />
action at the country level and for biodiversity to be integrated into sectoral and cross-sectoral plans,<br />
programmes and policies<br />
Article 8 In situ conservation In situ conservation calls for governments to establish protected area systems and undertake conservation<br />
activities to preserve ecosystems and the species they contain in the wild. These actions have<br />
implications for where a business can and cannot operate and provides the context for businesses to<br />
contribute to biodiversity by undertaking conservation activities in and around operations.<br />
Furthermore, Article 8(g) calls for means to regulate, manage or control risks associated with the release<br />
of living modified organisms resulting from biotechnology, and thus is of particular interest to the<br />
agriculture, forestry and pharmaceutical industries.<br />
Article 8(h) calls for preventing the introduction of, control or eradicate those alien species which<br />
threaten ecosystems, habitats or species, and is thus of particular importance to the exotic pet trade,<br />
the aquaculture industry and the horticulture industry.<br />
Article 9 Ex situ conservation Ex situ conservation calls for the preservation of natural resources outside the context of their natural environments.<br />
Article 10 Sustainable use Article 10(e) encourages cooperation between government authorities and the private sector in<br />
developing methods for sustainable use of biological resources.<br />
Article 11 Incentive measures Incentive measures create opportunities for new markets for biodiversity goods and services, using<br />
market instruments such as labelling, and establish innovative financial mechanisms for promoting<br />
responsible small and medium-sized companies in emerging economies.<br />
Article 14 Impact assessment Article 14.1 promotes the integration of biodiversity into Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)<br />
processes and therefore could result in government adopting new and different requirements for<br />
impact assessment procedures.<br />
Article 15<br />
Article 16<br />
Article 19<br />
Access to genetic<br />
resources<br />
Access to and transfer<br />
of technology<br />
Handling of biotechnology<br />
and distribution<br />
of its profits<br />
Article 14.2 addresses the issue of liability and redress, including restoration and compensation, for damage to<br />
biodiversity, posing a risk to companies that may be having deleterious impacts on biodiversity.<br />
The access to genetic resources debate in the CBD is raising important issues for business such as<br />
‘mutually agreed terms’, ‘prior informed consent’, and ‘fair and equitable distribution of benefits’.<br />
Promotes facilitating access to technology relevant to conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity<br />
or make use of genetic resources, so companies that are developing new technologies may find that<br />
new frameworks for technology transfer between countries provides new business opportunities.<br />
Article 16.2 looks into the transfer of technology which is subject to intellectual property rights.<br />
Article 16.4 calls for the parties to the CBD to take legislative, administrative or policy measures to<br />
ensure that the private sector facilitates access to technology for the benefit of both governmental<br />
institutions and the private sector of developing countries, offering opportunities for collaboration<br />
between the private sector in developed and developing countries.<br />
Of particular relevance to those businesses that are involved in biotechnology, even indirectly.<br />
17] Assistance to organizations in understanding the context of the CBD and implementing the same<br />
in policies can be derived from ‘Business and <strong>Biodiversity</strong>, A Guide for the Private Sector’ (Stone, D.,<br />
Ringwood, K., Vorhies, F. 1997), http://biodiversityeconomics.org/document.rm?id=144<br />
R e p o r t i n g o n B i o d i v e r s i t y<br />
43