- Page 2 and 3: TOXIC CHEMICALS IN THE GREAT LAKES
- Page 4: TABLE OF CONTENTS VOLUME I Contamin
- Page 7 and 8: C. Bishop R.W. Brecher W.D. Clement
- Page 10: TOXIC CHEMICALS IN THE GREAT LAKES
- Page 13 and 14: Detroit River corridor and the Niag
- Page 15 and 16: 3 . CONCLUSIONS ...................
- Page 17 and 18: LIST OF TABLES Table 1 . Physical f
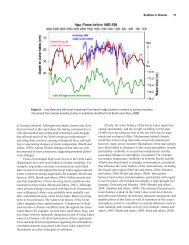
- Page 19 and 20: the Great Lakes show sediment conce
- Page 21 and 22: chemicals in the lakes is also gove
- Page 23 and 24: Lakes Ontario and Huron (Thomas, 19
- Page 25 and 26: tions of chemicals in water and sus
- Page 27 and 28: 2.1 Lake Superior has the largest s
- Page 29 and 30: esult of analytical artifacts. The
- Page 31: trations in Great Lakes sediments i
- Page 35 and 36: total DDT in surficial lake bottom
- Page 37 and 38: summarised in Table 8. Rossmann (19
- Page 39 and 40: cadmium in embayments. The highest
- Page 41 and 42: 2.4 ST. CLAIR RIVER/LAKE ST. CLAlR/
- Page 43 and 44: greater (90%) at the head of the ri
- Page 45 and 46: higher in the Detroit River than in
- Page 47 and 48: The main source, was the Dow chlor-
- Page 49 and 50: were 21 ppb (top 1 cm) and 5 ppb fo
- Page 51 and 52: smallest by volume and also the sha
- Page 53 and 54: There are limited data available on
- Page 55 and 56: indicating a retention of some psll
- Page 57 and 58: of 9.1 ppb (range 4.6 - 17 ppb); 2.
- Page 59 and 60: industries. The large petrochemical
- Page 61 and 62: fractions or both in 1984/86 and 19
- Page 63 and 64: epoxide, and endosulphan (DOE and M
- Page 65 and 66: sources (DOE and MOE, 1981). Mercur
- Page 67 and 68: and a larger section joining the ea
- Page 69 and 70: in Lakes Ontario and Erie were sign
- Page 71 and 72: sampling techniques were used. Back
- Page 73 and 74: probably because of improved extrac
- Page 75 and 76: 2.8.1 Water and Suspended Solids In
- Page 77 and 78: sides of the St. Lawrence River. Le
- Page 79 and 80: volatile halocarbon and PAHs in wat
- Page 81 and 82: of cores showed enrichment of lead,
- Page 83 and 84:
historical data on metals and organ
- Page 85 and 86:
ecovery of the Great Lakes from che
- Page 87 and 88:
5. Allan. R.J. 1986. The role of pa
- Page 89 and 90:
Chau. Y.K.. P.T. Wong. C.A. Bengert
- Page 91 and 92:
Niagara Mer plume. National Water R
- Page 93 and 94:
International Joint Commission. 198
- Page 95 and 96:
Lum. K.R.. and K.L. Kaiser. 1986. O
- Page 97 and 98:
from lakes Superior, Huron, Erie an
- Page 99 and 100:
Nriagu, and M.S. Simmons. (eds.) To
- Page 101 and 102:
6. 6.1 AOC CCREM DOE FE GLWQA IJC M
- Page 103 and 104:
6.3 GLOSSARY Area of Concern: a geo
- Page 105:
Objective (water quality): a numeri
- Page 109 and 110:
9.0 - - 160 8.0 - - 140 - 7.0- E Q
- Page 111 and 112:
PCDD + PCDF TIME years 18 0 z Q I-
- Page 113 and 114:
HCB uWkg OCS ug/kg PCB ug/kg 0 1M)m
- Page 115 and 116:
TIME (years) 1930 1940 1950 1970 19
- Page 117 and 118:
*". 0 BHC ._. Total PCB's 4Ql Figur
- Page 119 and 120:
a - BHC 1 0 . 0 1 8.0 L m 2 .o Tota
- Page 121 and 122:
CB's, PCB's, Mirex Time (Years) 191
- Page 123 and 124:
TABLE 1. PHYSICAL FEATURES OF THE G
- Page 125 and 126:
TABLE 3. UNITS OF MEASUREMENT Dry W
- Page 127 and 128:
TABLE 4. CONTINUED Testing % Chcmic
- Page 129 and 130:
4. Ollver and Nlcd 1982. Deposition
- Page 131 and 132:
TABLE 7. CONCENTRATIONS OF CONTAMIN
- Page 133 and 134:
TABLE 8. CONTINUED Twting % Chmical
- Page 135 and 136:
ND : not detected Sample : depth of
- Page 137 and 138:
TABLE 10. CONTINUED PCBs dis.
- Page 139 and 140:
- ND : not detected Sample : depth
- Page 141 and 142:
TABLE 12. CONTINUED Testing % Chmic
- Page 143 and 144:
1. DOE, USEPA. MOE & NYDEC 1988. Ml
- Page 145 and 146:
TABLE 13. CONTINUED Taating 0 Chemi
- Page 147 and 148:
ND : not detected Sample : depth of
- Page 149 and 150:
TABLE 15. CONTINUED Tuting Chemical
- Page 151 and 152:
TABLE 16. CONTINUED OCDD 1983 1 4.8
- Page 154 and 155:
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This part of the
- Page 156:
when a guideline to protect human h
- Page 159 and 160:
LIST OF FIGURES Figure 1. Mean conc
- Page 161 and 162:
Figure 32. Figure 33. Figure 34. Fi
- Page 163 and 164:
LIST OF TABLES Table 1. Historical
- Page 165 and 166:
Table 32. Table 33. Table 34. Table
- Page 167 and 168:
contributes significantly to the co
- Page 169 and 170:
portion of the fish analyzed. To de
- Page 171 and 172:
the Niagara River (Kauss et al., 19
- Page 173 and 174:
~~ - ~- ~ - ~ TABLE 3. INTER-LAKE C
- Page 175 and 176:
invertebrates for each lake and con
- Page 177 and 178:
TABLE 6: CONTINUED Organbm St. Lawm
- Page 179 and 180:
TABLE 6: CONTINUED Fluoranthene A 0
- Page 181 and 182:
fish are shown in Figure 3. In 1975
- Page 183 and 184:
2.2.1 lake Ontario Total PCBs Tempo
- Page 185 and 186:
Suns et al. (1985) determined mean
- Page 187 and 188:
~~~ Hexuchlorobenzene (HCB) Tempora
- Page 189 and 190:
TABLE 1 1. CONCENTRATIONSOFTOTALDDT
- Page 191 and 192:
TABLE 12. MEAN CONCENTRATIONS OF TO
- Page 193 and 194:
TABLE 14. MEANCONCENTRATIONSOFTOTAL
- Page 195 and 196:
TABLE 15. MEAN CONCENTRATIONS OF PC
- Page 197 and 198:
Dioxins and Furans Figure 16 and 17
- Page 199 and 200:
Spatial Distribution: The highest m
- Page 201 and 202:
TABLE 20. MEANCONCENTRATIONS OF TOT
- Page 203 and 204:
slightly higher in samples from sou
- Page 205 and 206:
DDT and Metabolites Temporal Trends
- Page 207 and 208:
in arsenic and selenium burdens in
- Page 209 and 210:
Chlordane In 1978-79, Chlordane bur
- Page 211 and 212:
TABLE 26. MEAN CONCENTRATIONS OF TO
- Page 213 and 214:
TABLE 28. MEAN CONCENTRATIONS OF ME
- Page 215 and 216:
a result, there are fish consumptio
- Page 217 and 218:
sucker from the Chippawa Channel of
- Page 219 and 220:
~~ TABLE 35. MEAN CONCENTRATIONS OF
- Page 221 and 222:
the closure of a nearby alkyl lead
- Page 223 and 224:
the St. Clair-Detroit River system,
- Page 225 and 226:
Maitland (St. Lawrence River) and C
- Page 227 and 228:
TABLE 42: CONTINUED Sf. Cklr- St. L
- Page 229 and 230:
contaminant burdens than those expo
- Page 231 and 232:
~~~ ~~~~ ~ ~~~~ ~ ~~~ ~ ~ TABLE a.
- Page 233 and 234:
TABLE 44: CONTAMINANTS ROUTINELY AN
- Page 235 and 236:
ainbow trout, coho salmon, chinook
- Page 237 and 238:
TABLE 46: FISH CONTAMINANT ISSUES I
- Page 239 and 240:
TABLE 46: FISH CONTAMINANT ISSUES I
- Page 241 and 242:
TABLE 44: FISH CONTAMINANT ISSUES I
- Page 243 and 244:
TABLE 46: FISH CONTAMINANT ISSUES I
- Page 245 and 246:
7. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We are gratefid
- Page 247 and 248:
Eadie, B.J., W. Faust, W.S. Gardner
- Page 249 and 250:
Ontario Ministry of the Environment
- Page 251 and 252:
LAKE ONTARIO DIELDRIN P P M D A v W
- Page 253 and 254:
LAKE ONTARIO ARSENIC CADMIUM P P M
- Page 255 and 256:
LAKE HURON -+- LAwR ST- RIVER 0 DFO
- Page 257 and 258:
Cataraqui River A WoIfe Island Darl
- Page 259 and 260:
LAKE ONTARIO M : 2 T HUMBER RIVER P
- Page 261 and 262:
LAKE ONTARIO MIREX I 0.3 0.25 ? P P
- Page 263 and 264:
LAKE ONTARIO NIAGARA-ON-THE-LAKE HC
- Page 265 and 266:
LAKE ONTARIO DDT 2.5 2 P M w 1.5 E
- Page 267 and 268:
LAKE ONTARIO NIAGARA-ON-THE-LAKE DD
- Page 269 and 270:
LAKE ONTARIO 2,3,7,8-TCDD 50 40 P P
- Page 271 and 272:
LAKE ONTARIO NIAGARA-ON-THE-LAKE CH
- Page 273 and 274:
LAKE ONTARIO 06, .~ SELENIUM * 04-
- Page 275 and 276:
LAKE ERIE PCB 5 i - . ". 1977 1979
- Page 277 and 278:
LAKE ERIE LEAMINGTON PCB BIG CREEK
- Page 279 and 280:
LAKE ERIE DDT 0.7 P M E T 0.6 0.5 0
- Page 281 and 282:
LEAMINGTON DDT BIG CREEK DDT 0.25 0
- Page 283 and 284:
LAKE ERIE MERCURY 0.25 0.2 P P M w
- Page 286 and 287:
LAKE HURON DIELDRIN 0.16 0.14 I I P
- Page 288 and 289:
LAKE HURON p,p'-DDE 0.8 r P M W E W
- Page 290 and 291:
LAKE HURON MERCURY 0.25 0.2 P P M w
- Page 292 and 293:
eninsula Harbour Batchawana Bay Fig
- Page 294 and 295:
LAKE SUPERIOR DDT 0.5 0.4 P M w 0.3
- Page 296 and 297:
LAKE SUPERIOR MERCURY 0.35 0.3 P M
- Page 298 and 299:
LAKE MICHIGAN PCB 25 P P M 20 w l5
- Page 300 and 301:
LAKE MICHIGAN DDT 20 P P M 15 W E 1
- Page 303 and 304:
LAKE ST. CLAIR PIKE CREEK PCB PIKE
- Page 306 and 307:
Macdonnell Isl. L A W R E N C E R I
- Page 308 and 309:
ST. LAWRENCE RIVER MAITLAND ALKYL L
- Page 310 and 311:
WHOLE FISH PCB LEVELS LAKE TROUT (A
- Page 312 and 313:
LAKE ONTARIO PCB & DDT 6 5 P L 4 ..
- Page 314 and 315:
LAKE ONTARIO MIREX 0.8 0.5 I R E x
- Page 316:
70 P E E N A G E 60 50 40 30 20 /+"
- Page 320 and 321:
Levels of organochlorine contaminan
- Page 322 and 323:
TABLE OF CONTENTS EXECUTIVESUMMARY
- Page 324 and 325:
Figure 14. Figure 15. Figure 16. Fi
- Page 326:
Table 12. Table 13. Table 14. Table
- Page 329 and 330:
the fat required to produce the yol
- Page 331 and 332:
are provided to illustrate temporal
- Page 333 and 334:
production of this chemical and con
- Page 335 and 336:
the relatively short half-life calc
- Page 337 and 338:
show no apparent decrease from 1980
- Page 339 and 340:
Island from 0.22 to 0.06 ppm is sub
- Page 341 and 342:
2.9 DISCUSSION The temporal trends
- Page 343 and 344:
temporal trends at any one site. Da
- Page 345 and 346:
TABLE 2. CONTINUED LAKE ERIE 1972 1
- Page 347 and 348:
TABLE 2. CONTINUED NORTH CHANNEL 19
- Page 349 and 350:
3.4 LAKE SUPERIOR Less than 5% of t
- Page 351 and 352:
DDE residues were highest in eggs f
- Page 353 and 354:
TABLE 6. COMPARISON BETWEEN HISTORI
- Page 355 and 356:
TABLE 8. HISTORICAL COMPARISON OF O
- Page 357 and 358:
the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service,
- Page 359 and 360:
8. MINK Mink are widely distributed
- Page 361 and 362:
these wild populations experienced
- Page 363 and 364:
~~~ TABLE 12. MEAN ORGANOCHLORINE C
- Page 365 and 366:
Lake Ontario such as those in Coote
- Page 367 and 368:
doubled in 1988 as compared to 1984
- Page 369 and 370:
TABLE 16. SUMMARYOFPCBANDDDECONCENT
- Page 371 and 372:
12. REFERENCES Bishop, CA. 1989. Th
- Page 373 and 374:
Morris, RA., RA. Hunter and J.F. Mc
- Page 376 and 377:
LAKE ONTARIO PCB CONCENTRATIONS 100
- Page 378 and 379:
LAKE ONTARIO DIELDRIN CONCENTRATION
- Page 380 and 381:
NIAGARA RIVER DIELDRIN CONCENTRATIO
- Page 382 and 383:
LAKE ERIE MIREX CONCENTRATIONS 1.4
- Page 384 and 385:
DETROIT RIVER PCB CONCENTRATIONS OD
- Page 386 and 387:
LAKE HURON E PCB CONCENTRATIONS 80
- Page 388 and 389:
HURON MIREX CONCENTRATIONS 46. 4. 3
- Page 390 and 391:
LAKE HURON DIELDRIN CONCENTRATIONS
- Page 392 and 393:
LAKE MICHIGAN E PCB CONCENTRATIONS
- Page 394 and 395:
LAKE MICHIGAN DIELDRIN CONCENTRATIO
- Page 396 and 397:
LAKE SUPERIOR MIREX CONCENTRATIONS
- Page 399:
Dieldrin (ppm wet wt.) 2 .oo 1.60 1
- Page 402:
TOXIC CHEMICALS IN THE GREAT LAKES
- Page 405 and 406:
Exposure to lead in soil is particu
- Page 407 and 408:
LIST OF TABLES Pathways of Human Ex
- Page 409 and 410:
Table 3.3~ Residue levels in human
- Page 412 and 413:
1. 1.1 OVERVIEW Over their lifetime
- Page 414 and 415:
2. 2.1 PATHWAYS OF HUMAN EXPOSURE T
- Page 416 and 417:
(unpublished) have estimated that t
- Page 418 and 419:
14.1 ppm (Frank et al., 1976). Weis
- Page 420 and 421:
of areolar (connective) tissue and
- Page 422 and 423:
3.2 BLOOD Blood is not often used f
- Page 424 and 425:
1984; Macpherson, 1987). Quality co
- Page 426 and 427:
in children. An extensive study of
- Page 428 and 429:
the two women ranged from 0.55 to 4
- Page 430 and 431:
4. CONCLUSIONS 1. Residents of the
- Page 432 and 433:
6. REFERENCES Armstrong.V.C..M.G. H
- Page 434 and 435:
Geyer, H.. I. Scheunert and F. Kort
- Page 436 and 437:
Mes, J. and D.J. Davies. 1979. Pres
- Page 438:
Weis, I.M. and G.F. Barclay. 1985.
- Page 442 and 443:
PATHWAYS OF HUMAN EXPOSURE TO TOXIC
- Page 444:
Table 2.1 b Canadian Dietary Intake
- Page 447 and 448:
a G: a 1 Table 2.2a Cbdcrl Yam8 N X
- Page 449 and 450:
~ Table 2.2~ Residue Levels in Wate
- Page 452 and 453:
PATHWAYS OF HUMAN EXPOSURE TO TOXIC
- Page 454 and 455:
Table 2.3b SAql. hCAt ion Ontario O
- Page 456:
Table 2.3d Residue Levels in Ambien
- Page 459 and 460:
Table 3.1 a -1. Loastion 1.1. OEtUi
- Page 461 and 462:
220 ~ 162 ~ 85 Table 3.ld Residuele
- Page 463 and 464:
Table 3.1 f ResidueLevelsinHumanAdi
- Page 465 and 466:
~ -1. Iautioa 1.1. Ontario 1.1. Ont
- Page 467 and 468:
?rank Table 3.1 k Suple Loution SD
- Page 469 and 470:
Coogrnor Y0.r Colloctod N Rofrrencw
- Page 471 and 472:
Table 3.1 t 8. Ontario 8. Ontario 8
- Page 474 and 475:
HUMAN TISSUE DATA: BLOOD
- Page 476:
Table 3.2~ Residue Levels in Human
- Page 479 and 480:
i m h I U P U I I h P I - w m d d .
- Page 481 and 482:
e h Table 3.3e Residue levels in Hu
- Page 483 and 484:
w w d d $. .. - w w w r r ~ r w w w
- Page 485 and 486:
~ 7, Table 3.31 Residue Levels in H
- Page 487 and 488:
Table 3.3k Residue Levels in Human
- Page 489 and 490:
Table 3.3q Residue Levels in Human
- Page 492 and 493:
HUMAN TISSUE DATA: OTHER TISSUES
- Page 494 and 495:
Table 3.4a Continued x itap0rt.d nm
- Page 496:
Table 3.4 Residue Levels in Human L