Chapter 2. POLAR ADDITION AND ELIMINATION REACTIONS
Chapter 2. POLAR ADDITION AND ELIMINATION REACTIONS
Chapter 2. POLAR ADDITION AND ELIMINATION REACTIONS
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
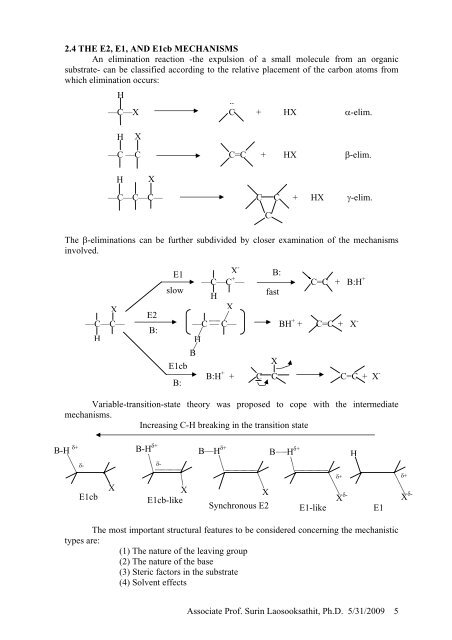
<strong>2.</strong>4 THE E2, E1, <strong>AND</strong> E1cb MECHANISMS<br />
An elimination reaction -the expulsion of a small molecule from an organic<br />
substrate- can be classified according to the relative placement of the carbon atoms from<br />
which elimination occurs:<br />
H<br />
..<br />
—C—X C + HX α-elim.<br />
H<br />
X<br />
—C —C C=C + HX β-elim.<br />
H<br />
X<br />
—C—C—C— C C + HX γ-elim.<br />
The β-eliminations can be further subdivided by closer examination of the mechanisms<br />
involved.<br />
E1<br />
B:<br />
—C—C + — C=C + B:H +<br />
slow<br />
H<br />
fast<br />
X<br />
X<br />
E2<br />
—C—C— —C — C— BH + + C=C + X -<br />
B:<br />
H<br />
H<br />
B<br />
E1cb<br />
B:<br />
X -<br />
B:H + + C C C=C + X -<br />
Variable-transition-state theory was proposed to cope with the intermediate<br />
mechanisms.<br />
Increasing C-H breaking in the transition state<br />
C<br />
X<br />
B-H δ+ δ-<br />
B-H δ+ δ-<br />
B—H δ+<br />
B H δ+<br />
H<br />
E1cb<br />
X<br />
X<br />
E1cb-like<br />
X<br />
Synchronous E2<br />
E1-like<br />
δ+<br />
X δ-<br />
E1<br />
δ+<br />
X δ-<br />
The most important structural features to be considered concerning the mechanistic<br />
types are:<br />
(1) The nature of the leaving group<br />
(2) The nature of the base<br />
(3) Steric factors in the substrate<br />
(4) Solvent effects<br />
Associate Prof. Surin Laosooksathit, Ph.D. 5/31/2009 5