Download Thesis in Pdf Format - Theoretical Nuclear Physics and ...
Download Thesis in Pdf Format - Theoretical Nuclear Physics and ...
Download Thesis in Pdf Format - Theoretical Nuclear Physics and ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
36 Chapter 5. The Eikonal F<strong>in</strong>al State<br />
/2<br />
k f<br />
K<br />
q<br />
<br />
<strong>in</strong>cident<br />
direction<br />
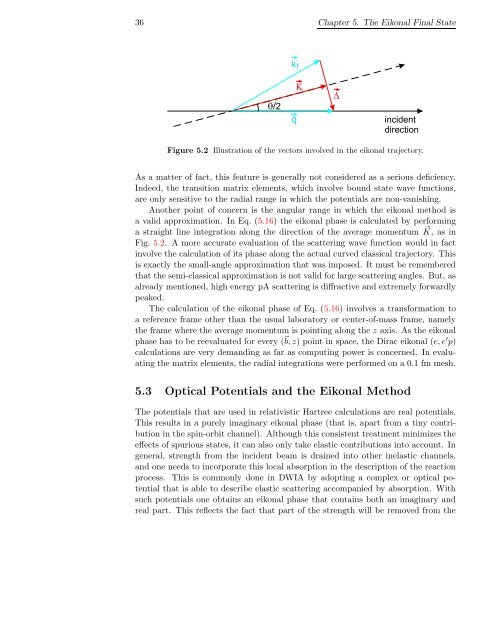
Figure 5.2 Illustration of the vectors <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> the eikonal trajectory.<br />
As a matter of fact, this feature is generally not considered as a serious deficiency.<br />
Indeed, the transition matrix elements, which <strong>in</strong>volve bound state wave functions,<br />
are only sensitive to the radial range <strong>in</strong> which the potentials are non-vanish<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
Another po<strong>in</strong>t of concern is the angular range <strong>in</strong> which the eikonal method is<br />
a valid approximation. In Eq. (5.16) the eikonal phase is calculated by perform<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a straight l<strong>in</strong>e <strong>in</strong>tegration along the direction of the average momentum ⃗ K, as <strong>in</strong><br />
Fig. 5.2. A more accurate evaluation of the scatter<strong>in</strong>g wave function would <strong>in</strong> fact<br />
<strong>in</strong>volve the calculation of its phase along the actual curved classical trajectory. This<br />
is exactly the small-angle approximation that was imposed. It must be remembered<br />
that the semi-classical approximation is not valid for large scatter<strong>in</strong>g angles. But, as<br />
already mentioned, high energy pA scatter<strong>in</strong>g is diffractive <strong>and</strong> extremely forwardly<br />
peaked.<br />
The calculation of the eikonal phase of Eq. (5.16) <strong>in</strong>volves a transformation to<br />
a reference frame other than the usual laboratory or center-of-mass frame, namely<br />
the frame where the average momentum is po<strong>in</strong>t<strong>in</strong>g along the z axis. As the eikonal<br />
phase has to be reevaluated for every ( ⃗ b, z) po<strong>in</strong>t <strong>in</strong> space, the Dirac eikonal (e, e ′ p)<br />
calculations are very dem<strong>and</strong><strong>in</strong>g as far as comput<strong>in</strong>g power is concerned. In evaluat<strong>in</strong>g<br />
the matrix elements, the radial <strong>in</strong>tegrations were performed on a 0.1 fm mesh.<br />
5.3 Optical Potentials <strong>and</strong> the Eikonal Method<br />
The potentials that are used <strong>in</strong> relativistic Hartree calculations are real potentials.<br />
This results <strong>in</strong> a purely imag<strong>in</strong>ary eikonal phase (that is, apart from a t<strong>in</strong>y contribution<br />
<strong>in</strong> the sp<strong>in</strong>-orbit channel). Although this consistent treatment m<strong>in</strong>imizes the<br />
effects of spurious states, it can also only take elastic contributions <strong>in</strong>to account. In<br />
general, strength from the <strong>in</strong>cident beam is dra<strong>in</strong>ed <strong>in</strong>to other <strong>in</strong>elastic channels,<br />
<strong>and</strong> one needs to <strong>in</strong>corporate this local absorption <strong>in</strong> the description of the reaction<br />
process. This is commonly done <strong>in</strong> DWIA by adopt<strong>in</strong>g a complex or optical potential<br />
that is able to describe elastic scatter<strong>in</strong>g accompanied by absorption. With<br />
such potentials one obta<strong>in</strong>s an eikonal phase that conta<strong>in</strong>s both an imag<strong>in</strong>ary <strong>and</strong><br />
real part. This reflects the fact that part of the strength will be removed from the