Download Thesis in Pdf Format - Theoretical Nuclear Physics and ...
Download Thesis in Pdf Format - Theoretical Nuclear Physics and ...
Download Thesis in Pdf Format - Theoretical Nuclear Physics and ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
66 Chapter 6. F<strong>in</strong>al State Interactions <strong>and</strong> the Eikonal Approximation<br />
R L+TT<br />
[fm 3 ]<br />
R TL<br />
[fm 3 ]<br />
R T<br />
[fm 3 ]<br />
4.5 5<br />
3.5 4<br />
2.5 3<br />
1.5 2<br />
0.5 1<br />
0<br />
0<br />
-1<br />
-2<br />
-3<br />
-4<br />
-5<br />
14<br />
12<br />
10<br />
8<br />
6<br />
4<br />
2<br />
0<br />
0 200 400<br />
p m<br />
[MeV/c]<br />
p 3/2<br />
p 1/2<br />
OMEA<br />
RMSGA<br />
0 200 400<br />
p m<br />
[MeV/c]<br />
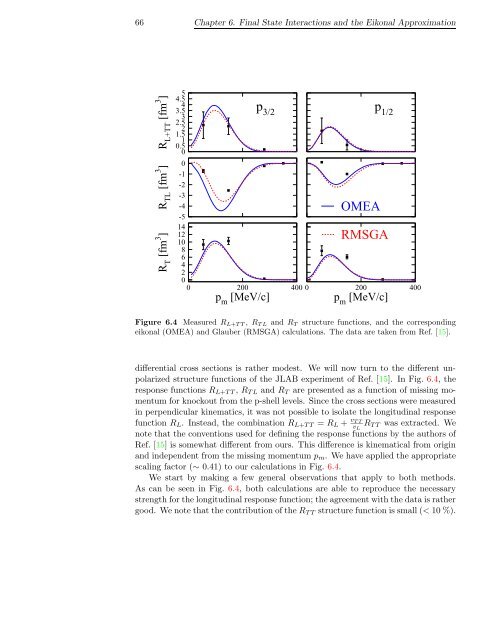
Figure 6.4 Measured R L+T T , R T L <strong>and</strong> R T structure functions, <strong>and</strong> the correspond<strong>in</strong>g<br />
eikonal (OMEA) <strong>and</strong> Glauber (RMSGA) calculations. The data are taken from Ref. [15].<br />
differential cross sections is rather modest. We will now turn to the different unpolarized<br />
structure functions of the JLAB experiment of Ref. [15]. In Fig. 6.4, the<br />
response functions R L+T T , R T L <strong>and</strong> R T are presented as a function of miss<strong>in</strong>g momentum<br />
for knockout from the p-shell levels. S<strong>in</strong>ce the cross sections were measured<br />
<strong>in</strong> perpendicular k<strong>in</strong>ematics, it was not possible to isolate the longitud<strong>in</strong>al response<br />
function R L . Instead, the comb<strong>in</strong>ation R L+T T = R L + v T T<br />
v L<br />
R T T was extracted. We<br />
note that the conventions used for def<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g the response functions by the authors of<br />
Ref. [15] is somewhat different from ours. This difference is k<strong>in</strong>ematical from orig<strong>in</strong><br />
<strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong>dependent from the miss<strong>in</strong>g momentum p m . We have applied the appropriate<br />
scal<strong>in</strong>g factor (∼ 0.41) to our calculations <strong>in</strong> Fig. 6.4.<br />
We start by mak<strong>in</strong>g a few general observations that apply to both methods.<br />
As can be seen <strong>in</strong> Fig. 6.4, both calculations are able to reproduce the necessary<br />
strength for the longitud<strong>in</strong>al response function; the agreement with the data is rather<br />
good. We note that the contribution of the R T T structure function is small (< 10 %).