UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI TRIESTE - OpenstarTs - Università ...
UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI TRIESTE - OpenstarTs - Università ...
UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI TRIESTE - OpenstarTs - Università ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Physiology of the respiratory system and mechanical models<br />
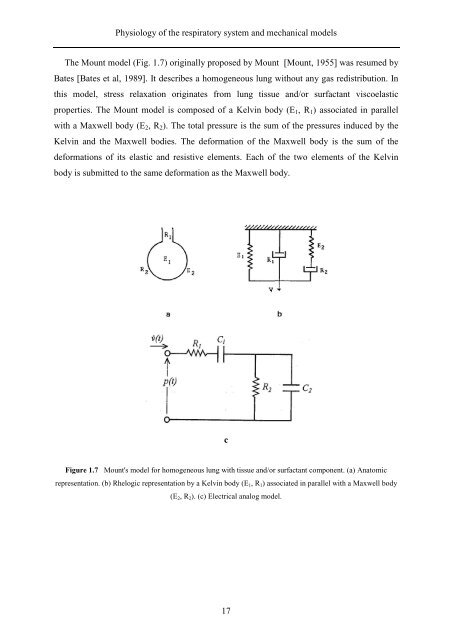
The Mount model (Fig. 1.7) originally proposed by Mount [Mount, 1955] was resumed by<br />
Bates [Bates et al, 1989]. It describes a homogeneous lung without any gas redistribution. In<br />
this model, stress relaxation originates from lung tissue and/or surfactant viscoelastic<br />
properties. The Mount model is composed of a Kelvin body (E 1 , R 1 ) associated in parallel<br />
with a Maxwell body (E 2 , R 2 ). The total pressure is the sum of the pressures induced by the<br />
Kelvin and the Maxwell bodies. The deformation of the Maxwell body is the sum of the<br />
deformations of its elastic and resistive elements. Each of the two elements of the Kelvin<br />
body is submitted to the same deformation as the Maxwell body.<br />
c<br />
Figure 1.7 Mount's model for homogeneous lung with tissue and/or surfactant component. (a) Anatomic<br />
representation. (b) Rhelogic representation by a Kelvin body (E 1 , R 1 ) associated in parallel with a Maxwell body<br />
(E 2 , R 2 ). (c) Electrical analog model.<br />
17