UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI TRIESTE - OpenstarTs - Università ...
UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI TRIESTE - OpenstarTs - Università ...
UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI TRIESTE - OpenstarTs - Università ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Chapter 2 – Intensive care: mechanical ventilation and HFPV<br />
release ventilation (IMPRV): like SIMV, the mandatory breaths can be synchronized to the<br />
patient’s inspiratory effort.<br />
2.2.7 Pressure-Controlled Ventilation (PCV)<br />
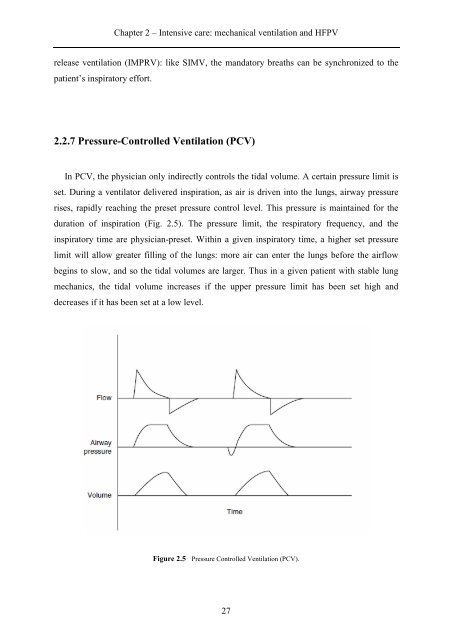
In PCV, the physician only indirectly controls the tidal volume. A certain pressure limit is<br />
set. During a ventilator delivered inspiration, as air is driven into the lungs, airway pressure<br />
rises, rapidly reaching the preset pressure control level. This pressure is maintained for the<br />
duration of inspiration (Fig. 2.5). The pressure limit, the respiratory frequency, and the<br />
inspiratory time are physician-preset. Within a given inspiratory time, a higher set pressure<br />
limit will allow greater filling of the lungs: more air can enter the lungs before the airflow<br />
begins to slow, and so the tidal volumes are larger. Thus in a given patient with stable lung<br />
mechanics, the tidal volume increases if the upper pressure limit has been set high and<br />
decreases if it has been set at a low level.<br />
Figure 2.5 Pressure Controlled Ventilation (PCV).<br />
27