14.4. Normal Curvature and the Second Fun- damental Form
14.4. Normal Curvature and the Second Fun- damental Form
14.4. Normal Curvature and the Second Fun- damental Form
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
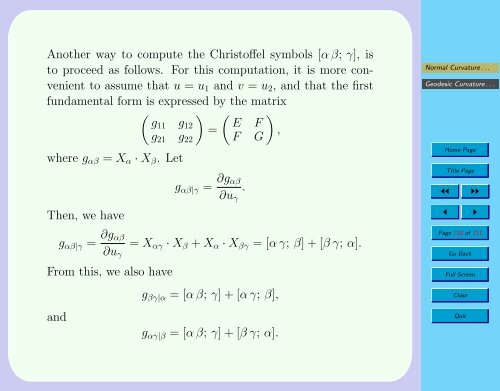
Ano<strong>the</strong>r way to compute <strong>the</strong> Christoffel symbols [α β; γ], is<br />
to proceed as follows. For this computation, it is more convenient<br />
to assume that u = u 1 <strong>and</strong> v = u 2 , <strong>and</strong> that <strong>the</strong> first<br />
fun<strong>damental</strong> form is expressed by <strong>the</strong> matrix<br />
( )<br />
g11 g 12<br />
=<br />
g 21 g 22<br />
where g αβ = X α · X β . Let<br />
Then, we have<br />
g αβ|γ = ∂g αβ<br />
∂u γ<br />
From this, we also have<br />
<strong>and</strong><br />
(<br />
E F<br />
F G<br />
g αβ|γ = ∂g αβ<br />
∂u γ<br />
.<br />
)<br />
,<br />
= X αγ · X β + X α · X βγ = [α γ; β] + [β γ; α].<br />
g βγ|α = [α β; γ] + [α γ; β],<br />
g αγ|β = [α β; γ] + [β γ; α].<br />
<strong>Normal</strong> <strong>Curvature</strong> . . .<br />
Geodesic <strong>Curvature</strong> . . .<br />
Home Page<br />
Title Page<br />
◭◭ ◮◮<br />
◭<br />
◮<br />
Page 710 of 711<br />
Go Back<br />
Full Screen<br />
Close<br />
Quit