Basic Concepts of Fluid and Electrolyte Therapy
Basic Concepts of Fluid and Electrolyte Therapy
Basic Concepts of Fluid and Electrolyte Therapy
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
to salt <strong>and</strong> water overload, but who still have a plasma volume deficit,<br />
as it helps draw fluid from the interstitial space into the intravascular<br />
space <strong>and</strong> improves renal perfusion allowing excretion <strong>of</strong> excess salt<br />
<strong>and</strong> water. Albumin is also used in patients with hepatic failure <strong>and</strong><br />
ascites. However, the prescription <strong>of</strong> this expensive preparation<br />
should be confined to senior clinicians.<br />
Although, in theory, colloids that are isooncotic with plasma should<br />
exp<strong>and</strong> the blood volume by the volume infused, in practice, the volume<br />
exp<strong>and</strong>ing capacity <strong>of</strong> these colloids is only 60-80%. Never -<br />
theless, a given volume <strong>of</strong> colloid results in greater volume expansion<br />
<strong>and</strong> less interstitial oedema than an equivalent volume <strong>of</strong> crystalloid.<br />
Although, in practice in the UK, we use a combination <strong>of</strong> crystalloids<br />
<strong>and</strong> colloids for resuscitation, there is, in fact, no firm evidence that<br />
the use <strong>of</strong> colloids rather than crystalloids in the acute phase <strong>of</strong> injury<br />
results in better outcome.<br />
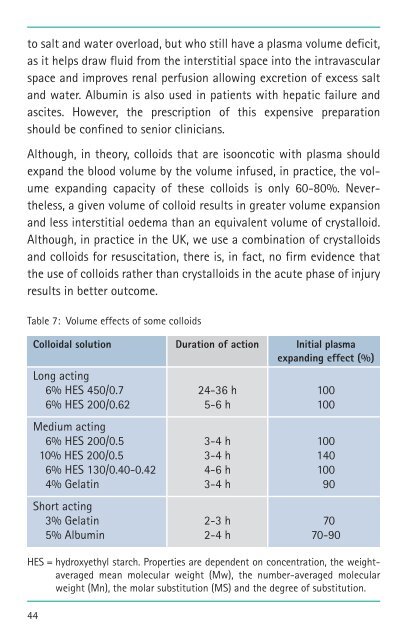
Table 7: Volume effects <strong>of</strong> some colloids<br />
44<br />
Colloidal solution Duration <strong>of</strong> action Initial plasma<br />
exp<strong>and</strong>ing effect (%)<br />
Long acting<br />
6% HES 450/0.7 24-36 h 100<br />
6% HES 200/0.62 5-6 h 100<br />
Medium acting<br />
6% HES 200/0.5 3-4 h 100<br />
10% HES 200/0.5 3-4 h 140<br />
6% HES 130/0.40-0.42 4-6 h 100<br />
4% Gelatin 3-4 h 90<br />
Short acting<br />
3% Gelatin 2-3 h 70<br />
5% Albumin 2-4 h 70-90<br />
HES = hydroxyethyl starch. Properties are dependent on concentration, the weightaveraged<br />
mean molecular weight (Mw), the number-averaged molecular<br />
weight (Mn), the molar substitution (MS) <strong>and</strong> the degree <strong>of</strong> substitution.