Basic Concepts of Fluid and Electrolyte Therapy
Basic Concepts of Fluid and Electrolyte Therapy
Basic Concepts of Fluid and Electrolyte Therapy
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
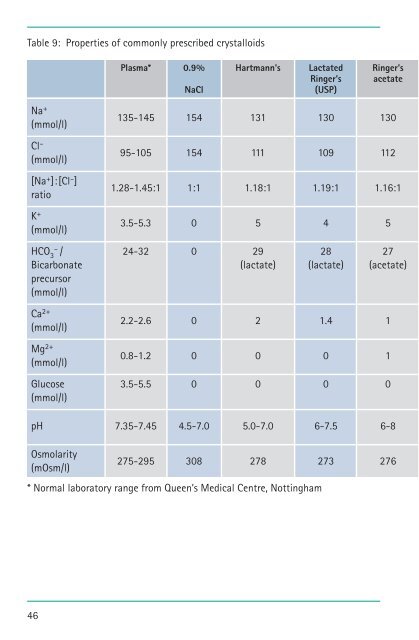
Table 9: Properties <strong>of</strong> commonly prescribed crystalloids<br />
Plasma* 0.9% Hartmann’s Lactated Ringer’s<br />
Ringer’s acetate<br />
NaCl<br />
(USP)<br />
Na + 135-145 154 131 130 130<br />
(mmol/l)<br />
Cl – 95-105 154 111 109 112<br />
(mmol/l)<br />
[Na + ]:[Cl – ]<br />
ratio<br />
1.28-1.45:1 1:1 1.18:1 1.19:1 1.16:1<br />
K + 3.5-5.3 0 5 4 5<br />
(mmol/l)<br />
HCO 3–<br />
/ 24-32 0 29 28 27<br />
Bicarbonate (lactate) (lactate) (acetate)<br />
precursor<br />
(mmol/l)<br />
Ca 2+ 2.2-2.6 0 2 1.4 1<br />
(mmol/l)<br />
Mg 2+ 0.8-1.2 0 0 0 1<br />
(mmol/l)<br />
Glucose 3.5-5.5 0 0 0 0<br />
(mmol/l)<br />
pH 7.35-7.45 4.5-7.0 5.0-7.0 6-7.5 6-8<br />
Osmolarity<br />
275-295 308 278 273 276<br />
(mOsm/l)<br />
* Normal laboratory range from Queen’s Medical Centre, Nottingham<br />
46