Project in Continuum Mechanics: - Division of Solid Mechanics
Project in Continuum Mechanics: - Division of Solid Mechanics
Project in Continuum Mechanics: - Division of Solid Mechanics
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Pr<strong>of</strong>. Larsgunnar Nilsson 2011-02-22<br />
<strong>Project</strong> <strong>in</strong> Cont<strong>in</strong>uum <strong>Mechanics</strong>:<br />
Large axial and shear deformation <strong>of</strong> a rubber material.<br />
Introduction<br />
A circular cyl<strong>in</strong>drical rubber specimen, see Figure 1, is tested <strong>in</strong> a comb<strong>in</strong>ed load<strong>in</strong>g<br />
sequence:<br />
1. The specimen is subjected to an axial compression, followed by (without unload<strong>in</strong>g), see<br />
Figure 2<br />
2. The specimen is subjected to a shear deformation, see Figure 3<br />
Fig 1. Rubber specimen before test<br />
Fig 2. After full axial load<strong>in</strong>g<br />
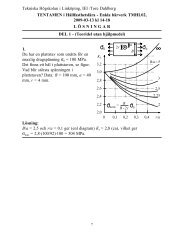
1
Pr<strong>of</strong>. Larsgunnar Nilsson 2011-02-22<br />
Fig. 3. After full axial and shear load<strong>in</strong>g<br />
The F<strong>in</strong>ite Element representation<br />
Your task is to evaluate certa<strong>in</strong> measures <strong>in</strong> one f<strong>in</strong>ite element. The specific element is<br />
<strong>in</strong>dividual to you. Each element is a hexahedron element, but you are supposed to construct a<br />
tetrahedron element based sequentially on the first three node numbers plus the fifth node<br />
number <strong>of</strong> that element. The sequence <strong>of</strong> four node numbers def<strong>in</strong>es a four nodes tetrahedron<br />
element, see Figure 4, which is your specific element.<br />
The project documents can be found at<br />
http://www.solid.iei.liu.se/Education/TMHL41/tmhl41.html<br />
The nodal coord<strong>in</strong>ates belong<strong>in</strong>g to the hexahedron elements are listed <strong>in</strong> the file<br />
ELEMENTS.<br />
The coord<strong>in</strong>ates <strong>of</strong> the nodes <strong>in</strong> the <strong>in</strong>itial configuration is given the file UNDEFORMED.<br />
The coord<strong>in</strong>ates <strong>of</strong> the nodes <strong>in</strong> the f<strong>in</strong>al configuration is given the file DEFORMED.<br />
Note: Length unit is mm.<br />
Element theory<br />
The current coord<strong>in</strong>ates <strong>of</strong> the element is given by<br />
x ( X,<br />
t)<br />
N ( X)<br />
x ( t)<br />
, i=1,3 I=1,2,3,4<br />
i<br />
I<br />
iI<br />
where N I (X) are the shape functions, which are functions <strong>of</strong> the Lagrangian (or material)<br />
coord<strong>in</strong>ates, and x iI =(x I ,y I ,z I ) are the nodal coord<strong>in</strong>ates <strong>of</strong> node I.<br />
The shape functions <strong>of</strong> a four node tetrahedron element can be obta<strong>in</strong>ed as follow:<br />
2
Pr<strong>of</strong>. Larsgunnar Nilsson 2011-02-22<br />
Def<strong>in</strong>e the matrix A<br />
1<br />
X<br />
1<br />
Y1<br />
Z1<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
1 X<br />
2<br />
Y2<br />
Z<br />
2<br />
A<br />
<br />
1<br />
X <br />
3<br />
Y3<br />
Z<br />
3<br />
<br />
<br />
1<br />
X<br />
4<br />
Y4<br />
Z<br />
4 <br />
where (X I ,Y I , Z I ) are the nodal coord<strong>in</strong>ates (I=1,4) and the local node number<strong>in</strong>g is def<strong>in</strong>ed by<br />
choos<strong>in</strong>g the first node number and then number<strong>in</strong>g the rema<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g three nodes <strong>in</strong> a counter<br />
clockwise direction as seen from the first. The shape functions are given by<br />
N ( X , Y,<br />
Z)<br />
m<br />
m<br />
I<br />
IJ<br />
1<br />
( 1)<br />
6V<br />
1I<br />
( I J<br />
)<br />
1<br />
m<br />
Aˆ<br />
IJ<br />
2I<br />
X<br />
m<br />
3I<br />
Y m<br />
4I<br />
Z<br />
4<br />
1<br />
2<br />
3<br />
1<br />
Fig 4. Four node tetrahedron element and its nodal number<strong>in</strong>g<br />
And where  IJ are the m<strong>in</strong>ors <strong>of</strong> A, i.e. the determ<strong>in</strong>ant <strong>of</strong> the matrix obta<strong>in</strong>ed by delet<strong>in</strong>g<br />
column I and row J <strong>of</strong> A. The element volume is given by V=detA/6.<br />
Note that the deformation gradient is given by<br />
1<br />
1<br />
F<br />
ij<br />
x<br />
<br />
X<br />
i<br />
j<br />
N<br />
<br />
X<br />
I<br />
j<br />
x<br />
iI<br />
Task<br />
Consider<strong>in</strong>g your specific element at its f<strong>in</strong>al deformed configuration, where you are<br />
supposed to evaluate, at the centroid <strong>of</strong> the element, the follow<strong>in</strong>g items:<br />
1. The deformation gradient (F)<br />
2. The Green Lagrange stra<strong>in</strong> (E)<br />
3. The pr<strong>in</strong>cipal Green Lagrange stra<strong>in</strong>s and the correspond<strong>in</strong>g directions<br />
4. The right stretch tensor (U), the pr<strong>in</strong>cipal stretches and the correspond<strong>in</strong>g pr<strong>in</strong>cipal<br />
directions<br />
5. The logarithmic stra<strong>in</strong> tensor<br />
6. The rotation tensor (R)<br />
3
Pr<strong>of</strong>. Larsgunnar Nilsson 2011-02-22<br />
7. Compare the result<strong>in</strong>g pr<strong>in</strong>cipal directions <strong>of</strong> E and U from 3 and 4. Prove that they<br />
are the same!<br />
8. Discuss the pr<strong>in</strong>cipal stretches and the pr<strong>in</strong>cipal directions with regard to the analysed<br />
rubber material test. Do these directions correspond to what you expected?<br />
The results should be presented <strong>in</strong> a typed report written <strong>in</strong> MS-Word (or similar program),<br />
clearly stat<strong>in</strong>g the start<strong>in</strong>g values and each step <strong>of</strong> the derivation <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g a discussion <strong>of</strong> all<br />
results. Text from the Matlab program is not allowed <strong>in</strong> the report.<br />
Credits<br />
A correct solution <strong>of</strong> all tasks gives 3 credit po<strong>in</strong>ts, which can be summed to the credit po<strong>in</strong>ts<br />
<strong>of</strong> the written exam<strong>in</strong>e. These credits can be used just once at the exam<strong>in</strong>e occasion on<br />
March 19, 2011.<br />
Dead l<strong>in</strong>e<br />
The report must be delivered to the undersigned not later than March 11, at 15.00.<br />
Larsgunnar Nilsson<br />
4