Experimental - Spectroscopy
Experimental - Spectroscopy
Experimental - Spectroscopy
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
ADVERTISEMENT<br />
Atomic <strong>Spectroscopy</strong><br />
Determination of Hg in Environmental Samples Using a Direct<br />
Mercury Analyzer<br />
Johan Nortje, Milestone Inc.<br />
As emphasis is continually being placed on the monitoring<br />
of mercury emissions, both private and public<br />
institutions are looking to characterize the soil, and<br />
in some cases water, on their facilities. Direct mercury<br />
analysis, an alternative to these methods, has been<br />
used successfully to determine total mercury in soil<br />
and other environmental matrices. This technique requires<br />
no sample preparation and delivers results in<br />
as little as 6 min per sample.<br />
<strong>Experimental</strong><br />
Determine mercury content at various concentrations in environmental<br />
samples. In addition to the environmental samples, NIST<br />
2709 San Joaquin Soil, a matrix-matched standard reference material<br />
(SRM) is periodically analyzed to ensure accuracy.<br />
Principle of Operation<br />
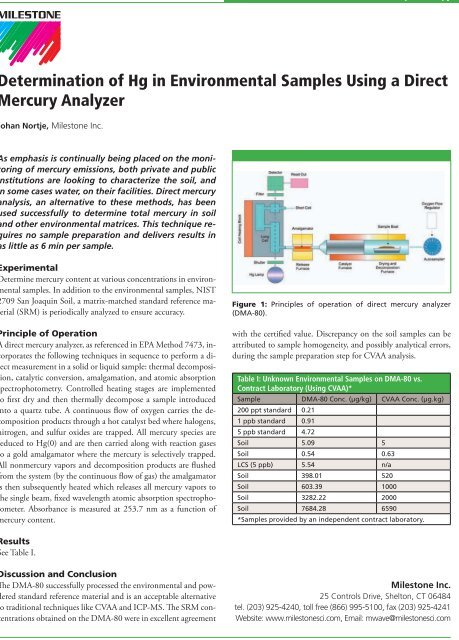
A direct mercury analyzer, as referenced in EPA Method 7473, incorporates<br />
the following techniques in sequence to perform a direct<br />
measurement in a solid or liquid sample: thermal decomposition,<br />
catalytic conversion, amalgamation, and atomic absorption<br />
spectrophotometry. Controlled heating stages are implemented<br />
to first dry and then thermally decompose a sample introduced<br />
into a quartz tube. A continuous flow of oxygen carries the decomposition<br />
products through a hot catalyst bed where halogens,<br />
nitrogen, and sulfur oxides are trapped. All mercury species are<br />
reduced to Hg(0) and are then carried along with reaction gases<br />
to a gold amalgamator where the mercury is selectively trapped.<br />
All nonmercury vapors and decomposition products are flushed<br />
from the system (by the continuous flow of gas) the amalgamator<br />
is then subsequently heated which releases all mercury vapors to<br />
the single beam, fixed wavelength atomic absorption spectrophotometer.<br />
Absorbance is measured at 253.7 nm as a function of<br />
mercury content.<br />
Figure 1: Principles of operation of direct mercury analyzer<br />
(DMA-80).<br />
with the certified value. Discrepancy on the soil samples can be<br />
attributed to sample homogeneity, and possibly analytical errors,<br />
during the sample preparation step for CVAA analysis.<br />
Table I: Unknown Environmental Samples on DMA-80 vs.<br />
Contract Laboratory (Using CVAA)*<br />
Sample DMA-80 Conc. (µg/kg) CVAA Conc. (µg.kg)<br />
200 ppt standard 0.21<br />
1 ppb standard 0.91<br />
5 ppb standard 4.72<br />
Soil 5.09 5<br />
Soil 0.54 0.63<br />
LCS (5 ppb) 5.54 n/a<br />
Soil 398.01 520<br />
Soil 603.39 1000<br />
Soil 3282.22 2000<br />
Soil 7684.28 6590<br />
*Samples provided by an independent contract laboratory.<br />
Results<br />
See Table I.<br />
Discussion and Conclusion<br />
The DMA-80 successfully processed the environmental and powdered<br />
standard reference material and is an acceptable alternative<br />
to traditional techniques like CVAA and ICP-MS. The SRM concentrations<br />
obtained on the DMA-80 were in excellent agreement<br />
Milestone Inc.<br />
25 Controls Drive, Shelton, CT 06484<br />
tel. (203) 925-4240, toll free (866) 995-5100, fax (203) 925-4241<br />
Website: www.milestonesci.com, Email: mwave@milestonesci.com