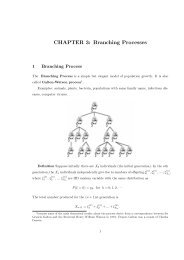
CHAPTER 2: Markov Chains (part 3)
CHAPTER 2: Markov Chains (part 3)
CHAPTER 2: Markov Chains (part 3)
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
w 35 = 0<br />
w 45 = 1 3 w 15 + 1 3 w 55 + 1 3 w 75<br />
w 55 = 1 + 1 4 w 25 + 1 4 w 45 + 1 4 w 65 + 1 4 w 85<br />
w 65 = 1 3 w 35 + 1 3 w 55 + 1 3 w 95<br />
w 75 = 0<br />
w 85 = 1 3 w 55 + 1 3 w 75 + 1 3 w 95<br />
w 95 = 0<br />
[You can find the answers by solving these set of equations]<br />
4. If the rat starts in com<strong>part</strong>ment 1, what is the probability that the rat is in 4 before it is<br />
shocked?<br />
Let<br />
z i = P (X T −1 = 4|X 0 = i)<br />
then<br />
z 1 = p 12 z 2 + p 14 z 4<br />
z 2 = p 21 z 1 + p 25 z 5 + p 23 z 3<br />
z 3 = 0;<br />
z 4 = p 41 z 1 + p 45 z 5 + p 47<br />
z 5 = p 52 z 2 + p 54 z 4 + p 56 z 6 + p 58 z 8<br />
z 6 = p 63 z 3 + p 65 z 5 + p 69 z 9<br />
z 7 = 0<br />
z 8 = p 85 z 5 + p 87 0 + p 89 0<br />
z 9 = 0<br />
Example A model of Fecundity Changes in sociological patterns such as increase in age at<br />
marriage, more remarriages after widowhood, and increased divorce rates have profound effects<br />
on overall population growth rates. Here we attempt to model the life span of a female in a<br />
population in order to provide a framework for analyzing the effect of social changes on average<br />
fecundity.<br />
For a typical woman, we may categorize her in one of the follows states<br />
E 0 : Prepuberty E 1 : Single E 2 : Married E 3 : Divorced,<br />
4